protein translocation.
... translated, they are translocated into the ER until a hydrophobic domain is encountered. Alpha helices serve as a 'stop transfer' signal and leaves the protein inserted in the ER ...
... translated, they are translocated into the ER until a hydrophobic domain is encountered. Alpha helices serve as a 'stop transfer' signal and leaves the protein inserted in the ER ...
No Slide Title
... KDEL receptor and other membrane proteins to be returned to ER - have KKXX sequence at end of C-terminus. This binds COP a and b. This sequence necessary and sufficient to drive transport to ER. Yeast mutants lacking COP a and b can’t do retrograde transport Retrograde transport - in Golgi Moving sp ...
... KDEL receptor and other membrane proteins to be returned to ER - have KKXX sequence at end of C-terminus. This binds COP a and b. This sequence necessary and sufficient to drive transport to ER. Yeast mutants lacking COP a and b can’t do retrograde transport Retrograde transport - in Golgi Moving sp ...
Protein Electrophoresis
... Unused portions of the protein samples can be frozen for later use. When 4. INCUBATE the samples for 5 minutes. needed, repeat steps 1-4 and proceed 5. Immediately PROCEED to loading the gel while the samples to Loading the Protein Samples. ...
... Unused portions of the protein samples can be frozen for later use. When 4. INCUBATE the samples for 5 minutes. needed, repeat steps 1-4 and proceed 5. Immediately PROCEED to loading the gel while the samples to Loading the Protein Samples. ...
FoldNucleus: web server for the prediction of RNA
... conformation, which is analogous to the relationship between the function and folding structure of proteins, researchers have successfully applied methods developed for proteins, such as the A analysis (Matouschek et al., 1990). In the folding process, the RNA strand, like a protein globule, passes ...
... conformation, which is analogous to the relationship between the function and folding structure of proteins, researchers have successfully applied methods developed for proteins, such as the A analysis (Matouschek et al., 1990). In the folding process, the RNA strand, like a protein globule, passes ...
elucidate the contribution of proteins to tears. a challenge for
... Meibomian lipids alone, are needed for lowering the surface tension to that found in whole tears. Moreover, these proteins include the major tear proteins such as lysozyme and mucins (3,4). Enigmatically lipocalin is giving confounding results (unpublished) which are indicating that apolipocalin is ...
... Meibomian lipids alone, are needed for lowering the surface tension to that found in whole tears. Moreover, these proteins include the major tear proteins such as lysozyme and mucins (3,4). Enigmatically lipocalin is giving confounding results (unpublished) which are indicating that apolipocalin is ...
Functional proteome analysis of wheat: systematic classification of
... in six wheat cultivars. These results would confirm previous work describing to determine the genetic nature of these mechanisms. Several cold-responsive genes of unknown function were identified from coldacclimated wheat (Breton et al. 2003). The most common plant stress in soils is salinity. Some ...
... in six wheat cultivars. These results would confirm previous work describing to determine the genetic nature of these mechanisms. Several cold-responsive genes of unknown function were identified from coldacclimated wheat (Breton et al. 2003). The most common plant stress in soils is salinity. Some ...
Document
... Introns typically begin with 5’-GU, and end with AG-3’, but mRNA splicing signals involve more than just these two small sequences. ◦ a. Spliceosomes are small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs) associated with pre-mRNAs. ◦ b.Spliceosome principal snRNAs are U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6. i. Ea ...
... Introns typically begin with 5’-GU, and end with AG-3’, but mRNA splicing signals involve more than just these two small sequences. ◦ a. Spliceosomes are small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs) associated with pre-mRNAs. ◦ b.Spliceosome principal snRNAs are U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6. i. Ea ...
Helicobacter-Mammalian Host jump is mediated by targeted gene
... IP31758 genome Designation (Figure 1a) ...
... IP31758 genome Designation (Figure 1a) ...
