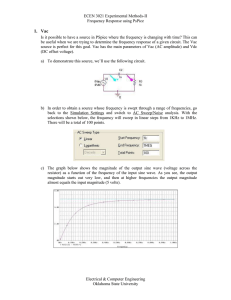
AC Series Notes
... b. Apply Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law and the voltage divider rule to AC series circuits c. Graph impedances, voltages and current as a function of phase d. Graph voltages and current as a function of time The general approach to solving AC circuit problems is to convert sine waves (voltages a ...
... b. Apply Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law and the voltage divider rule to AC series circuits c. Graph impedances, voltages and current as a function of phase d. Graph voltages and current as a function of time The general approach to solving AC circuit problems is to convert sine waves (voltages a ...
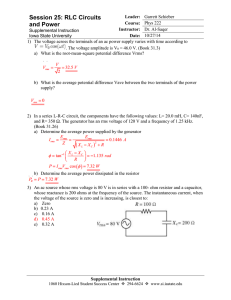
Session 25 Answers - Iowa State University
... 4) An R-L-C series circuit is constructed using a 175-ohm resistor, a 12.5-µF capacitor, and an 8.00-mH inductor, all connected across an ac source having a variable frequency and a voltage amplitude of 25.0 V. a) At what angular frequency will the impedance be smallest? ...
... 4) An R-L-C series circuit is constructed using a 175-ohm resistor, a 12.5-µF capacitor, and an 8.00-mH inductor, all connected across an ac source having a variable frequency and a voltage amplitude of 25.0 V. a) At what angular frequency will the impedance be smallest? ...
lecture 5 revised
... The impedance is given by Z =V/I Impedance is a vector quantity and can be defined using complex numbers ...
... The impedance is given by Z =V/I Impedance is a vector quantity and can be defined using complex numbers ...
BSNL JTO Question Paper 2 2014
... 35. The advantages of wave guides over co-axial lines would include which of the following features 1. 1. Easier to use 2. lower power losses 2. 3. Higher operating frequencies possible a) 1 and 2 b) 1 and 3 c) 2 and 3 d) 1,2 and 3 3. 36. When a 75 ohm transmission line is to be terminated in two re ...
... 35. The advantages of wave guides over co-axial lines would include which of the following features 1. 1. Easier to use 2. lower power losses 2. 3. Higher operating frequencies possible a) 1 and 2 b) 1 and 3 c) 2 and 3 d) 1,2 and 3 3. 36. When a 75 ohm transmission line is to be terminated in two re ...
No Slide Title
... one second due to a difference of potential at the two ends is a current of one ampere (1A) • One coulomb: the total charge possessed by 6.25 X 1018 electrons • A single electron has a charge of 1.6 X 10-19 C ...
... one second due to a difference of potential at the two ends is a current of one ampere (1A) • One coulomb: the total charge possessed by 6.25 X 1018 electrons • A single electron has a charge of 1.6 X 10-19 C ...
MP-50 Current monitoring probe
... The Current Monitoring probes may be used whenever RF current measurements are required. Current measurements are made by placing a current carrying conductor within the “sensing” window of the probe and measuring the probe’s output voltage with an RF detector. Calibration of the probe permits the c ...
... The Current Monitoring probes may be used whenever RF current measurements are required. Current measurements are made by placing a current carrying conductor within the “sensing” window of the probe and measuring the probe’s output voltage with an RF detector. Calibration of the probe permits the c ...
Ohm`s Law
... • To ensure sufficient current level in the loop (20 mA) the resistance of the wire should not exceed certain limit. This limits the length of the twisted pair line from central office to the subscriber. 1700 Ohms is a typical value. ...
... • To ensure sufficient current level in the loop (20 mA) the resistance of the wire should not exceed certain limit. This limits the length of the twisted pair line from central office to the subscriber. 1700 Ohms is a typical value. ...
So…What is the use of transmission line??
... Voltage Reflection Coefficient • Every transmission line has a resistance associated with it, and comes about because of its construction. This is called its characteristic impedance, Z0. • The standard characteristic impedance value is 50Ω. However when the transmission line is terminated with an ...
... Voltage Reflection Coefficient • Every transmission line has a resistance associated with it, and comes about because of its construction. This is called its characteristic impedance, Z0. • The standard characteristic impedance value is 50Ω. However when the transmission line is terminated with an ...
141 EBI100C Electrical Bio-Impedance Amplifier The EBI100C
... current through the measurement tissue volume defined by the placement of a set of current source electrodes. A separate set of monitoring electrodes then measures the voltage developed across the tissue volume. Because the current is constant, the voltage measured is proportional to the characteris ...
... current through the measurement tissue volume defined by the placement of a set of current source electrodes. A separate set of monitoring electrodes then measures the voltage developed across the tissue volume. Because the current is constant, the voltage measured is proportional to the characteris ...
Standing wave ratio

In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the transmission line, and SWR is defined as the ratio of the partial standing wave's amplitude at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at a node (minimum) along the line.The SWR is usually thought of in terms of the maximum and minimum AC voltages along the transmission line, thus called the voltage standing wave ratio or VSWR (sometimes pronounced ""viswar""). For example, the VSWR value 1.2:1 denotes an AC voltage due to standing waves along the transmission line reaching a peak value 1.2 times that of the minimum AC voltage along that line. The SWR can as well be defined as the ratio of the maximum amplitude to minimum amplitude of the transmission line's currents, electric field strength, or the magnetic field strength. Neglecting transmission line loss, these ratios are identical.The power standing wave ratio (PSWR) is defined as the square of the VSWR, however this terminology has no physical relation to actual powers involved in transmission.The SWR can be measured with an instrument called an SWR meter. Since SWR is defined relative to the transmission line's characteristic impedance, the SWR meter must be constructed for that impedance; in practice most transmission lines used in these applications are coaxial cables with an impedance of either 50 or 75 ohms. Checking the SWR is a standard procedure in a radio station, for instance, to verify impedance matching of the antenna to the transmission line (and transmitter). Unlike connecting an impedance analyzer (or ""impedance bridge"") directly to the antenna (or other load), the SWR does not measure the actual impedance of the load, but quantifies the magnitude of the impedance mismatch just performing a measurement on the transmitter side of the transmission line.