Characterizing the O-glycosylation landscape of human plasma
... O-glycosylation is a ubiquitous modification of extracellular proteins. Investigation of the general properties of O-glycosylation established that it is a heterogeneous modification, frequently occurring at low density within disordered regions in a cell-dependent manner. Using an unbiased screen to ...
... O-glycosylation is a ubiquitous modification of extracellular proteins. Investigation of the general properties of O-glycosylation established that it is a heterogeneous modification, frequently occurring at low density within disordered regions in a cell-dependent manner. Using an unbiased screen to ...
Osmoadaptative Strategy and Its Molecular
... of halophilic proteins possibly allows them to avoid overly rigid folded conformations. On the other hand, the proteomes of halophiles that use organic solutes as their main osmolytes (salt-out organisms) are not enriched in highly acidic proteins, although they typically produce extracellular prote ...
... of halophilic proteins possibly allows them to avoid overly rigid folded conformations. On the other hand, the proteomes of halophiles that use organic solutes as their main osmolytes (salt-out organisms) are not enriched in highly acidic proteins, although they typically produce extracellular prote ...
WAVE/Scars in platelets
... likely to regulate cortical actin filament reorganization in response to extracellular stimuli, although not all of these proteins have been linked to actin polymerization.1,2 Each of these proteins has a verprolin-homology (V) domain, cofilin-homology (C) domain, and an acidic (A) region at the C-t ...
... likely to regulate cortical actin filament reorganization in response to extracellular stimuli, although not all of these proteins have been linked to actin polymerization.1,2 Each of these proteins has a verprolin-homology (V) domain, cofilin-homology (C) domain, and an acidic (A) region at the C-t ...
Brooker Chapter 12 - Volunteer State Community College
... gene expression Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display ...
... gene expression Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display ...
Endoplasmic Reticulum Protein Quality Control and
... Protein folding in the ER, in particular, is aided by chaperones and cochaperones. Chaperones are proteins that interact transiently with other non-native proteins to help them acquire a native state. Chaperones do not direct the outcome of the folding process; instead, they enhance the efficiency o ...
... Protein folding in the ER, in particular, is aided by chaperones and cochaperones. Chaperones are proteins that interact transiently with other non-native proteins to help them acquire a native state. Chaperones do not direct the outcome of the folding process; instead, they enhance the efficiency o ...
Regulation of Photochemical Energy Transfer Accompanied
... The amount of D1/D2 phosphorylated proteins was the highest at 25 °C during 0.5–1 h after heat stress. The 4–8 h heat stress-recovered samples showed comparable phosphorylation levels with L25. A similar result was observed in Lhcb2 dephosphorylation analysis. Phosphorylated thylakoid proteins were ...
... The amount of D1/D2 phosphorylated proteins was the highest at 25 °C during 0.5–1 h after heat stress. The 4–8 h heat stress-recovered samples showed comparable phosphorylation levels with L25. A similar result was observed in Lhcb2 dephosphorylation analysis. Phosphorylated thylakoid proteins were ...
Pavel Doležal
... ubiquinone, but unlike the mitochondrial enzyme it can also reduce ferredoxin. Phylogenetic analyses show that the T. vaginalis shares common ancestry with the mitochondrial enzyme. ...
... ubiquinone, but unlike the mitochondrial enzyme it can also reduce ferredoxin. Phylogenetic analyses show that the T. vaginalis shares common ancestry with the mitochondrial enzyme. ...
Pavel Doležal
... ubiquinone, but unlike the mitochondrial enzyme it can also reduce ferredoxin. Phylogenetic analyses show that the T. vaginalis shares common ancestry with the mitochondrial enzyme. ...
... ubiquinone, but unlike the mitochondrial enzyme it can also reduce ferredoxin. Phylogenetic analyses show that the T. vaginalis shares common ancestry with the mitochondrial enzyme. ...
Protein Folding at the Exit Tunnel
... to C terminus, Phillips formulated the hypothesis that the N-terminal portion of nascent proteins may start folding during translation (57). Two years later, Taniuchi and coworkers responded showing that cotranslational folding is unlikely for small-/medium-size single-domain proteins (71) because i ...
... to C terminus, Phillips formulated the hypothesis that the N-terminal portion of nascent proteins may start folding during translation (57). Two years later, Taniuchi and coworkers responded showing that cotranslational folding is unlikely for small-/medium-size single-domain proteins (71) because i ...
The potato tuber mitochondrial proteome
... which were significantly higher. Unclassified proteins, that is, proteins not confidently ...
... which were significantly higher. Unclassified proteins, that is, proteins not confidently ...
The Generic Nature of Protein Folding and Misfolding
... as “nucleation-condensation,” in which a folding nucleus of a small number of residues forms, about which the remainder of the structure can then condense (Fersht, 2000). Detailed insight into how such a generic mechanism can generate unique folds for specific sequences of amino acids has come from a ...
... as “nucleation-condensation,” in which a folding nucleus of a small number of residues forms, about which the remainder of the structure can then condense (Fersht, 2000). Detailed insight into how such a generic mechanism can generate unique folds for specific sequences of amino acids has come from a ...
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
... Caryophyllales (e.g., quinoa and amaranth) are closely related. Our data rather indicate occurrence of significant genetic distance (similarity coefficients 0.05-0.10). Also, it is doubtful that amaranth and quinoa species are also closely related (similarity coefficients varied from 0.16 to 0.25). ...