Probabilistic Approaches to Predicting the Secondary Structure of Proteins
... hand-written script recognition and, more relevantly, the modeling of protein chains. The idea of using a HMM to predict secondary structure was first introduced by K. Asai et. al. in 1993. A programmed HMM can ‘learn’ protein secondary structures such as the α-helix, β-sheet, and the turn, and the ...
... hand-written script recognition and, more relevantly, the modeling of protein chains. The idea of using a HMM to predict secondary structure was first introduced by K. Asai et. al. in 1993. A programmed HMM can ‘learn’ protein secondary structures such as the α-helix, β-sheet, and the turn, and the ...
A-Ag
... Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Gel electrophoresis is a widely used technique for the analysis of nucleic acids and proteins. Agarose gel electrophoresis is routinely used for the preparation and analysis of DNA. Gel electrophoresis is a procedure that separates molecules on the basis of their rate of ...
... Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Gel electrophoresis is a widely used technique for the analysis of nucleic acids and proteins. Agarose gel electrophoresis is routinely used for the preparation and analysis of DNA. Gel electrophoresis is a procedure that separates molecules on the basis of their rate of ...
Anton Supercomputer, a computational microscope.
... Determined for each protein how many folding pathways are traversed that are distinct in the sense that native interactions are formed in different orders and that the pathways do not interconvert on the transition path time scale. Examined the thermodynamics and kinetics of the folding process, and ...
... Determined for each protein how many folding pathways are traversed that are distinct in the sense that native interactions are formed in different orders and that the pathways do not interconvert on the transition path time scale. Examined the thermodynamics and kinetics of the folding process, and ...
Transcription Translation
... Helps with export from nucleus Protection from degradation of enzymes Attachment to ribosomes ...
... Helps with export from nucleus Protection from degradation of enzymes Attachment to ribosomes ...
Hybrid enzymes Pierre Béguin
... protein, glutathione S-transferase, cellulose- and chitinbinding domains, hexahistidine etc.) that can be easily purified by affinity chromatography. An interesting development in this area is the construction of a tagging vector, also commercially available, in which the carboxyl terminus of the pr ...
... protein, glutathione S-transferase, cellulose- and chitinbinding domains, hexahistidine etc.) that can be easily purified by affinity chromatography. An interesting development in this area is the construction of a tagging vector, also commercially available, in which the carboxyl terminus of the pr ...
Genetic Code and Transcription
... Translational Initiation • Small subunit and initiator tRNA bind to start codon. – tRNAi is in P site • Large subunit binds clamping down on mRNA • GTP is hydrolyzed to allow large subunit binding ...
... Translational Initiation • Small subunit and initiator tRNA bind to start codon. – tRNAi is in P site • Large subunit binds clamping down on mRNA • GTP is hydrolyzed to allow large subunit binding ...
PowerPoint-RNA
... beginning of an mRNA molecule 2. A tRNA molecule carrying an amino acid matches up to a complementary triplet on mRNA on the ribosome 3. The ribosome attaches one amino acid to another as it moves along the mRNA molecule 4. The tRNA molecules are released after the amino acids they carry are attache ...
... beginning of an mRNA molecule 2. A tRNA molecule carrying an amino acid matches up to a complementary triplet on mRNA on the ribosome 3. The ribosome attaches one amino acid to another as it moves along the mRNA molecule 4. The tRNA molecules are released after the amino acids they carry are attache ...
pancreatic beta cells - Wiley Online Library
... ER export category, a large number of proteins involved in ER to Golgi transport have been identified including COPII coat proteins Sec31a, Sec13, Sec24a, Sar1b, and its guanine nucleotide exchange factor mSec12; known or potential cargo receptors such as Lman1, Lman2, p24 family members, Surf4, and ...
... ER export category, a large number of proteins involved in ER to Golgi transport have been identified including COPII coat proteins Sec31a, Sec13, Sec24a, Sar1b, and its guanine nucleotide exchange factor mSec12; known or potential cargo receptors such as Lman1, Lman2, p24 family members, Surf4, and ...
