Biology DNA MCAS questions
... In phenylketonuria (PKU), an enzyme that converts one amino acid into another does not work properly. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this genetic condition? A. an error in the transcription of the gene for the enzyme B. a mutation in the DNA sequence that codes for the enzyme C. ...
... In phenylketonuria (PKU), an enzyme that converts one amino acid into another does not work properly. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this genetic condition? A. an error in the transcription of the gene for the enzyme B. a mutation in the DNA sequence that codes for the enzyme C. ...
Document
... increased the rate of ubiquitination of cyclin D1; attaching ubiquitin to the cyclin D1 protein deactivates it (10). Decreasing levels of cyclin D1 are closely associated with G1 phase arrest ...
... increased the rate of ubiquitination of cyclin D1; attaching ubiquitin to the cyclin D1 protein deactivates it (10). Decreasing levels of cyclin D1 are closely associated with G1 phase arrest ...
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
... 7. How do vaccines work? 8. Describe the bacterial genome. 9. What is a plasmid? 10. What are the 4 sources of genetic recombination in bacteria? How do they occur? 11. Understand the trp operon as an example of a repressible operon. 12. Understand the lac operon as an example of an inducible operon ...
... 7. How do vaccines work? 8. Describe the bacterial genome. 9. What is a plasmid? 10. What are the 4 sources of genetic recombination in bacteria? How do they occur? 11. Understand the trp operon as an example of a repressible operon. 12. Understand the lac operon as an example of an inducible operon ...
Slides
... Genome Database (MGD) in 1998. Since then, the GO Consortium has grown to include many databases, including several of the world's major repositories for plant, animal and microbial genomes. ...
... Genome Database (MGD) in 1998. Since then, the GO Consortium has grown to include many databases, including several of the world's major repositories for plant, animal and microbial genomes. ...
Anatomy of the Gene - University of Missouri
... If the origin of life was in the “RNA world”, then they could be early participants in formation of genomes as we know them today. Kazazian. 2004. Science 303: 1626-1632. ...
... If the origin of life was in the “RNA world”, then they could be early participants in formation of genomes as we know them today. Kazazian. 2004. Science 303: 1626-1632. ...
Gene Section TCL1B (T-cell leukemia/lymphoma 1B) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... 6.5 kb TCL1B cDNA. 4 exons (181, 171, 69, 697 bp); centromere - exons 1 to 4 - telomere orientation; only the first three exons are coding. Located 15-16 kb centromeric of TCL1A. ...
... 6.5 kb TCL1B cDNA. 4 exons (181, 171, 69, 697 bp); centromere - exons 1 to 4 - telomere orientation; only the first three exons are coding. Located 15-16 kb centromeric of TCL1A. ...
Characteristics of Viruses-Parts 1_2_3
... (page 3: Characteristics of Viruses--Part III) A prion is a protein molecule that can cause disease in animals. Prions are the only known infectious agents that do not contain DNA or RNA but can, nonetheless, spread throughout an organism. A prion causes a fatal disease called scrapie in sheep. Pri ...
... (page 3: Characteristics of Viruses--Part III) A prion is a protein molecule that can cause disease in animals. Prions are the only known infectious agents that do not contain DNA or RNA but can, nonetheless, spread throughout an organism. A prion causes a fatal disease called scrapie in sheep. Pri ...
Genome Editing Using Cas9 Nickases
... for recombination but repairs DSBs with high fidelity, and nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ), which functions without a template and frequently produces insertions or deletions (indels) as a consequence of repair. Exogenous HDR templates can be designed and introduced along with Cas9 and sgRNA to pro ...
... for recombination but repairs DSBs with high fidelity, and nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ), which functions without a template and frequently produces insertions or deletions (indels) as a consequence of repair. Exogenous HDR templates can be designed and introduced along with Cas9 and sgRNA to pro ...
CHAPTER 15 Manipulating genes in organisms
... into the genome of plant cells is used by biotechnologists. This behaviour of Agrobacterium can be used to transfer foreign DNA into plant cells to develop genetically modified plant crops. The foreign DNA must be inserted into the plasmid within the T-DNA region. However, before they are used to tr ...
... into the genome of plant cells is used by biotechnologists. This behaviour of Agrobacterium can be used to transfer foreign DNA into plant cells to develop genetically modified plant crops. The foreign DNA must be inserted into the plasmid within the T-DNA region. However, before they are used to tr ...
