MAX3040–MAX3045 ±10kV ESD-Protected
... an immunity test for the evaluation of electrical and electronic systems during operating conditions. The test was adapted for evaluation of integrated circuits with power applied. Repetitive fast transients with severe pulsed EMI were applied to signal and control ports. Over 15,000 distinct discha ...
... an immunity test for the evaluation of electrical and electronic systems during operating conditions. The test was adapted for evaluation of integrated circuits with power applied. Repetitive fast transients with severe pulsed EMI were applied to signal and control ports. Over 15,000 distinct discha ...
Chapter 9 – AC Circuits
... Solve for the current and all component voltages both as phasors and functions of time. Sketch the time waveforms. ...
... Solve for the current and all component voltages both as phasors and functions of time. Sketch the time waveforms. ...
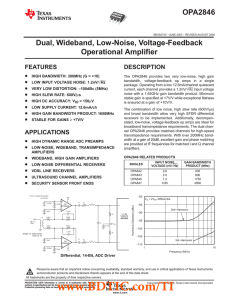
FEATURES DESCRIPTION D
... Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade device reliability. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those specified is not implied. ...
... Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade device reliability. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those specified is not implied. ...
OPER_MAN A1010 (English)
... No external antenna tuner is required as long as the antenna VSWR is 3:1 or lower. The amplifier will perform the functions of an antenna tuner, enabling you to change antennas faster and use them over wide frequency ranges. A durable amplifier. This amplifier is both user-friendly and self-monitori ...
... No external antenna tuner is required as long as the antenna VSWR is 3:1 or lower. The amplifier will perform the functions of an antenna tuner, enabling you to change antennas faster and use them over wide frequency ranges. A durable amplifier. This amplifier is both user-friendly and self-monitori ...
AD810 AnaDev 80MHz 1KV_uS 36V, disable and trim.pdf
... (G = +2) and the differential gain and phase of 0.02% and 0.04° (NTSC) make the AD810 ideal for any broadcast quality video system. All these specifications are under load conditions of 150 Ω (one 75 Ω back terminated cable). The AD810 is ideal for power sensitive applications such as video cameras, ...
... (G = +2) and the differential gain and phase of 0.02% and 0.04° (NTSC) make the AD810 ideal for any broadcast quality video system. All these specifications are under load conditions of 150 Ω (one 75 Ω back terminated cable). The AD810 is ideal for power sensitive applications such as video cameras, ...
Document
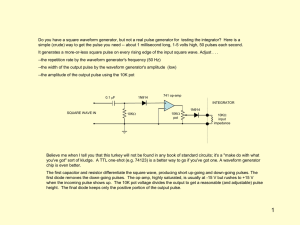
... Do you have a square waveform generator, but not a real pulse generator for testing the integrator? Here is a simple (crude) way to get the pulse you need -- about 1 millisecond long, 1-5 volts high, 50 pulses each second. It generates a more-or-less square pulse on every rising edge of the input sq ...
... Do you have a square waveform generator, but not a real pulse generator for testing the integrator? Here is a simple (crude) way to get the pulse you need -- about 1 millisecond long, 1-5 volts high, 50 pulses each second. It generates a more-or-less square pulse on every rising edge of the input sq ...
OPA692 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling and installation procedures can cause damage. ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete devi ...
... This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling and installation procedures can cause damage. ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete devi ...
W. Inam, K.K. Afridi and D.J. Perreault, “High Efficiency Resonant dc/dc Converter Utilizing a Resistance Compression Network,” 2013 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference , pp. 1399-1405, March 2013.
... increased slightly to provide slightly inductive loading of the inverter to achieve ZVS switching of the inverter switches. For the design of the magnetic structure, a trade-off was made between loss and size. For the transformer and inductors, different core sizes (RM10, RM12 and RM14) and types of ...
... increased slightly to provide slightly inductive loading of the inverter to achieve ZVS switching of the inverter switches. For the design of the magnetic structure, a trade-off was made between loss and size. For the transformer and inductors, different core sizes (RM10, RM12 and RM14) and types of ...
Aalborg Universitet
... been shown in [3,4], that insufficient representation of the radial circuit breaker in the simulation tool is the main contributor to discrepancies between measurement and simulation results for radial energisation in OWFs. The vacuum circuit breaker (VCB) is the preferred choice as the radial circu ...
... been shown in [3,4], that insufficient representation of the radial circuit breaker in the simulation tool is the main contributor to discrepancies between measurement and simulation results for radial energisation in OWFs. The vacuum circuit breaker (VCB) is the preferred choice as the radial circu ...
transparencies - Indico
... Similar to current preamp : Rf -> Cf Vout(ω)/iin(ω) = - Zf = - 1/jω Cf Integrator : vout(t) = -1/Cf ∫ iin(t)dt ...
... Similar to current preamp : Rf -> Cf Vout(ω)/iin(ω) = - Zf = - 1/jω Cf Integrator : vout(t) = -1/Cf ∫ iin(t)dt ...
Standing wave ratio

In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the transmission line, and SWR is defined as the ratio of the partial standing wave's amplitude at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at a node (minimum) along the line.The SWR is usually thought of in terms of the maximum and minimum AC voltages along the transmission line, thus called the voltage standing wave ratio or VSWR (sometimes pronounced ""viswar""). For example, the VSWR value 1.2:1 denotes an AC voltage due to standing waves along the transmission line reaching a peak value 1.2 times that of the minimum AC voltage along that line. The SWR can as well be defined as the ratio of the maximum amplitude to minimum amplitude of the transmission line's currents, electric field strength, or the magnetic field strength. Neglecting transmission line loss, these ratios are identical.The power standing wave ratio (PSWR) is defined as the square of the VSWR, however this terminology has no physical relation to actual powers involved in transmission.The SWR can be measured with an instrument called an SWR meter. Since SWR is defined relative to the transmission line's characteristic impedance, the SWR meter must be constructed for that impedance; in practice most transmission lines used in these applications are coaxial cables with an impedance of either 50 or 75 ohms. Checking the SWR is a standard procedure in a radio station, for instance, to verify impedance matching of the antenna to the transmission line (and transmitter). Unlike connecting an impedance analyzer (or ""impedance bridge"") directly to the antenna (or other load), the SWR does not measure the actual impedance of the load, but quantifies the magnitude of the impedance mismatch just performing a measurement on the transmitter side of the transmission line.