Membrane targeting of proteins
... 3.27 Import into mitochondria begins with signal sequence recognition at the outer membrane • Mitochondria have an inner and an outer membrane, each of which has a translocation ...
... 3.27 Import into mitochondria begins with signal sequence recognition at the outer membrane • Mitochondria have an inner and an outer membrane, each of which has a translocation ...
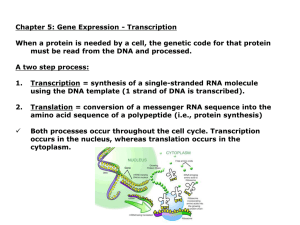
Gene expression: Transcription
... Both processes occur throughout the cell cycle. Transcription occurs in the nucleus, whereas translation occurs in the cytoplasm. ...
... Both processes occur throughout the cell cycle. Transcription occurs in the nucleus, whereas translation occurs in the cytoplasm. ...
Module 7: The Central Dogma
... Repressor and promotor proteins can bind with high specificity to the “outside” of the DNA helix (more on this next week). ...
... Repressor and promotor proteins can bind with high specificity to the “outside” of the DNA helix (more on this next week). ...
Molecular Genetics - Fall River Public Schools
... Describe the structure and function of the 3 types of RNA. – Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a single, uncoiled strand of nucleotides that carries genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytosol. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a single coil of RNA in a hairpin shape that binds to a certain amino ac ...
... Describe the structure and function of the 3 types of RNA. – Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a single, uncoiled strand of nucleotides that carries genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytosol. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a single coil of RNA in a hairpin shape that binds to a certain amino ac ...
Transcription & Translation
... complements a site on 16SrRNA of ribosome; used to bind a ribosome to mRNA for translation. ...
... complements a site on 16SrRNA of ribosome; used to bind a ribosome to mRNA for translation. ...
Methods in Molecular Biology 1297: RNA Nanotechnology and
... a catalyst for chemical reactions. The diversity of RNA biological functions relies on complex architectures that fold from single strands into a hierarchical sequence of secondary and tertiary structures, which rely predominantly on basepair formation through hydrogen bonding between nucleobases. T ...
... a catalyst for chemical reactions. The diversity of RNA biological functions relies on complex architectures that fold from single strands into a hierarchical sequence of secondary and tertiary structures, which rely predominantly on basepair formation through hydrogen bonding between nucleobases. T ...
LSm
In molecular biology, LSm proteins are a family of RNA-binding proteins found in virtually every cellular organism. LSm is a contraction of 'like Sm', because the first identified members of the LSm protein family were the Sm proteins. LSm proteins are defined by a characteristic three-dimensional structure and their assembly into rings of six or seven individual LSm protein molecules, and play a large number of various roles in mRNA processing and regulation.The Sm proteins were first discovered as antigens targeted by so-called Anti-Sm antibodies in a patient with a form of Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a debilitating autoimmune disease. They were named Sm proteins in honor of Stephanie Smith, a patient who suffered from SLE. Other proteins with very similar structures were subsequently discovered and named LSm proteins. New members of the LSm protein family continue to be identified and reported.Proteins with similar structures are grouped into a hierarchy of protein families, superfamilies, and folds. The LSm protein structure is an example of a small beta sheet folded into a short barrel. Individual LSm proteins assemble into a six or seven member doughnut ring (more properly termed a torus), which usually binds to a small RNA molecule to form a ribonucleoprotein complex. The LSm torus assists the RNA molecule to assume and maintain its proper three-dimensional structure. Depending on which LSm proteins and RNA molecule are involved, this ribonucleoprotein complex facilitates a wide variety of RNA processing including degradation, editing, splicing, and regulation.Alternate terms for LSm family are LSm fold and Sm-like fold, and alternate capitalization styles such as lsm, LSM, and Lsm are common and equally acceptable.