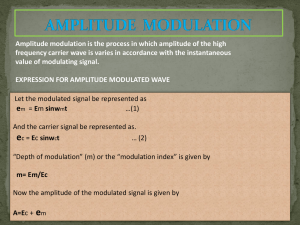
Click Here (.doc)
... For this step we had to build the circuit of figure 10 and then use the triple output power supply for Vin and the other power supply for Vdc = 1.5V. Then we connected the com of the triple output power supply to the negative terminal of the other power supply. Then We measured Vout while varying Vi ...
... For this step we had to build the circuit of figure 10 and then use the triple output power supply for Vin and the other power supply for Vdc = 1.5V. Then we connected the com of the triple output power supply to the negative terminal of the other power supply. Then We measured Vout while varying Vi ...
ultrabass bx 200 - Meteoro Amplificadores
... down before moving it and certainly before putting into the back of the truck on a cold night. ...
... down before moving it and certainly before putting into the back of the truck on a cold night. ...
Function generators, 5 MHz with integral feedback voltage
... signal frequencies. The high output voltage of max. Vpp = 30 V will satisfy the requirements of most general-purpose laboratory or service tasks as well as the needs of applications in production plants or educational institutions. All inputs and outputs are absolutely no-load and short-circuit proo ...
... signal frequencies. The high output voltage of max. Vpp = 30 V will satisfy the requirements of most general-purpose laboratory or service tasks as well as the needs of applications in production plants or educational institutions. All inputs and outputs are absolutely no-load and short-circuit proo ...
click here
... The dual gate MOSFET was an especially popular device for commercial applications in the late 1970 and early 1980 period. Discrete components still dominated, especially when dealing with RF. It was not long after this that monolithic ICs began to take over, causing familiar parts to become scarce o ...
... The dual gate MOSFET was an especially popular device for commercial applications in the late 1970 and early 1980 period. Discrete components still dominated, especially when dealing with RF. It was not long after this that monolithic ICs began to take over, causing familiar parts to become scarce o ...
AS lab 4
... i) Connect 3 resistors R1, R2 and R3 having different values in the ratio 1:10:100 (for example 100 Ohms, 1000 Ohms and 10,000 ohms) respectively in series with a DC power supply and an ammeter as shown in figure 1. ii) Connect DC voltmeter (0 to 10 volts range) across each resistors iii) Switch on ...
... i) Connect 3 resistors R1, R2 and R3 having different values in the ratio 1:10:100 (for example 100 Ohms, 1000 Ohms and 10,000 ohms) respectively in series with a DC power supply and an ammeter as shown in figure 1. ii) Connect DC voltmeter (0 to 10 volts range) across each resistors iii) Switch on ...
Here - CAR AUDIO PERU
... The very nature of the RCA design makes it less than ideal for automotive use. We have two major problems in cars that are not found in the home. First, the car has an alternator that produces electrical current and sends it to all areas of the car through the car’s electrical system. This noise wil ...
... The very nature of the RCA design makes it less than ideal for automotive use. We have two major problems in cars that are not found in the home. First, the car has an alternator that produces electrical current and sends it to all areas of the car through the car’s electrical system. This noise wil ...
Lecture 2: Complex Power, Reactive Compensation, Three Phase
... three voltage sources with equal magnitude, but with an angle shift of 120 equal loads on each phase equal impedance on the lines connecting the generators to the loads ...
... three voltage sources with equal magnitude, but with an angle shift of 120 equal loads on each phase equal impedance on the lines connecting the generators to the loads ...
Standing wave ratio

In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the transmission line, and SWR is defined as the ratio of the partial standing wave's amplitude at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at a node (minimum) along the line.The SWR is usually thought of in terms of the maximum and minimum AC voltages along the transmission line, thus called the voltage standing wave ratio or VSWR (sometimes pronounced ""viswar""). For example, the VSWR value 1.2:1 denotes an AC voltage due to standing waves along the transmission line reaching a peak value 1.2 times that of the minimum AC voltage along that line. The SWR can as well be defined as the ratio of the maximum amplitude to minimum amplitude of the transmission line's currents, electric field strength, or the magnetic field strength. Neglecting transmission line loss, these ratios are identical.The power standing wave ratio (PSWR) is defined as the square of the VSWR, however this terminology has no physical relation to actual powers involved in transmission.The SWR can be measured with an instrument called an SWR meter. Since SWR is defined relative to the transmission line's characteristic impedance, the SWR meter must be constructed for that impedance; in practice most transmission lines used in these applications are coaxial cables with an impedance of either 50 or 75 ohms. Checking the SWR is a standard procedure in a radio station, for instance, to verify impedance matching of the antenna to the transmission line (and transmitter). Unlike connecting an impedance analyzer (or ""impedance bridge"") directly to the antenna (or other load), the SWR does not measure the actual impedance of the load, but quantifies the magnitude of the impedance mismatch just performing a measurement on the transmitter side of the transmission line.