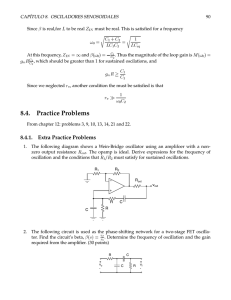
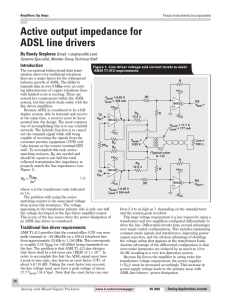
MAE212.X - UCI bioMEMS
... •Concept of complex impedance: from R to Z •Ohm's law defines resistance in terms of the ratio between voltage E and current I : ...
... •Concept of complex impedance: from R to Z •Ohm's law defines resistance in terms of the ratio between voltage E and current I : ...
Nyquist plot
... •Concept of complex impedance: from R to Z •Ohm's law defines resistance in terms of the ratio between voltage E and current I : ...
... •Concept of complex impedance: from R to Z •Ohm's law defines resistance in terms of the ratio between voltage E and current I : ...
Review of Resonance
... The role of capacitance and inductance are also interchanged. In principle, therefore, we don’t have to repeat all the detailed calculations we just performed for the series case, but in practice it’s a worthwhile exercise. The admittance of the circuit is given by ...
... The role of capacitance and inductance are also interchanged. In principle, therefore, we don’t have to repeat all the detailed calculations we just performed for the series case, but in practice it’s a worthwhile exercise. The admittance of the circuit is given by ...
Introduction
... In order to reduce the cost of the card, a less expensive optomodule is needed. In order to be able to test other optomodules, a design needs to be built that incorporates the current optomodule, but can also be used to test replacement optomodules. The optical module that is used on the Intel card, ...
... In order to reduce the cost of the card, a less expensive optomodule is needed. In order to be able to test other optomodules, a design needs to be built that incorporates the current optomodule, but can also be used to test replacement optomodules. The optical module that is used on the Intel card, ...
university of massachusetts dartmouth
... First we will determine the amount of phase shift between the two sinusoidal waveforms. Let’s take a look at just the waveform of the input voltage. One cycle of that voltage is contained within 10 horizontal divisions, or, we could say that there is 360/10, or 36/division worth of phase. In order ...
... First we will determine the amount of phase shift between the two sinusoidal waveforms. Let’s take a look at just the waveform of the input voltage. One cycle of that voltage is contained within 10 horizontal divisions, or, we could say that there is 360/10, or 36/division worth of phase. In order ...
answers
... secondary winding – closer to the desired d.c. output voltage than the original mains voltage. The transformer also provides electrical isolation between the mains supply and the load. The diodes D1 to D4 perform rectification. On positive half cycles of the secondary voltage, D2 and D4 are forward ...
... secondary winding – closer to the desired d.c. output voltage than the original mains voltage. The transformer also provides electrical isolation between the mains supply and the load. The diodes D1 to D4 perform rectification. On positive half cycles of the secondary voltage, D2 and D4 are forward ...
Series RLC at resonance
... input is an impulse at t = 0. Thus, the capacitor reaches full charge very quickly and becomes an open circuit— the well-known DC behaviour of a capacitor. ...
... input is an impulse at t = 0. Thus, the capacitor reaches full charge very quickly and becomes an open circuit— the well-known DC behaviour of a capacitor. ...
15-16 ac power and power factor
... In theory, the power factor can be corrected to unity by putting a capacitor in series with the load. However, it is found (ex. 7.9) that this configuration will result in significant increase in the current, and thus increase the power required by the generator. ...
... In theory, the power factor can be corrected to unity by putting a capacitor in series with the load. However, it is found (ex. 7.9) that this configuration will result in significant increase in the current, and thus increase the power required by the generator. ...
Operator´s Manual Charge Preamplifiers ICP100 / 110 / 120
... Because of the high sensitivity of the charge input against interference it is recommended to use special low noise cable only, for example Metra´s Model 009 or 010. With other cables the shielding effect is often insufficient. At mechanical strain, for example bending strain, an interfering signal, ...
... Because of the high sensitivity of the charge input against interference it is recommended to use special low noise cable only, for example Metra´s Model 009 or 010. With other cables the shielding effect is often insufficient. At mechanical strain, for example bending strain, an interfering signal, ...
Standing wave ratio

In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the transmission line, and SWR is defined as the ratio of the partial standing wave's amplitude at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at a node (minimum) along the line.The SWR is usually thought of in terms of the maximum and minimum AC voltages along the transmission line, thus called the voltage standing wave ratio or VSWR (sometimes pronounced ""viswar""). For example, the VSWR value 1.2:1 denotes an AC voltage due to standing waves along the transmission line reaching a peak value 1.2 times that of the minimum AC voltage along that line. The SWR can as well be defined as the ratio of the maximum amplitude to minimum amplitude of the transmission line's currents, electric field strength, or the magnetic field strength. Neglecting transmission line loss, these ratios are identical.The power standing wave ratio (PSWR) is defined as the square of the VSWR, however this terminology has no physical relation to actual powers involved in transmission.The SWR can be measured with an instrument called an SWR meter. Since SWR is defined relative to the transmission line's characteristic impedance, the SWR meter must be constructed for that impedance; in practice most transmission lines used in these applications are coaxial cables with an impedance of either 50 or 75 ohms. Checking the SWR is a standard procedure in a radio station, for instance, to verify impedance matching of the antenna to the transmission line (and transmitter). Unlike connecting an impedance analyzer (or ""impedance bridge"") directly to the antenna (or other load), the SWR does not measure the actual impedance of the load, but quantifies the magnitude of the impedance mismatch just performing a measurement on the transmitter side of the transmission line.