Reliable transfer of transcriptional gene regulatory networks
... uncover hidden architectures behind gene regulatory networks [7,8]. In addition, specialized approaches, based on the evolutionary conservation of the responsible transcription factors and the controlled target genes, are used to transfer knowledge on gene regulatory networks between different organ ...
... uncover hidden architectures behind gene regulatory networks [7,8]. In addition, specialized approaches, based on the evolutionary conservation of the responsible transcription factors and the controlled target genes, are used to transfer knowledge on gene regulatory networks between different organ ...
Nucleic Acids Research
... Our current picture of human C y genes is that they have diverged recently from one another, and that hinge regions have evolved rapidly since that divergence. What is not clear is the nature of the genetic event(s) giving rise to the identical Cy genes which were the ancestors of the present-day ge ...
... Our current picture of human C y genes is that they have diverged recently from one another, and that hinge regions have evolved rapidly since that divergence. What is not clear is the nature of the genetic event(s) giving rise to the identical Cy genes which were the ancestors of the present-day ge ...
Pre – AP Biology
... this new inserted DNA and thus make that protein. This has been done for numerous human medicines such as Insulin or Human Growth Hormone. – Eukaryotes DO have introns. This allows them to take out the introns and rearrange the important exon pieces to make an almost unlimited number of different pr ...
... this new inserted DNA and thus make that protein. This has been done for numerous human medicines such as Insulin or Human Growth Hormone. – Eukaryotes DO have introns. This allows them to take out the introns and rearrange the important exon pieces to make an almost unlimited number of different pr ...
DNA Notesheet
... 19. In what two ways is mRNA different from the DNA it is copying? 1_ 2_ 20. What is polymerase? 21. If the DNA strand being copied is T-G-C-A-G-T, what would be the mRNA strand? 22. What is transcription? _ 23. After detaching from DNA, mRNA leaves the ...
... 19. In what two ways is mRNA different from the DNA it is copying? 1_ 2_ 20. What is polymerase? 21. If the DNA strand being copied is T-G-C-A-G-T, what would be the mRNA strand? 22. What is transcription? _ 23. After detaching from DNA, mRNA leaves the ...
Lecture 14 Dev Bio JS
... How is it that different concentrations of Bcd at different points along the A/P axis of the embryo lead to transcription of different target genes? The Bcd gradient provides positional information along the axis in a dosedependent manner and efforts have been made to understand how this could be ...
... How is it that different concentrations of Bcd at different points along the A/P axis of the embryo lead to transcription of different target genes? The Bcd gradient provides positional information along the axis in a dosedependent manner and efforts have been made to understand how this could be ...
A8xb1e3x8x1 (2)
... Write a random DNA sequence on a long strip of paper to represent an organism’s genome Have your partner write a short DNA sequence on a short strip of paper to represent a marker gene Using the chart provided, work with your partner to figure out how to insert the marker gene into the genome ...
... Write a random DNA sequence on a long strip of paper to represent an organism’s genome Have your partner write a short DNA sequence on a short strip of paper to represent a marker gene Using the chart provided, work with your partner to figure out how to insert the marker gene into the genome ...
BMB 400 PART THREE - ANSWERS ANSWERS to Questions from
... needed to respond to upstream activating sequences. In the second set of experiments, the heterologous promoter will substitute for it. ...
... needed to respond to upstream activating sequences. In the second set of experiments, the heterologous promoter will substitute for it. ...
15.2_Recombinant_DNA
... Write a random DNA sequence on a long strip of paper to represent an organism’s genome Have your partner write a short DNA sequence on a short strip of paper to represent a marker gene Using the chart provided, work with your partner to figure out how to insert the marker gene into the genome ...
... Write a random DNA sequence on a long strip of paper to represent an organism’s genome Have your partner write a short DNA sequence on a short strip of paper to represent a marker gene Using the chart provided, work with your partner to figure out how to insert the marker gene into the genome ...
12-5 Gene Regulation
... Bacteria turn on/off genes, too. An example of this are the “lac” genes The lac genes (genes to use lactose) are turned off by repressors and turned on by the presence of lactose. You only want to make the digestive proteins when needed…. Thus, being able to turn on/off genes is an example Slide of ...
... Bacteria turn on/off genes, too. An example of this are the “lac” genes The lac genes (genes to use lactose) are turned off by repressors and turned on by the presence of lactose. You only want to make the digestive proteins when needed…. Thus, being able to turn on/off genes is an example Slide of ...
DNA-Polymerase
... of injecting DNA into agarose gel and then applying an electric current to the gel. As a result, the smaller DNA strands move faster than the larger strands through the gel toward the positive current. The size of the PCR product can be determined by comparing it with a DNA ladder, which contains DN ...
... of injecting DNA into agarose gel and then applying an electric current to the gel. As a result, the smaller DNA strands move faster than the larger strands through the gel toward the positive current. The size of the PCR product can be determined by comparing it with a DNA ladder, which contains DN ...
Zoology 145 course
... – The terminator منطقة النهايةends the transcription. • Bacteria have a single type of RNA polymerase that synthesizes all RNA molecules. • In contrast, eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases (I, II, and III) in their nuclei. – RNA polymerase II is used for mRNA synthesis. ...
... – The terminator منطقة النهايةends the transcription. • Bacteria have a single type of RNA polymerase that synthesizes all RNA molecules. • In contrast, eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases (I, II, and III) in their nuclei. – RNA polymerase II is used for mRNA synthesis. ...
