What Does the Microsporidian E. cuniculi Tell Us About the Origin of
... 44% of which have known functions (Katinka et al. 2001). These data imply that E. cuniculi is approaching the size of a minimal eukaryotic cell. To understand the differences between minimal cells of Eukarya and Bacteria, we need to characterize the set of proteins in E. cuniculi that is unique to th ...
... 44% of which have known functions (Katinka et al. 2001). These data imply that E. cuniculi is approaching the size of a minimal eukaryotic cell. To understand the differences between minimal cells of Eukarya and Bacteria, we need to characterize the set of proteins in E. cuniculi that is unique to th ...
Lipids affect the function of membrane proteins
... to breaking up the protein complex. When the complex fragments, the researchers can see which subunits have lipids bound to them. For example, the scientists found that the functional form of a bacterial amino acid transporter called LeuT has three phospholipids and one cardiolipin per subunit. A ba ...
... to breaking up the protein complex. When the complex fragments, the researchers can see which subunits have lipids bound to them. For example, the scientists found that the functional form of a bacterial amino acid transporter called LeuT has three phospholipids and one cardiolipin per subunit. A ba ...
Srivastava, Sanjay: Analysis of Methods for Predicting Protein Fold and Remote Homologue Recognition
... recognition where observations were sounds forming a word. In that case the model described the random process that produces these sounds with high probability. In speech recognition, the “alphabet” forms the phonemes in a particular language and in protein folding, the “alphabets” are the 20 amino ...
... recognition where observations were sounds forming a word. In that case the model described the random process that produces these sounds with high probability. In speech recognition, the “alphabet” forms the phonemes in a particular language and in protein folding, the “alphabets” are the 20 amino ...
Hutational analysis of the influenza virus A/Victoria/3/75 PA protein
... could not be distinguished if the active site of PA, complex additional deletion mutant (PAASA) in the N-terminal half formation or just the general folding of PA was affected by the (A186-280) of PA were analysed (data not shown). The mutation. Thus, we further studied the PA-PB1 association of pol ...
... could not be distinguished if the active site of PA, complex additional deletion mutant (PAASA) in the N-terminal half formation or just the general folding of PA was affected by the (A186-280) of PA were analysed (data not shown). The mutation. Thus, we further studied the PA-PB1 association of pol ...
5-Cell and Molecular Biology (Golgi etc)
... Similarly, if signal is transferred to a protein that is normally secreted, the protein is now retained in the lumen of ER The retention signal works not by anchoring resident proteins in the lumen of the ER But by selective retrieval of ER-resident proteins after they have escaped in transpor ...
... Similarly, if signal is transferred to a protein that is normally secreted, the protein is now retained in the lumen of ER The retention signal works not by anchoring resident proteins in the lumen of the ER But by selective retrieval of ER-resident proteins after they have escaped in transpor ...
She2p Is a Novel RNA Binding Protein
... probe radius of 1.4 Å. The surface electrostatic potential is color coded red and blue, representing electrostatic potentials between ⬍ ⫺14 to ⬎ ⫹14 kBT, where kB is the Boltzmann constant and T is the temperature. Orientation is identical to (A). (C) Stereoview of (A) rotated 90⬚ around the vertic ...
... probe radius of 1.4 Å. The surface electrostatic potential is color coded red and blue, representing electrostatic potentials between ⬍ ⫺14 to ⬎ ⫹14 kBT, where kB is the Boltzmann constant and T is the temperature. Orientation is identical to (A). (C) Stereoview of (A) rotated 90⬚ around the vertic ...
Replacement Matrices for Transmembrane Proteins
... Since 1985, GenBank, the sequence database maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information, has doubled in size every 18 months [4]. At this pace, novel sequences cannot be characterized by experimental methods alone. The emergence of phylogenetics software in the past decades allows ...
... Since 1985, GenBank, the sequence database maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information, has doubled in size every 18 months [4]. At this pace, novel sequences cannot be characterized by experimental methods alone. The emergence of phylogenetics software in the past decades allows ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
... successive runs of helix or ß conformation where the polypeptide chain reverses direction in space (Fig. 4-7). ß turns therefore, commonly are located at the surface of a globular protein. Particularly common are ß turns that connect the ends of two adjacent strands of an antiparallel ß sheet. The ...
... successive runs of helix or ß conformation where the polypeptide chain reverses direction in space (Fig. 4-7). ß turns therefore, commonly are located at the surface of a globular protein. Particularly common are ß turns that connect the ends of two adjacent strands of an antiparallel ß sheet. The ...
authors` original image
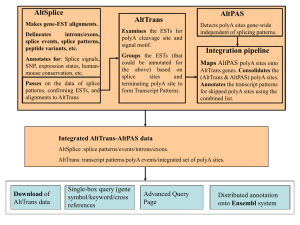
... introns/exons, splice events, splice patterns, peptide variants, etc. Annotates for: Splice signals, SNP, expression states, humanmouse conservation, etc. ...
