* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Capacitors Capacitor i-v Characteristic Capacitor Values C is Open
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Distributed element filter wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
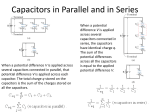
1/22/2014 Capacitor Capacitors • A capacitor consists of two metal plates separated by a dielectric with permittivity є. Peter Mathys ECEN 1400 i-v Characteristic Capacitor Values • Values for small capacitors range from 10 pF (1 pF = 10-12 F) to several 100 nF (1 nF = 10-9 F) • Larger capacitors in the range from 1 μF (1 μF = 10-6 F) to several mF (1 mF = 10-3 F) usually come in the form of electrolytic capacitors which use an electrolyte in liquid or paste form as dielectric. • Important: Electrolytic capacitors are polarized. Wrong polarity leads to destruction! C is Open Circuit for dc Energy Stored in Capacitor 1 1/22/2014 Power and Energy Energy Stored in Electric Field Capacitors in Parallel Capacitors in Series Capacitor Charge/Discharge Differential Equation 2 1/22/2014 Differential Equation Solution Capacitor Charge Capacitor Discharge Sinusoidal Waveforms Euler’s Relation Using Complex Numbers 3 1/22/2014 Voltage/Current Phasors “Ohm’s Law” for Capacitors I and V are called phasors. They only depend on the phase of the sinusoidal waveform and not on the frequency. Impedance Series RC Impedance • The generalization of Ohm’s law for phasors is • • • • The quantity Z = R + j·X is called impedance. R is resistance with units ohms (Ω). X is reactance with units ohms (Ω). Reminder: Phasors can only be used with sinusoidal waveforms. • The equivalent impedance Zeq of the series RC circuit is computed as: • For small f Zeq approaches ZC, for large f Zeq approaches ZR=R. Parallel RC Impedance • The equivalent impedance Zeq of the parallel RC circuit is computed as: • For small f Zeq approaches ZR=R, for large f Zeq approaches ZC. 4