Slide 1
... enzyme, e.g., by promoting a conformational change. Alternatively, altered activity may result from binding another protein that specifically recognizes a phosphorylated domain. E.g., 14-3-3 proteins bind to domains that include phosphorylated Ser or Thr in the sequence RXXX[pS/pT]XP, where X can ...
... enzyme, e.g., by promoting a conformational change. Alternatively, altered activity may result from binding another protein that specifically recognizes a phosphorylated domain. E.g., 14-3-3 proteins bind to domains that include phosphorylated Ser or Thr in the sequence RXXX[pS/pT]XP, where X can ...
17GeneToProtein
... suggested that genes coded for enzymes each disease (phenotype) is caused by non-functional gene product ...
... suggested that genes coded for enzymes each disease (phenotype) is caused by non-functional gene product ...
Computational Biology
... Prokaryotic operon organization Although the operon structure has been well studied at the biochemical level in microorganisms such as E.coli , genome-wide operon organization in pathogenic organisms, such as M. tuberculosis, remains largely unknown. One can exploit the conservation of certain gene ...
... Prokaryotic operon organization Although the operon structure has been well studied at the biochemical level in microorganisms such as E.coli , genome-wide operon organization in pathogenic organisms, such as M. tuberculosis, remains largely unknown. One can exploit the conservation of certain gene ...
The Two Major Membrane Skeletal Proteins (Articulins) of Euglena
... Bouck, 1988) from mice immunized with membrane affinity-enriched articulins, mAb isotyping (courtesy of Dr. Thorn Rosiere) using a kit (Hyclone Laboratories, Logan, UT) showed that mAb 3G1 was an IgG3. Polyclonal antisera were generated against protein bands excised from preparative SDS polyacrylami ...
... Bouck, 1988) from mice immunized with membrane affinity-enriched articulins, mAb isotyping (courtesy of Dr. Thorn Rosiere) using a kit (Hyclone Laboratories, Logan, UT) showed that mAb 3G1 was an IgG3. Polyclonal antisera were generated against protein bands excised from preparative SDS polyacrylami ...
Bio 251 07 TLN Genet..
... mRNA, rRNA, tRNA and protein synthesis In translation, the language of nucleic acids is translated into a new language, that of proteins mRNA provides the code, in linear digital form, for making a protein tRNA provides an adaptor that links the code in a polynucleotide chain to amino acids that ma ...
... mRNA, rRNA, tRNA and protein synthesis In translation, the language of nucleic acids is translated into a new language, that of proteins mRNA provides the code, in linear digital form, for making a protein tRNA provides an adaptor that links the code in a polynucleotide chain to amino acids that ma ...
Signaling Through Scaffold, Anchoring, and Adaptor Proteins
... Channel mutations that disrupt this interaction cause a human hypertensive disorder, Liddle’s syndrome (27). WW domains may also regulate catalytic function, as suggested by a structural analysis of the peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase Pin1. Pin1, which interacts with cell cycle components such a ...
... Channel mutations that disrupt this interaction cause a human hypertensive disorder, Liddle’s syndrome (27). WW domains may also regulate catalytic function, as suggested by a structural analysis of the peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase Pin1. Pin1, which interacts with cell cycle components such a ...
Oxidative stress in bacteria and protein damage by reactive oxygen
... oxygen species is not released into the surrounding medium; it preferentially reacts with functional groups of amino acid residues at the metal-binding site. In this mechanism, it is assumed that the hydroxyl radical (·OH) is the reactive oxygen species formed by the reaction of Fe2+ with H2O2 (Fent ...
... oxygen species is not released into the surrounding medium; it preferentially reacts with functional groups of amino acid residues at the metal-binding site. In this mechanism, it is assumed that the hydroxyl radical (·OH) is the reactive oxygen species formed by the reaction of Fe2+ with H2O2 (Fent ...
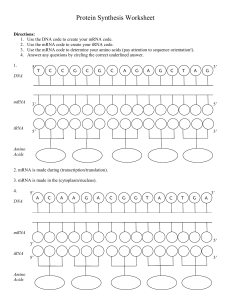
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucl ...
... 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucl ...