The dnrM gene in Streptomyces peucetius contains a
... endonuclease digestions, and ligations were performed according to standard techniques (Sambrook e t al., 1989). Hybridization analysis was carried out using the Genius nonradioactive kit (Boehringer Mannheim) according to the manufacturer's instructions. DNA was electrophoresed on 0.7 YO agarose ge ...
... endonuclease digestions, and ligations were performed according to standard techniques (Sambrook e t al., 1989). Hybridization analysis was carried out using the Genius nonradioactive kit (Boehringer Mannheim) according to the manufacturer's instructions. DNA was electrophoresed on 0.7 YO agarose ge ...
Todd Eckdahl - Davidson College
... Minor Groove Binding Drugs Anti-tumor properties Conformational change in the 3D structure of DNA Prior Knowledge of MGBD/DNA interaction As models for minor groove binding proteins ...
... Minor Groove Binding Drugs Anti-tumor properties Conformational change in the 3D structure of DNA Prior Knowledge of MGBD/DNA interaction As models for minor groove binding proteins ...
File - western undergrad. by the students, for the students.
... The Central Dogma defines transcription (copying of DNA into RNA) and translation (process of decoding an RNA to synthesize protein) as two key processes in gene expression. The RNA intermediary allows a step of amplification (in contrast to DNA where single copies exist, the RNAs for any single mes ...
... The Central Dogma defines transcription (copying of DNA into RNA) and translation (process of decoding an RNA to synthesize protein) as two key processes in gene expression. The RNA intermediary allows a step of amplification (in contrast to DNA where single copies exist, the RNAs for any single mes ...
Example: search for regulatory binding sites
... the so-called promoter region (TATA-box; or -10, -35) – Regulated by some (regulatory) proteins on DNA “near” the promoter region. – These binding sites on DNA are often “similar” in composition. Enhancers and repressors ...
... the so-called promoter region (TATA-box; or -10, -35) – Regulated by some (regulatory) proteins on DNA “near” the promoter region. – These binding sites on DNA are often “similar” in composition. Enhancers and repressors ...
Lecture 4: bioenergetics and metabolism (mitochondria and
... A fertilized human egg carries 2000 copies of the human mitochondrial genome, all but one or two inherited from the mother. A human in whom all of these mitochondrial genomes carried a deleterious mutation would generally not survive. But some mothers carry a mixed population of both mutant and norm ...
... A fertilized human egg carries 2000 copies of the human mitochondrial genome, all but one or two inherited from the mother. A human in whom all of these mitochondrial genomes carried a deleterious mutation would generally not survive. But some mothers carry a mixed population of both mutant and norm ...
"PHIP1 as a novel regulator of beta-cell proliferation and survival" at
... Cloning of PHIP1 cDNA - Full-length human PHIP1 (hPHIP1) complementary DNA (cDNA) was amplified from a human MCF7 cDNA library using High-fidelity Taq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen, Canada). The amplicon (size 5.53 kb) spanning the entire 1821 aa open reading frame (ORF) was digested with ClaI and BamH ...
... Cloning of PHIP1 cDNA - Full-length human PHIP1 (hPHIP1) complementary DNA (cDNA) was amplified from a human MCF7 cDNA library using High-fidelity Taq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen, Canada). The amplicon (size 5.53 kb) spanning the entire 1821 aa open reading frame (ORF) was digested with ClaI and BamH ...
1 - chem.msu.su
... sionally causes "red tides") are also deadly poisons, which block neurotransmission by preventing the opening of Na + channels. Tumors and cancer are the result of uncontrolled cell division. Normally, cell division is highly regulated by a family of growth factors, proteins that cause resting cells ...
... sionally causes "red tides") are also deadly poisons, which block neurotransmission by preventing the opening of Na + channels. Tumors and cancer are the result of uncontrolled cell division. Normally, cell division is highly regulated by a family of growth factors, proteins that cause resting cells ...
Mitochondrial DNA
... Eyes can be affected several months apart, or simultaneously. About 85% are male (no good reason why). Recurrence risk for siblings around 20% (heteroplasmy); many spontaneous cases. Due to death of optic nerve fibers. Most due to change in conserved Arg to His in NADH dehydrogenase, but 18 total mu ...
... Eyes can be affected several months apart, or simultaneously. About 85% are male (no good reason why). Recurrence risk for siblings around 20% (heteroplasmy); many spontaneous cases. Due to death of optic nerve fibers. Most due to change in conserved Arg to His in NADH dehydrogenase, but 18 total mu ...