... introns/exons, splice events, splice patterns, peptide variants, etc. Annotates for: Splice signals, SNP, expression states, humanmouse conservation, etc. ...
RNA-Seq Sample Recommendations (Craig Praul, PSU and Caitlyn
... is recommended. The core facility strongly encourages pilot projects to confirm that the chosen methods will reproducibly produce sufficient quantities of cells/tissues to ultimately yield the required amount of high quality RNA. Once an isolation protocol or a storage and isolation protocol is esta ...
... is recommended. The core facility strongly encourages pilot projects to confirm that the chosen methods will reproducibly produce sufficient quantities of cells/tissues to ultimately yield the required amount of high quality RNA. Once an isolation protocol or a storage and isolation protocol is esta ...
Design and Evolution of Artificial M13 Coat Proteins
... The design and evolution of ACP-7 depended on the use of a phagemid system in which all the wild-type phage coat proteins were supplied by a helper phage. As a consequence, non-functional coat proteins could be selected, provided they incorporated into the wild-type coat without signi®cantly impairi ...
... The design and evolution of ACP-7 depended on the use of a phagemid system in which all the wild-type phage coat proteins were supplied by a helper phage. As a consequence, non-functional coat proteins could be selected, provided they incorporated into the wild-type coat without signi®cantly impairi ...
NZY First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit
... primers are included in the NZYRT 2× Master Mix, which also contains dNTPs, MgCl2 and an optimized RT buffer. NZYRT Enzyme Mix includes both the NZY Reverse Transcriptase (RNase H minus) and the NZY Ribonuclease Inhibitor in order to protect RNA against degradation due to ribonuclease contamination. ...
... primers are included in the NZYRT 2× Master Mix, which also contains dNTPs, MgCl2 and an optimized RT buffer. NZYRT Enzyme Mix includes both the NZY Reverse Transcriptase (RNase H minus) and the NZY Ribonuclease Inhibitor in order to protect RNA against degradation due to ribonuclease contamination. ...
J-Domain Protein CDJ2 and HSP70B Are a Plastidic Chaperone
... cochaperones, of which the J-domain cochaperones represent an important class. J-domain cochaperones contain a highly conserved J-domain that is responsible for the interaction with Hsp70. In addition, these cochaperones contain domains typical for protein–protein interactions, such as zinc finger or ...
... cochaperones, of which the J-domain cochaperones represent an important class. J-domain cochaperones contain a highly conserved J-domain that is responsible for the interaction with Hsp70. In addition, these cochaperones contain domains typical for protein–protein interactions, such as zinc finger or ...
Protein translocation across mitochondrial membranes
... hand, have strongly suggested an important function for cytosolic heat shock proteins (ct-hsps) in protein import, at least in yeast cells. A mutant defective in three of the four genes for cytosolic hsp70s (ssal-4) showed a reduced import into mitochondria accompanied by the accumulation in the cyt ...
... hand, have strongly suggested an important function for cytosolic heat shock proteins (ct-hsps) in protein import, at least in yeast cells. A mutant defective in three of the four genes for cytosolic hsp70s (ssal-4) showed a reduced import into mitochondria accompanied by the accumulation in the cyt ...
What more do we need to know to optimize the
... • Lowering pH, especially in young birds, can help with protease efficacy ...
... • Lowering pH, especially in young birds, can help with protease efficacy ...
CHMI 2227E Biochemistry I
... Specific activity (units/mg): Total activity (U)/ Total protein (mg) Yield: (Total activity at Step Y / Total activity in crude extract) x 100; Purification level: Specific activity at Step Y / Specific activity in crude extract; CHMI 2227 - E.R. Gauthier, Ph.D. ...
... Specific activity (units/mg): Total activity (U)/ Total protein (mg) Yield: (Total activity at Step Y / Total activity in crude extract) x 100; Purification level: Specific activity at Step Y / Specific activity in crude extract; CHMI 2227 - E.R. Gauthier, Ph.D. ...
Distribution of major serum proteins in an airbrea
... resolution of fastest migrating β-globulin bands (Fig. 1A, lanes 1,4 and 5) labeled as transferrins (Trf), while that labeled as albumin (Alb) was not visualized if the quantity of loaded serum was too low (Fig. 1A, lane-2). The unlabelled band that stacks at the buffer line may be prealbumin. Howev ...
