Protein and Carbohydrate Chemistry
... amino acid to form a dipeptide. The peptide bond is unique in that it appears to be a single bond, but has the characteristic of a double bond, i.e., it is a rigid bond. This kind of bond only occurs between amino acids. As the amino acid chain increases in length, the next amino acid adds onto the ...
... amino acid to form a dipeptide. The peptide bond is unique in that it appears to be a single bond, but has the characteristic of a double bond, i.e., it is a rigid bond. This kind of bond only occurs between amino acids. As the amino acid chain increases in length, the next amino acid adds onto the ...
Ion Exchange Chromatography
... molecules based on ionic interactions. The stationary phase surface displays ionic functional groups (R-X) that interact with analyte ions of opposite charge. This type of chromatography is further subdivided into: cation exchange chromatography anion exchange chromatography. Dr Gihan Gawish ...
... molecules based on ionic interactions. The stationary phase surface displays ionic functional groups (R-X) that interact with analyte ions of opposite charge. This type of chromatography is further subdivided into: cation exchange chromatography anion exchange chromatography. Dr Gihan Gawish ...
ribosomes - Mircea Leabu
... •The acceptor stem (3’-CCA) carries the amino acid •The anticodon associates with the mRNA codon (via complementary base pairing) •The T arm associates with the ribosome (via the E, P and A binding sites) •The D arm associates with the tRNA activating enzyme (responsible for adding the amino acid to ...
... •The acceptor stem (3’-CCA) carries the amino acid •The anticodon associates with the mRNA codon (via complementary base pairing) •The T arm associates with the ribosome (via the E, P and A binding sites) •The D arm associates with the tRNA activating enzyme (responsible for adding the amino acid to ...
Lecture 6
... All molecules will travel in the same direction Each additional nucleoside confers an additional charge, so charge is directly proportional to size. All molecules will have the same e The solution is to use a gel which consists of pores surrounded by cross-linked fibers This will make e dependent ...
... All molecules will travel in the same direction Each additional nucleoside confers an additional charge, so charge is directly proportional to size. All molecules will have the same e The solution is to use a gel which consists of pores surrounded by cross-linked fibers This will make e dependent ...
Tutorial section Hydropathy — A window on the evasion of water
... and researchers worldwide are working to increase this volume. Structure and function are closely related in terms of understanding what these proteins do and how they govern processes within an organism. In the absence of structural information derived from X-ray crystallography or other experiment ...
... and researchers worldwide are working to increase this volume. Structure and function are closely related in terms of understanding what these proteins do and how they govern processes within an organism. In the absence of structural information derived from X-ray crystallography or other experiment ...
Quant-iT™ Assay Kits for microplate
... linear detection range of 0.2–100 ng and is selective for dsDNA, even in the presence of an equal mass of RNA. The x-axis gives the mass of nucleic acid when DNA or RNA is assayed alone; in the 1:1 mixture, the total mass of nucleic acid is double the amount shown. The inset shows the sensitivity of ...
... linear detection range of 0.2–100 ng and is selective for dsDNA, even in the presence of an equal mass of RNA. The x-axis gives the mass of nucleic acid when DNA or RNA is assayed alone; in the 1:1 mixture, the total mass of nucleic acid is double the amount shown. The inset shows the sensitivity of ...
Methods in Molecular Biology 1297: RNA Nanotechnology and
... pertinent topics along with detailed laboratory protocols and experimental procedures. Novices to the field of RNA nanotechnology will find the first chapter particularly useful, as it provides an introductory overview of methods for the design, preparation, purification, and characterization of RNA ...
... pertinent topics along with detailed laboratory protocols and experimental procedures. Novices to the field of RNA nanotechnology will find the first chapter particularly useful, as it provides an introductory overview of methods for the design, preparation, purification, and characterization of RNA ...
CM22555559
... encoding 19 proteins. Three of these genes, gag, pol, and env, contain information needed to make the structural proteins for new virus particles [5]. For example, env codes for a protein called gp160 that is broken down by a viral enzyme to form gp120 and gp41. The six remaining genes, tat, rev, ne ...