RNA is synthesized by a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (uses
... Transcription and RNA Processing The first stage in the expression of genetic information is transcription of the information in the base sequence of a double-stranded DNA molecule to form the base sequence of a single-stranded molecule of RNA. For any particular gene, only one strand of the DNA mol ...
... Transcription and RNA Processing The first stage in the expression of genetic information is transcription of the information in the base sequence of a double-stranded DNA molecule to form the base sequence of a single-stranded molecule of RNA. For any particular gene, only one strand of the DNA mol ...
Supplementary Methods
... uridine (U), according to standard solid phase oligonucleotide synthesis protocols1. For antagomirs. i.e., cholesterol conjugated RNAs, the synthesis started from a controlledpore glass solid support carrying a cholesterol- hydroxyprolinol linker2. Antagomirs with phosphorothioate backbone at a give ...
... uridine (U), according to standard solid phase oligonucleotide synthesis protocols1. For antagomirs. i.e., cholesterol conjugated RNAs, the synthesis started from a controlledpore glass solid support carrying a cholesterol- hydroxyprolinol linker2. Antagomirs with phosphorothioate backbone at a give ...
Ch. 13 end of chapter review
... It binds transcription factor proteins that help position RNA polymerase at the point where transcription should begin. When transcription factors bind to the TATA box, they form a binding site for RNA polymerase, which can then start transcription. 33. A homeobox gene is a gene that codes for a tra ...
... It binds transcription factor proteins that help position RNA polymerase at the point where transcription should begin. When transcription factors bind to the TATA box, they form a binding site for RNA polymerase, which can then start transcription. 33. A homeobox gene is a gene that codes for a tra ...
Lecture 03 Ch2and3
... Where are nucleic acids in a cell? DNA is in the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts ...
... Where are nucleic acids in a cell? DNA is in the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts ...
Genomes 3/e - Illinois Institute of Technology
... • Initiation of transcription. Assembly of upstream protein complex (e.g. RNA polymerase & accessory proteins) This step determines whether a gene should be expressed or not. • Synthesis & processing of RNA (next Chapter). RNA polymerase synthesizes mRNA & subsequently processes or ...
... • Initiation of transcription. Assembly of upstream protein complex (e.g. RNA polymerase & accessory proteins) This step determines whether a gene should be expressed or not. • Synthesis & processing of RNA (next Chapter). RNA polymerase synthesizes mRNA & subsequently processes or ...
Globular Protein Structure
... The up-and-down structures are the simplest to visualize. The topologies are shown in the figure. They can exist as flat sheets or barrels. The Greek Key is a four stranded beta sheet motif which is characterized by +3, -1, -1 connectivities in a 2-dimensional schematic diagram of a protein structur ...
... The up-and-down structures are the simplest to visualize. The topologies are shown in the figure. They can exist as flat sheets or barrels. The Greek Key is a four stranded beta sheet motif which is characterized by +3, -1, -1 connectivities in a 2-dimensional schematic diagram of a protein structur ...
From Gene to Protein
... (a) Two-dimensional structure. The four base-paired regions and three G C U A loops are characteristic of all tRNAs, as is the base sequence of the * G amino acid attachment site at the 3 end. The anticodon triplet is A A* unique to each tRNA type. (The asterisks mark bases that have been C U ...
... (a) Two-dimensional structure. The four base-paired regions and three G C U A loops are characteristic of all tRNAs, as is the base sequence of the * G amino acid attachment site at the 3 end. The anticodon triplet is A A* unique to each tRNA type. (The asterisks mark bases that have been C U ...
Protein structure and Function
... that can participate in hydrogen bond formation. Additionally this polar hydroxyl group can serve as a site of attachment of structure such as phosphate group or an important component of active site of many enzymes. Asparagine and glutamine: Each contain carbonyle group and amide group can particip ...
... that can participate in hydrogen bond formation. Additionally this polar hydroxyl group can serve as a site of attachment of structure such as phosphate group or an important component of active site of many enzymes. Asparagine and glutamine: Each contain carbonyle group and amide group can particip ...
Signaling9
... enzyme, e.g., by promoting a conformational change. Alternatively, altered activity may result from binding another protein that specifically recognizes a phosphorylated domain. E.g., 14-3-3 proteins bind to domains that include phosphorylated Ser or Thr in the sequence RXXX[pS/pT]XP, where X can ...