UNIT 1: DNA and the Genome
... keratin (hair); the cells found in heart tissue do not produce any digestive enzymes like pepsin or amylase, as they are not required. ...
... keratin (hair); the cells found in heart tissue do not produce any digestive enzymes like pepsin or amylase, as they are not required. ...
The Effects of Arsenic Toxicity in PLHC-1 Cell Line
... problems and it could be trypsin or cell growth pattern. DNA ladder assay: PLHC-1 may have different pathway MTT assay: I am repeating this assay for my class, if it works I will add to the thesis. Western blot: I am repeating this assay for my class, if it works I will add to the thesis. Other expe ...
... problems and it could be trypsin or cell growth pattern. DNA ladder assay: PLHC-1 may have different pathway MTT assay: I am repeating this assay for my class, if it works I will add to the thesis. Western blot: I am repeating this assay for my class, if it works I will add to the thesis. Other expe ...
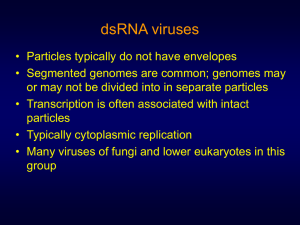
dsRNA viruses
... to give two or more dsRNA molecules per particle (headful replication). The positive ssRNA of ScVL-A is the species encapsidated to form progeny virus particles. The encapsidation signal on ScV-LA or M1 positive sense ssRNA is a 24 b stem-loop sequence located 400 nts from the 3 -end in each case. T ...
... to give two or more dsRNA molecules per particle (headful replication). The positive ssRNA of ScVL-A is the species encapsidated to form progeny virus particles. The encapsidation signal on ScV-LA or M1 positive sense ssRNA is a 24 b stem-loop sequence located 400 nts from the 3 -end in each case. T ...
Biology - Cincinnati Christian School
... What is the pattern for organization and storage of genetic information? What is the purpose of a gene? How can genes be altered? What factors influence what genes are expressed in a specific cell? How can use probability to predict traits inherited by offspring? What causes variations? How can pedi ...
... What is the pattern for organization and storage of genetic information? What is the purpose of a gene? How can genes be altered? What factors influence what genes are expressed in a specific cell? How can use probability to predict traits inherited by offspring? What causes variations? How can pedi ...
Chapter 20
... • Reverse transcriptase is added to mRNA to make cDNA, which serves as a template for PCR amplification of the gene of interest • The products are run on a gel and the mRNA of ...
... • Reverse transcriptase is added to mRNA to make cDNA, which serves as a template for PCR amplification of the gene of interest • The products are run on a gel and the mRNA of ...
Leptin is a 16 kDa, 146 amino acid residue non
... predominantly by adipocytes consistent with the fact that body weight is sensed mainly as the total mass of fat in the body. Leptin is also secreted by cells in the epithelium of the stomach and in the placenta in smaller amounts. Leptin receptors (OB-R) are highly expressed in areas of the hypothal ...
... predominantly by adipocytes consistent with the fact that body weight is sensed mainly as the total mass of fat in the body. Leptin is also secreted by cells in the epithelium of the stomach and in the placenta in smaller amounts. Leptin receptors (OB-R) are highly expressed in areas of the hypothal ...
LS1a Fall 09
... the A-site. The mRNA advances by three nucleotides, placing the tRNAs in the E- and P-sites. o Step 3: The spent tRNA is ejected from the E-site and the ribosome is reset to bind another aminoacyl-tRNA at the A-site. ...
... the A-site. The mRNA advances by three nucleotides, placing the tRNAs in the E- and P-sites. o Step 3: The spent tRNA is ejected from the E-site and the ribosome is reset to bind another aminoacyl-tRNA at the A-site. ...
Endogenous retrovirus
Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) are endogenous viral elements in the genome that closely resemble and can be derived from retroviruses. They are abundant in the genomes of jawed vertebrates, and they comprise up to 5–8% of the human genome (lower estimates of ~1%). ERVs are a subclass of a type of gene called a transposon, which can be packaged and moved within the genome to serve a vital role in gene expression and in regulation. Researchers have suggested that retroviruses evolved from a type of transposable gene called a retrotransposon, which includes ERVs; these genes can mutate and instead of moving to another location in the genome they can become exogenous or pathogenic. This means that all ERVs may not have originated as an insertion by a retrovirus but that some may have been the source for the genetic information in the retroviruses they resemble.