... encoding 19 proteins. Three of these genes, gag, pol, and env, contain information needed to make the structural proteins for new virus particles [5]. For example, env codes for a protein called gp160 that is broken down by a viral enzyme to form gp120 and gp41. The six remaining genes, tat, rev, ne ...
Silk-inspired polymers and proteins
... to biological stimuli such as enzymes. This principle was first proved with proteins incorporating phosphorylation sites near the β-sheet, forming Ala5 peptides. Phosphorylation of the serine residues (with cAMP-dependent kinase) yielded highly soluble protein, and subsequent dephosphorylation (with ...
... to biological stimuli such as enzymes. This principle was first proved with proteins incorporating phosphorylation sites near the β-sheet, forming Ala5 peptides. Phosphorylation of the serine residues (with cAMP-dependent kinase) yielded highly soluble protein, and subsequent dephosphorylation (with ...
Xanthomonas campestris
... The GO analysis revealed that most proteins with increased abundance in REK (61%), when compared to the control, were related to cellular metabolism (citrate cycle, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, oxidative phosphorylation, other carbohydrate metabolism, and pentose phosphate pathway) (Supporting Inform ...
... The GO analysis revealed that most proteins with increased abundance in REK (61%), when compared to the control, were related to cellular metabolism (citrate cycle, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, oxidative phosphorylation, other carbohydrate metabolism, and pentose phosphate pathway) (Supporting Inform ...
Protein expression during exponential growth in 0.7 M NaCl medium
... gel electrophoresis (2D-PAGE) generated images of isotopically labelled protein extracts have been performed in a quantitative investigation of the cellular adaptation process to NaCl containing medium [8]. It was reported that drastic expression changes occurred during the osmotic adaptation, with ...
... gel electrophoresis (2D-PAGE) generated images of isotopically labelled protein extracts have been performed in a quantitative investigation of the cellular adaptation process to NaCl containing medium [8]. It was reported that drastic expression changes occurred during the osmotic adaptation, with ...
Predicting functional linkages from gene fusions with
... Abstract: Pairs of genes that function together in a pathway or cellular system can sometimes be found fused together in another organism as a Rosetta Stone protein – a fusion protein whose separate domains are homologous to the two functionally-related proteins. The finding of such a Rosetta Stone ...
... Abstract: Pairs of genes that function together in a pathway or cellular system can sometimes be found fused together in another organism as a Rosetta Stone protein – a fusion protein whose separate domains are homologous to the two functionally-related proteins. The finding of such a Rosetta Stone ...
Chapter 17
... receptor creates an occupied receptor that undergoes a conformational change and is then able to interact with the G protein. (A ligand is a molecule that binds specifically to a particular receptor. Hormones and neurotransmitters are ligands of G protein–linked receptors.) In response to the recepto ...
... receptor creates an occupied receptor that undergoes a conformational change and is then able to interact with the G protein. (A ligand is a molecule that binds specifically to a particular receptor. Hormones and neurotransmitters are ligands of G protein–linked receptors.) In response to the recepto ...
Chapter 21 (part 1) - University of Nevada, Reno
... • CTD is essential and this domain may project away from the globular portion of the enzyme (up to 50 nm!) • Only RNA Pol II whose CTD is NOT phosphorylated can initiate transcription • TATA box (TATAAA) is a consensus promoter • 7 general transcription factors are required ...
... • CTD is essential and this domain may project away from the globular portion of the enzyme (up to 50 nm!) • Only RNA Pol II whose CTD is NOT phosphorylated can initiate transcription • TATA box (TATAAA) is a consensus promoter • 7 general transcription factors are required ...
Chapter 9 Proteins - Angelo State University
... positive or negative charge, the like charges cause the molecules to repel one another, and they remain dispersed. ...
... positive or negative charge, the like charges cause the molecules to repel one another, and they remain dispersed. ...