... enzyme, e.g., by promoting a conformational change. Alternatively, altered activity may result from binding another protein that specifically recognizes a phosphorylated domain. E.g., 14-3-3 proteins bind to domains that include phosphorylated Ser or Thr in the sequence RXXX[pS/pT]XP, where X can ...
Assembly and function of cell surface structures of the
... FlaB and the glucose binding protein GlcS are both processed by PibD. Subsequently, the bindosome assembly system (bas) mediates the assembly of the sugar binding proteins into the bindosome structure. This might correspond to a positioning of the binding proteins in the S-layer. The subunits of the ...
... FlaB and the glucose binding protein GlcS are both processed by PibD. Subsequently, the bindosome assembly system (bas) mediates the assembly of the sugar binding proteins into the bindosome structure. This might correspond to a positioning of the binding proteins in the S-layer. The subunits of the ...
Differentially Expressed Soluble Proteins in Aortic Cells from
... that are the biological determinants of phenotype. Changes in health status are the result of proteome changes in response to endogenous or exogenous, or both, stimuli. Healthy vs. diseased states can be distinguished by their respective proteomic profiles. The goal of clinical proteomics is to crea ...
... that are the biological determinants of phenotype. Changes in health status are the result of proteome changes in response to endogenous or exogenous, or both, stimuli. Healthy vs. diseased states can be distinguished by their respective proteomic profiles. The goal of clinical proteomics is to crea ...
Chapter 1
... shapes, not the least important is pure chance. For example, stability, biological activity, and adaptation to different environments suggest a wide range of restrictions on protein design, native and non-native alike. In many cases it is necessary to investigate the problem including its environme ...
... shapes, not the least important is pure chance. For example, stability, biological activity, and adaptation to different environments suggest a wide range of restrictions on protein design, native and non-native alike. In many cases it is necessary to investigate the problem including its environme ...
EF-Tu PROTEIN DOMAINS
... 1. Evaluation of the effect of individual domains of EF-Tu proteins from E. coli and B. stearothermophilus on their basic functions, namely GDP/GTP binding, GTPase activity and on the thermostability. We showed that (i) B. stearothermophilus EF-Tu and B. stearothermophilus G-domain bound GDP and GTP ...
... 1. Evaluation of the effect of individual domains of EF-Tu proteins from E. coli and B. stearothermophilus on their basic functions, namely GDP/GTP binding, GTPase activity and on the thermostability. We showed that (i) B. stearothermophilus EF-Tu and B. stearothermophilus G-domain bound GDP and GTP ...
Lesson Plan
... 8/28 structure and functions of different types of biomolecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
... 8/28 structure and functions of different types of biomolecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
PartThreeAnswers.doc
... 13.10 Some amino acids are encoded by 6 different codons, some 4 different codons, some 3 different codons, some 2 different codons, and some one codon. To minimize the degree of ambiguity in codon assignment for a given peptide sequence, one must select a region of the peptide that contains mostly ...
... 13.10 Some amino acids are encoded by 6 different codons, some 4 different codons, some 3 different codons, some 2 different codons, and some one codon. To minimize the degree of ambiguity in codon assignment for a given peptide sequence, one must select a region of the peptide that contains mostly ...
Chemical biology beyond binary codes
... af¢nity complexes with FKBP and can compete with each other for binding. Both of these compounds are immunosupressants, and the most signi¢cant early discovery concerning their mechanisms of action was that their biological effects required as an obligatory but not suf¢cient formation of a complex w ...
... af¢nity complexes with FKBP and can compete with each other for binding. Both of these compounds are immunosupressants, and the most signi¢cant early discovery concerning their mechanisms of action was that their biological effects required as an obligatory but not suf¢cient formation of a complex w ...
University of North Carolina researchers provide evidence for how
... University of North Carolina researchers provide evidence for how the genetic code developed in two distinct stages to help primordial chemicals evolve into cells. CHAPEL HILL, NC – In the beginning, there were simple chemicals. And they produced amino acids that eventually became the proteins neces ...
... University of North Carolina researchers provide evidence for how the genetic code developed in two distinct stages to help primordial chemicals evolve into cells. CHAPEL HILL, NC – In the beginning, there were simple chemicals. And they produced amino acids that eventually became the proteins neces ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.