1. Introduction - About the journal
... loaded by a capacitor, it leads to improper transfer functions. Due to the effect of this parasitic resistance Rx at the x port of DVCC, the filters with x port loaded by a capacitor do not exhibit good performance at high frequency. Several voltage-mode universal biquads each with three input termi ...
... loaded by a capacitor, it leads to improper transfer functions. Due to the effect of this parasitic resistance Rx at the x port of DVCC, the filters with x port loaded by a capacitor do not exhibit good performance at high frequency. Several voltage-mode universal biquads each with three input termi ...
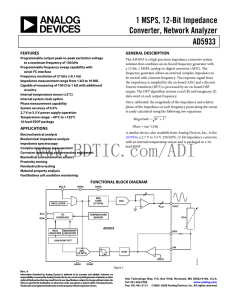
+/-200V Common-Mode Voltage Difference
... voltage. Figure 2 shows an optional circuit for trimming the offset voltage. To maintain high common-mode rejection (CMR), the source impedance of any signal applied to the Ref terminal should be very low (≤5Ω). A source impedance of only 10Ω at the Ref pin will reduce the INA148’s CMR to approximat ...
... voltage. Figure 2 shows an optional circuit for trimming the offset voltage. To maintain high common-mode rejection (CMR), the source impedance of any signal applied to the Ref terminal should be very low (≤5Ω). A source impedance of only 10Ω at the Ref pin will reduce the INA148’s CMR to approximat ...
Reciprocity condition in terms of two port parameters
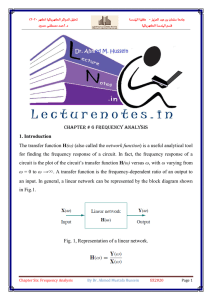
... Mesh current or node voltage methods are general methods which are applicable to any network. A number of simultaneous equations are to be set up. Solving these equations, the response in all the branches of the network may be attained. But in many cases, we require the response in one branch or in ...
... Mesh current or node voltage methods are general methods which are applicable to any network. A number of simultaneous equations are to be set up. Solving these equations, the response in all the branches of the network may be attained. But in many cases, we require the response in one branch or in ...
Optimized design of antenna systems for radar - iTEAM
... on dipoles are expanded into a single basis function per slot/dipole, with cosine distribution in the longitudinal dimension and uniform distribution in the transversal dimension. This equivalence in the analysis method (one basis function per element) turns out to be fundamental for a time efficien ...
... on dipoles are expanded into a single basis function per slot/dipole, with cosine distribution in the longitudinal dimension and uniform distribution in the transversal dimension. This equivalence in the analysis method (one basis function per element) turns out to be fundamental for a time efficien ...
Manual - DPA Microphones
... foam windscreen on the mic head whenever used outdoors or in air tur(2 ft) situations distance:such as close miking voice in order to prevent wind- or pop noise. bulent Grids ...
... foam windscreen on the mic head whenever used outdoors or in air tur(2 ft) situations distance:such as close miking voice in order to prevent wind- or pop noise. bulent Grids ...
EEEE 381 Lab 3_Current Source - RIT - People
... achieved the same output impedance without using the fourth transistor M4, in which case this circuit becomes a Wilson current source instead of a modified Wilson current source (as shown in chapter 8.6.3 of Sedra and Smith, 7th Ed).. However, in the case of modified Wilson current source, the drain ...
... achieved the same output impedance without using the fourth transistor M4, in which case this circuit becomes a Wilson current source instead of a modified Wilson current source (as shown in chapter 8.6.3 of Sedra and Smith, 7th Ed).. However, in the case of modified Wilson current source, the drain ...
0-2 Operations with Complex Numbers
... 17. ELECTRICITY Engineers use imaginary numbers to express the two-dimensional quantity of alternating current, which involves both amplitude and angle. In these imaginary numbers, i is replaced with j because engineers use I as a variable for the entire quantity of current. Impedance is the measure ...
... 17. ELECTRICITY Engineers use imaginary numbers to express the two-dimensional quantity of alternating current, which involves both amplitude and angle. In these imaginary numbers, i is replaced with j because engineers use I as a variable for the entire quantity of current. Impedance is the measure ...
OPA2822 Dual, Wideband, Low-Noise Operational Amplifier FEATURES
... DISCHARGE SENSITIVITY Electrostatic discharge can cause damage ranging from performance degradation to complete device failure. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled and stored using appropriate ESD protection methods. ESD damage can range from subtle performance degra ...
... DISCHARGE SENSITIVITY Electrostatic discharge can cause damage ranging from performance degradation to complete device failure. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled and stored using appropriate ESD protection methods. ESD damage can range from subtle performance degra ...
Different Self Excitation Techniques for Slip Ring Self
... The paper discusses the different possible techniques to self excite the slip ring induction machine working as self excited induction generator. The generated voltage due to self excitation is initiated and sustained with constant value of power capacitors connected across the stator windings. Atte ...
... The paper discusses the different possible techniques to self excite the slip ring induction machine working as self excited induction generator. The generated voltage due to self excitation is initiated and sustained with constant value of power capacitors connected across the stator windings. Atte ...
Standing wave ratio

In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the transmission line, and SWR is defined as the ratio of the partial standing wave's amplitude at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at a node (minimum) along the line.The SWR is usually thought of in terms of the maximum and minimum AC voltages along the transmission line, thus called the voltage standing wave ratio or VSWR (sometimes pronounced ""viswar""). For example, the VSWR value 1.2:1 denotes an AC voltage due to standing waves along the transmission line reaching a peak value 1.2 times that of the minimum AC voltage along that line. The SWR can as well be defined as the ratio of the maximum amplitude to minimum amplitude of the transmission line's currents, electric field strength, or the magnetic field strength. Neglecting transmission line loss, these ratios are identical.The power standing wave ratio (PSWR) is defined as the square of the VSWR, however this terminology has no physical relation to actual powers involved in transmission.The SWR can be measured with an instrument called an SWR meter. Since SWR is defined relative to the transmission line's characteristic impedance, the SWR meter must be constructed for that impedance; in practice most transmission lines used in these applications are coaxial cables with an impedance of either 50 or 75 ohms. Checking the SWR is a standard procedure in a radio station, for instance, to verify impedance matching of the antenna to the transmission line (and transmitter). Unlike connecting an impedance analyzer (or ""impedance bridge"") directly to the antenna (or other load), the SWR does not measure the actual impedance of the load, but quantifies the magnitude of the impedance mismatch just performing a measurement on the transmitter side of the transmission line.