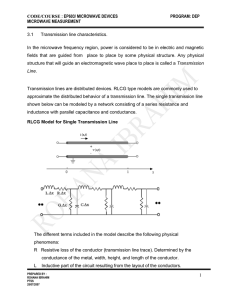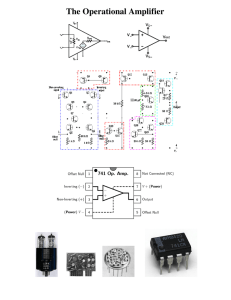
The Operational Amplifier
... Nevertheless the circuit may become unstable when connected to a capacitive load. A solution may be to use two inverting amplifiers configuration with R1 and Rf being of equal value. ...
... Nevertheless the circuit may become unstable when connected to a capacitive load. A solution may be to use two inverting amplifiers configuration with R1 and Rf being of equal value. ...
Transmission Lines — a review and explanation
... RL =∞ (no reflected power). A short or open has RL = 0 dB; everything reflected. ...
... RL =∞ (no reflected power). A short or open has RL = 0 dB; everything reflected. ...
Print this article - International Journal of Innovative Research and
... reason is device protection – If RF circuit is not matched we get reflected power. This reflected power builds standing waves on the transmission line between the source and load. Depending on the phase between the forward and reflected both waves can either subtract or add. Because of that on the l ...
... reason is device protection – If RF circuit is not matched we get reflected power. This reflected power builds standing waves on the transmission line between the source and load. Depending on the phase between the forward and reflected both waves can either subtract or add. Because of that on the l ...
Complex impedance method for AC circuits
... of Ohm’s law, V = IR. The impedance is most directly interpreted when written in polar form, Z = |Z|eiφ . The magnitude |Z| = V0 /I0 is called the reactance, and it determines the real amplitude of the current given the real amplitude of the voltage. The phase φ of Z encodes the phase relation betwe ...
... of Ohm’s law, V = IR. The impedance is most directly interpreted when written in polar form, Z = |Z|eiφ . The magnitude |Z| = V0 /I0 is called the reactance, and it determines the real amplitude of the current given the real amplitude of the voltage. The phase φ of Z encodes the phase relation betwe ...
Technician Study Sheet
... This section refers to actual knobs and buttons on an amateur radio (and many others). Up/Down buttons on the radio or microphone allow tuning different frequencies or memory channels. Shift allows changing the transmit and receive frequencies for working through repeaters. The Noise Blanker is desi ...
... This section refers to actual knobs and buttons on an amateur radio (and many others). Up/Down buttons on the radio or microphone allow tuning different frequencies or memory channels. Shift allows changing the transmit and receive frequencies for working through repeaters. The Noise Blanker is desi ...
BDS-MF Generator
... BDS-MF 5/10kW @ 40kHz, High|Low Voltage AC plasma generator The BDS-MF is a 40 kHz plasma generator with max power delivery of 5kW or10 kW is specifically designed for plasma excitation on PECVD or plasma cleaning applications. The unit is capable of delivery up to 10kW at 7000V RMS output. The outp ...
... BDS-MF 5/10kW @ 40kHz, High|Low Voltage AC plasma generator The BDS-MF is a 40 kHz plasma generator with max power delivery of 5kW or10 kW is specifically designed for plasma excitation on PECVD or plasma cleaning applications. The unit is capable of delivery up to 10kW at 7000V RMS output. The outp ...
17510 Sample Question Paper
... a) i) Define the generalized circuit & generalized circuit constants. ii) Prove that the complex power in power system is defined as S=VI* instead of S=V*I. b) A 220 kV, 50Hz , 200Km long, 3-phase line has its conductors on the corners of a triangle with sides 6m, 6m, & 12m. The Conductor radius is ...
... a) i) Define the generalized circuit & generalized circuit constants. ii) Prove that the complex power in power system is defined as S=VI* instead of S=V*I. b) A 220 kV, 50Hz , 200Km long, 3-phase line has its conductors on the corners of a triangle with sides 6m, 6m, & 12m. The Conductor radius is ...
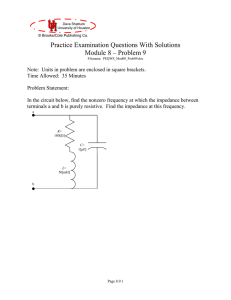
PEQWS_Mod08_Prob09_v06
... denominator is due to round off errors. The answer, then, is that Zab (2,650[rad/s]) 278[W]. ...
... denominator is due to round off errors. The answer, then, is that Zab (2,650[rad/s]) 278[W]. ...
EECS 420 – Electromagnetics II Lab
... wave. The information carried by the reflected wave is valuable since it reveals the nature of the mismatch. The reflection coefficient in the frequency domain, then, is expressed as ...
... wave. The information carried by the reflected wave is valuable since it reveals the nature of the mismatch. The reflection coefficient in the frequency domain, then, is expressed as ...
Advanced Lab Course Impedance Spectroscopy M208 Content
... ωmax is the frequency belonging to the maximum value of the imaginary part. But this easy way of data evaluation is not possible if only a part of the semi circle can be measured. This may be due to frequency limitation or due to noise. If this is the case, a fitting routine has to be applied. "Bad" ...
... ωmax is the frequency belonging to the maximum value of the imaginary part. But this easy way of data evaluation is not possible if only a part of the semi circle can be measured. This may be due to frequency limitation or due to noise. If this is the case, a fitting routine has to be applied. "Bad" ...
IMPEDANCE Matching
... is driving its complex conjugate load impedance consisting of a −jX reactance (capacitor) in series with RL. The +jX component of the source and the−jX component of the load are in series and, thus,cancel each other, leaving only Rs and RL, which are equal by definition. Since Rs and RL are equal, m ...
... is driving its complex conjugate load impedance consisting of a −jX reactance (capacitor) in series with RL. The +jX component of the source and the−jX component of the load are in series and, thus,cancel each other, leaving only Rs and RL, which are equal by definition. Since Rs and RL are equal, m ...
Capacitors Capacitor i-v Characteristic Capacitor Values C is Open
... Capacitor Charge/Discharge ...
... Capacitor Charge/Discharge ...
Standing wave ratio

In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the transmission line, and SWR is defined as the ratio of the partial standing wave's amplitude at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at a node (minimum) along the line.The SWR is usually thought of in terms of the maximum and minimum AC voltages along the transmission line, thus called the voltage standing wave ratio or VSWR (sometimes pronounced ""viswar""). For example, the VSWR value 1.2:1 denotes an AC voltage due to standing waves along the transmission line reaching a peak value 1.2 times that of the minimum AC voltage along that line. The SWR can as well be defined as the ratio of the maximum amplitude to minimum amplitude of the transmission line's currents, electric field strength, or the magnetic field strength. Neglecting transmission line loss, these ratios are identical.The power standing wave ratio (PSWR) is defined as the square of the VSWR, however this terminology has no physical relation to actual powers involved in transmission.The SWR can be measured with an instrument called an SWR meter. Since SWR is defined relative to the transmission line's characteristic impedance, the SWR meter must be constructed for that impedance; in practice most transmission lines used in these applications are coaxial cables with an impedance of either 50 or 75 ohms. Checking the SWR is a standard procedure in a radio station, for instance, to verify impedance matching of the antenna to the transmission line (and transmitter). Unlike connecting an impedance analyzer (or ""impedance bridge"") directly to the antenna (or other load), the SWR does not measure the actual impedance of the load, but quantifies the magnitude of the impedance mismatch just performing a measurement on the transmitter side of the transmission line.