The hnRNP C Proteins Contain a Nuclear Retention Sequence That
... which has a myc epitope (MGEQKLISEEDL) just upstream of the EcoRI site (Siomi and Dreyfuss, 1995). Myc-C1 was made by PCR amplification of the C1 cDNA pHC12 (Swanson et al., 1987) to generate at the 5' end an EcoRI site immediately upstream of the second codon of C1, and at the 3' end an XhoI site d ...
... which has a myc epitope (MGEQKLISEEDL) just upstream of the EcoRI site (Siomi and Dreyfuss, 1995). Myc-C1 was made by PCR amplification of the C1 cDNA pHC12 (Swanson et al., 1987) to generate at the 5' end an EcoRI site immediately upstream of the second codon of C1, and at the 3' end an XhoI site d ...
AIBSTCT Nucleic Acids Research - Walter Lab
... particle into two subparticles; the S segment and a segment containing the Alu sequences (12). The protein subunits of SRP can be released from the RNA molecule under nondenaturing conditions. Four of the SRP proteins are released as heterodimers (SRP68/72 and SRP9/14) and two as monomers (SRP19 and ...
... particle into two subparticles; the S segment and a segment containing the Alu sequences (12). The protein subunits of SRP can be released from the RNA molecule under nondenaturing conditions. Four of the SRP proteins are released as heterodimers (SRP68/72 and SRP9/14) and two as monomers (SRP19 and ...
video slide - CARNES AP BIO
... polypeptide, depending on which segments are treated as exons during RNA splicing • Such variations are called alternative RNA splicing • Because of alternative splicing, the number of different proteins an organism can produce is much greater than its number of genes ...
... polypeptide, depending on which segments are treated as exons during RNA splicing • Such variations are called alternative RNA splicing • Because of alternative splicing, the number of different proteins an organism can produce is much greater than its number of genes ...
Proteins - Food Science & Human Nutrition
... conditions, processing treatments and interactions with other ingredients ...
... conditions, processing treatments and interactions with other ingredients ...
or protein
... different amino acids, namely, the amino acid composition was used to distinguish different proteins before the days of protein sequencing. ...
... different amino acids, namely, the amino acid composition was used to distinguish different proteins before the days of protein sequencing. ...
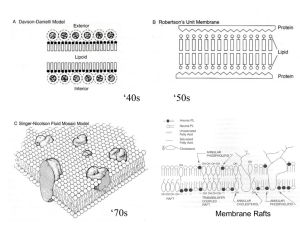
lecture 11
... Hydrophobic mismatch: if there is a mismatch between the length of the TMD and the hydrocarbon thickness, then the bilayer would need to deform to prevent exposure of the hydrophobic amino acids to water. This would be energetically unfavorable. So, if the protein can “move” to a “raft” of different ...
... Hydrophobic mismatch: if there is a mismatch between the length of the TMD and the hydrocarbon thickness, then the bilayer would need to deform to prevent exposure of the hydrophobic amino acids to water. This would be energetically unfavorable. So, if the protein can “move” to a “raft” of different ...
Improved topology prediction using the terminal
... The positive-inside rule is used to allow for less hydrophobic TMsegments to be recognized if this results in that more positive residues are found in periplasmic loops. Exactly how the balance between the hydrophobicity cut-off and the positive-inside rule is optimized varies between methods. In so ...
... The positive-inside rule is used to allow for less hydrophobic TMsegments to be recognized if this results in that more positive residues are found in periplasmic loops. Exactly how the balance between the hydrophobicity cut-off and the positive-inside rule is optimized varies between methods. In so ...
FMR1 - IS MU
... Repeat expansions can occur in 5′UTRs, coding regions, introns, or 3′UTRs. Normal and premutation alleles do not show usually disease symptoms, but premutation alleles are primed to expand in the next generation. As repeats get longer, symptoms are seen at an earlier age and are more severe. Repeat ...
... Repeat expansions can occur in 5′UTRs, coding regions, introns, or 3′UTRs. Normal and premutation alleles do not show usually disease symptoms, but premutation alleles are primed to expand in the next generation. As repeats get longer, symptoms are seen at an earlier age and are more severe. Repeat ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.