Geometry Opener(s) 11/10
... How do I (HDI) name and label geometric figures? HDI name angles? HDI determine measures of unknown angles? Objective(s) Students will be able to (SWBAT) correlate antiblobbiness with geometry. SWBAT use appropriate notation to name figures. SWBAT name angle types. SWBAT determine the ...
... How do I (HDI) name and label geometric figures? HDI name angles? HDI determine measures of unknown angles? Objective(s) Students will be able to (SWBAT) correlate antiblobbiness with geometry. SWBAT use appropriate notation to name figures. SWBAT name angle types. SWBAT determine the ...
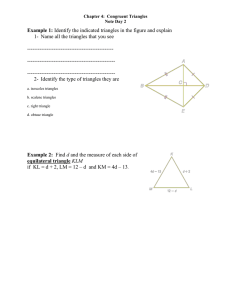
Classifying Triangles
... S ay: We can categorize these shapes in two separate ways: by color or by shape. Today, we are going to the do the same thing with triangles. We can categorize them by side length or by angle measure. Write on the board: Triangles by Sides E q u ila t e r a l – a triangle with all equal sides I s o ...
... S ay: We can categorize these shapes in two separate ways: by color or by shape. Today, we are going to the do the same thing with triangles. We can categorize them by side length or by angle measure. Write on the board: Triangles by Sides E q u ila t e r a l – a triangle with all equal sides I s o ...
FP3: Complex Numbers - Schoolworkout.co.uk
... Write 5 – 12i in modulus-argument form: 5 – 12i = [13, -1.1760052] Using de Moivre’s theorem: Therefore ...
... Write 5 – 12i in modulus-argument form: 5 – 12i = [13, -1.1760052] Using de Moivre’s theorem: Therefore ...
Name
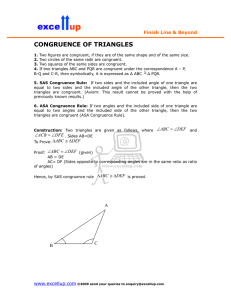
... Lesson Topics: Lesson 1: Congruent Figures (PH text 4.1) Lesson 2: Triangle Congruence by SSS and SAS (PH text 4.2) Lesson 3: Triangle Congruence by ASA and AAS (PH text 4.3) Lesson 4: Using Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles (PH text 4.4) Lesson 5: Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles (PH te ...
... Lesson Topics: Lesson 1: Congruent Figures (PH text 4.1) Lesson 2: Triangle Congruence by SSS and SAS (PH text 4.2) Lesson 3: Triangle Congruence by ASA and AAS (PH text 4.3) Lesson 4: Using Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles (PH text 4.4) Lesson 5: Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles (PH te ...
Jeopardy
... If two angles have measure 90, then the angles are congruent. Converse: If two angles are congruent, then they have measure 90. Truth Value: False Inverse: If two angles do not have measure 90, then they are not congruent. Truth Value: False Contrapositive: If two angles are not congruent, then they ...
... If two angles have measure 90, then the angles are congruent. Converse: If two angles are congruent, then they have measure 90. Truth Value: False Inverse: If two angles do not have measure 90, then they are not congruent. Truth Value: False Contrapositive: If two angles are not congruent, then they ...