Poster. - Stanford University
... ICA mixture model of genomic expression patterns, linear and nonlinear ICA finds components that are specific to certain biological processes. Genes that exhibit significant up-regulation or downregulation within each component are grouped into clusters. We test the statistical significance of enric ...
... ICA mixture model of genomic expression patterns, linear and nonlinear ICA finds components that are specific to certain biological processes. Genes that exhibit significant up-regulation or downregulation within each component are grouped into clusters. We test the statistical significance of enric ...
Taxonomy of Life • Three domains: Eukaryotes, Bacteria (Eubacteria
... 3. Regions that control the expression of proteins and ncRNA’s (regulatory regions). 4. Regions associated with DNA replication (centromere, telomere, replication origins). • In humans, around 93% of the mitochondrial genome is used for one of these four roles. This is true of only around 50% of the ...
... 3. Regions that control the expression of proteins and ncRNA’s (regulatory regions). 4. Regions associated with DNA replication (centromere, telomere, replication origins). • In humans, around 93% of the mitochondrial genome is used for one of these four roles. This is true of only around 50% of the ...
File
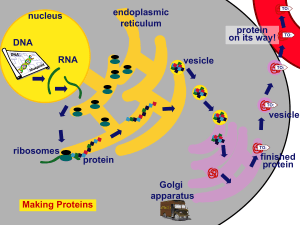
... • Takes place in the nucleus. • A specific gene of DNA is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase. • The instructions for making a protein are transferred from the nucleus to the ribosome. ...
... • Takes place in the nucleus. • A specific gene of DNA is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase. • The instructions for making a protein are transferred from the nucleus to the ribosome. ...
Connect the dots…DNA to Disease, Oltmann
... 4. If you were a scientist working with mice and discovered a gene that had something to do with obesity in mice, describe how you might find out if there is a similar gene that is known to exist in humans? 5. If you had more nucleotides in your sequence to enter into BLAST (say 1000 instead of 100) ...
... 4. If you were a scientist working with mice and discovered a gene that had something to do with obesity in mice, describe how you might find out if there is a similar gene that is known to exist in humans? 5. If you had more nucleotides in your sequence to enter into BLAST (say 1000 instead of 100) ...
Lambda Vectors and their replication
... • Phage can alternate between lysogenic (non-productive) and lytic (productive) growth cycles. ...
... • Phage can alternate between lysogenic (non-productive) and lytic (productive) growth cycles. ...
Lecture 5
... 1) the majority of DNA in the human genome is transcribed into functional molecules RNA, and that these transcripts extensively overlap one another. This broad pattern of transcription challenges the long-standing view that the human genome consists of a relatively small set of discrete genes, along ...
... 1) the majority of DNA in the human genome is transcribed into functional molecules RNA, and that these transcripts extensively overlap one another. This broad pattern of transcription challenges the long-standing view that the human genome consists of a relatively small set of discrete genes, along ...
mouse. However, some technical and prac-
... exchanging fragments of closely homologous genes provides an efficient way to generate proteins with new traits1,2. The resulting molecules are very different, at least in sequence, from those that might be obtained by more local searches of protein space, for example by random mutagenesis. The DNA ...
... exchanging fragments of closely homologous genes provides an efficient way to generate proteins with new traits1,2. The resulting molecules are very different, at least in sequence, from those that might be obtained by more local searches of protein space, for example by random mutagenesis. The DNA ...
ENVI 30 Environmental Issues
... Genealogies often represented as phylogenetic trees that reflect relationships among species Systematics deals with classification of taxa according to evolutionary history ...
... Genealogies often represented as phylogenetic trees that reflect relationships among species Systematics deals with classification of taxa according to evolutionary history ...
26 DNA Transcription - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... acids are transfered from tRNAs to a nascent (growing) polypeptide chain, with the amino acid sequence controlled by the mRNA. The peptidyl transferase center, which is the catalytic site of the ribosome, is all rRNA. So technically the ribosome is a ribozyme, not a protein enzyme. 3)Transfer RNAs ( ...
... acids are transfered from tRNAs to a nascent (growing) polypeptide chain, with the amino acid sequence controlled by the mRNA. The peptidyl transferase center, which is the catalytic site of the ribosome, is all rRNA. So technically the ribosome is a ribozyme, not a protein enzyme. 3)Transfer RNAs ( ...
Today`s Plan: 4/25/03
... • DNA can be manipulated to contain certain genes. Manipulations are performed by cutting DNA, inserting what we want, and inserting the DNA back into a cell. • A manipulated piece of DNA, that contains “spliced” pieces is called recombinant DNA • The recombinant DNA comes from cloning vectors-carri ...
... • DNA can be manipulated to contain certain genes. Manipulations are performed by cutting DNA, inserting what we want, and inserting the DNA back into a cell. • A manipulated piece of DNA, that contains “spliced” pieces is called recombinant DNA • The recombinant DNA comes from cloning vectors-carri ...
Studying the Human Genome
... polymerase and four bases (ATGC) DNA polymerase uses unknown strand as template to make new strands Some of the added bases have dyes attached, Each time a labeled base is added, replication stops End up with a series of fragments that are color coded Separate fragments with electrophoresis, colored ...
... polymerase and four bases (ATGC) DNA polymerase uses unknown strand as template to make new strands Some of the added bases have dyes attached, Each time a labeled base is added, replication stops End up with a series of fragments that are color coded Separate fragments with electrophoresis, colored ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.