... resolution of fastest migrating β-globulin bands (Fig. 1A, lanes 1,4 and 5) labeled as transferrins (Trf), while that labeled as albumin (Alb) was not visualized if the quantity of loaded serum was too low (Fig. 1A, lane-2). The unlabelled band that stacks at the buffer line may be prealbumin. Howev ...
Misincorporation of free m-tyrosine into cellular proteins: a potential
... Incubation of CHO cells with m-tyrosine inhibited colony formation in a concentration-dependent manner. Survival and proliferation of the cells was inhibited approx. 60 % by 0.25 mM m-tyrosine (Figure 1). In contrast, 1 mM L-tyrosine had little effect on the fraction of CHO cells that survived. Sinc ...
... Incubation of CHO cells with m-tyrosine inhibited colony formation in a concentration-dependent manner. Survival and proliferation of the cells was inhibited approx. 60 % by 0.25 mM m-tyrosine (Figure 1). In contrast, 1 mM L-tyrosine had little effect on the fraction of CHO cells that survived. Sinc ...
AF4 Encodes a Ubiquitous Protein That in Both
... of the genes. Recently, a third gene (FMR2) has been recognized as a member of AF4/LAF4 gene family. FMR2 maps to X chromosome at position Xq28. Mutations of FMR2 are associated with mild hereditary mental retardation.7,8 Members of the homologous AF4/LAF4/FMR2 gene family are expected to have trans ...
... of the genes. Recently, a third gene (FMR2) has been recognized as a member of AF4/LAF4 gene family. FMR2 maps to X chromosome at position Xq28. Mutations of FMR2 are associated with mild hereditary mental retardation.7,8 Members of the homologous AF4/LAF4/FMR2 gene family are expected to have trans ...
Plant–pathogen interactions: what is proteomics telling us?
... studies. Transcriptional changes do not reflect the complete cellular regulatory mechanism, as post-transcriptional processes which alter the amount of active protein, such as synthesis, degradation, processing and post-translational modification, are not taken into account. Thus, complementary approa ...
... studies. Transcriptional changes do not reflect the complete cellular regulatory mechanism, as post-transcriptional processes which alter the amount of active protein, such as synthesis, degradation, processing and post-translational modification, are not taken into account. Thus, complementary approa ...
Биохимия жидкостей полости рта
... molecular mass proteins of the salive Cystatins perform antimicrobial and antiviral function by the inhibition of enzyme activity of cysteine proteases that hydrolyze proteins of the oral cavity. They inhibit the activity of cysteine proteases by specific binding in the active site of the enzyme wit ...
... molecular mass proteins of the salive Cystatins perform antimicrobial and antiviral function by the inhibition of enzyme activity of cysteine proteases that hydrolyze proteins of the oral cavity. They inhibit the activity of cysteine proteases by specific binding in the active site of the enzyme wit ...
Localization of Low-sulfur Keratin Proteins in the Wool Follicle Using
... with the panel of monoclonal antibodies was investigated using indirect immunofluorescent. The results are listed in Table I and shown schematically in Fig. 3. Despite the disadvantage that the monoclonal antibodies all recognize more than one protein component, the studies indicate a specific patte ...
... with the panel of monoclonal antibodies was investigated using indirect immunofluorescent. The results are listed in Table I and shown schematically in Fig. 3. Despite the disadvantage that the monoclonal antibodies all recognize more than one protein component, the studies indicate a specific patte ...
The Plant Journal
... (a) Comparison of the predicted catalytic domains of LeCBDGK (accession number AF198258, residues 30±427), Arabidopsis AtDGK1 (accession number D63787, residues 351±684) and human DGK-g (accession number N48667, residues 427±772). Identical amino acid residues are shaded in black, conserved changes ...
... (a) Comparison of the predicted catalytic domains of LeCBDGK (accession number AF198258, residues 30±427), Arabidopsis AtDGK1 (accession number D63787, residues 351±684) and human DGK-g (accession number N48667, residues 427±772). Identical amino acid residues are shaded in black, conserved changes ...
Changes of cellular redox homeostasis and protein - LINK
... on these mechanisms become exhausted, and oxidative damage develops. The elevated concentration of the oxidative stressors is the result of the disorganized function of the mitochondria, the altered metabolism of the arachidonic acid, protein kinase C activation, glucose autooxidation, and the free ...
... on these mechanisms become exhausted, and oxidative damage develops. The elevated concentration of the oxidative stressors is the result of the disorganized function of the mitochondria, the altered metabolism of the arachidonic acid, protein kinase C activation, glucose autooxidation, and the free ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.