Cabri Investigations
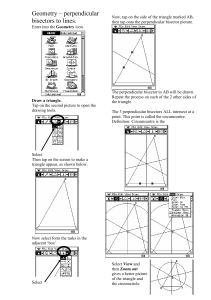
... This is a quadrilateral together with the perpendicular bisectors of the 4 sides. * Can you find a quadrilateral which has 4 perpendicular bisectors crossing at one point? Find as many answers as you can. Try to find out what is special about the quadrilaterals which work, and why. Explore the perpe ...
... This is a quadrilateral together with the perpendicular bisectors of the 4 sides. * Can you find a quadrilateral which has 4 perpendicular bisectors crossing at one point? Find as many answers as you can. Try to find out what is special about the quadrilaterals which work, and why. Explore the perpe ...
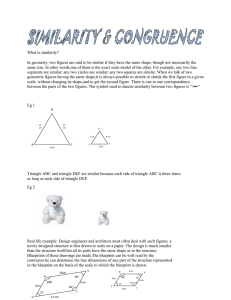
Key Stage 4 Maths Curriculum
... power of ten, number of decimal places and significant figures. Use the concepts and vocabulary of factor (divisor), multiple, common factor, common multiple, highest common factor, least common multiple, prime number and prime factor decomposition. Understand that factors of a number can be derived ...
... power of ten, number of decimal places and significant figures. Use the concepts and vocabulary of factor (divisor), multiple, common factor, common multiple, highest common factor, least common multiple, prime number and prime factor decomposition. Understand that factors of a number can be derived ...
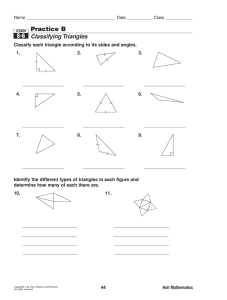
tpc maths (part a) - nswtmth307a
... 1. Line up the base line of the protractor with one arm of the angle (the arms of the angle may have to be extended). 2. Line up the vertical centre line with the apex of the angle. 3. Read off the scale in degrees – check whether the angle is acute or obtuse and make sure that you read off the corr ...
... 1. Line up the base line of the protractor with one arm of the angle (the arms of the angle may have to be extended). 2. Line up the vertical centre line with the apex of the angle. 3. Read off the scale in degrees – check whether the angle is acute or obtuse and make sure that you read off the corr ...