... Caryophyllales (e.g., quinoa and amaranth) are closely related. Our data rather indicate occurrence of significant genetic distance (similarity coefficients 0.05-0.10). Also, it is doubtful that amaranth and quinoa species are also closely related (similarity coefficients varied from 0.16 to 0.25). ...
Zeeberg - Gene Ontology Consortium
... John Weinstein plus a lot of help from Rich Einstein and Mike Brenner of ExonHit ...
... John Weinstein plus a lot of help from Rich Einstein and Mike Brenner of ExonHit ...
Mader 11 ch 3 Chemistry of Organic Molecules Part 2
... initiates a series of events within the cells that results in the increased uptake of glucose into the cells, where it is converted into metabolic energy or stored as glycogen and fat. ...
... initiates a series of events within the cells that results in the increased uptake of glucose into the cells, where it is converted into metabolic energy or stored as glycogen and fat. ...
Analysis - The Journal of Cell Biology
... and MAPKAP kinase families (the last four of which are found in C. elegans but not yeast). Like worms, flies do not encode a complete ortholog of the mammalian Trio kinase, but do have a protein that is related to the entire Trio regulatory domain. CaMK members revealed by the fly genome project inc ...
... and MAPKAP kinase families (the last four of which are found in C. elegans but not yeast). Like worms, flies do not encode a complete ortholog of the mammalian Trio kinase, but do have a protein that is related to the entire Trio regulatory domain. CaMK members revealed by the fly genome project inc ...
Genetically encoded phenyl azide photochemistry drives
... Replacement of F145 in superfolder GFP (sfGFP17) with azF also led to loss of uorescence on irradiation14 but by a different mechanism; the phenyl nitrene forms a crosslink to the chromophore so restricting chromophore mobility and reducing the extended conjugated double bond system. In contrast, th ...
... Replacement of F145 in superfolder GFP (sfGFP17) with azF also led to loss of uorescence on irradiation14 but by a different mechanism; the phenyl nitrene forms a crosslink to the chromophore so restricting chromophore mobility and reducing the extended conjugated double bond system. In contrast, th ...
Post-transcriptional control of gene expression: a genome
... Puf4 and Cth2 that regulate the stability of dozens or hundreds of mRNAs [16,28]. At the other extreme, microarray data suggest that the yeast Edc3 protein specifically regulates a single mRNA [29]. Thus, genomewide studies can reveal both widespread and highly specialized roles of regulatory factor ...
... Puf4 and Cth2 that regulate the stability of dozens or hundreds of mRNAs [16,28]. At the other extreme, microarray data suggest that the yeast Edc3 protein specifically regulates a single mRNA [29]. Thus, genomewide studies can reveal both widespread and highly specialized roles of regulatory factor ...
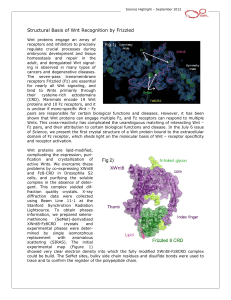
Structural Basis of Wnt Recognition by Frizzled
... XWnt8 has an unusual two-domain structure (Figure 2), and each domain extends a betastrand or ‘finger’, which ‘grasps’ the Fz8-CRD on opposite faces. Site 1 interaction is primarily mediated by a palmitoleic acid covalently attached to a conserved Serine at the tip of ‘thumb’, which binds within a ...
... XWnt8 has an unusual two-domain structure (Figure 2), and each domain extends a betastrand or ‘finger’, which ‘grasps’ the Fz8-CRD on opposite faces. Site 1 interaction is primarily mediated by a palmitoleic acid covalently attached to a conserved Serine at the tip of ‘thumb’, which binds within a ...
Invited Chapter One
... study showed that human and fly Smads that cluster together in the tree generate the same phenotype (Marquez et al., 2001). Taken together the amino acid similarity and functional conservation studies indicate that human and fly proteins in the same subfamily are encoded by homologous genes. Further ...
... study showed that human and fly Smads that cluster together in the tree generate the same phenotype (Marquez et al., 2001). Taken together the amino acid similarity and functional conservation studies indicate that human and fly proteins in the same subfamily are encoded by homologous genes. Further ...
Judge, P.J. and Watts, A.
... software was used [59], and several key residues at the junction between the TM and amphipathic helices which facilitates the close approach of adjacent monomers (d) to help in understanding the channel blocking mechanism. (d) Structural model of a polytopic (7-helical), membraneembedded photorecept ...
... software was used [59], and several key residues at the junction between the TM and amphipathic helices which facilitates the close approach of adjacent monomers (d) to help in understanding the channel blocking mechanism. (d) Structural model of a polytopic (7-helical), membraneembedded photorecept ...
RNA-binding proteins
... RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) play key roles in post-transcriptional control of RNAs, which, along with transcriptional regulation, is a major way to regulate patterns of gene expression during development. Post-transcriptional control can occur at many different steps in RNA metabolism, including spl ...
... RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) play key roles in post-transcriptional control of RNAs, which, along with transcriptional regulation, is a major way to regulate patterns of gene expression during development. Post-transcriptional control can occur at many different steps in RNA metabolism, including spl ...
Use of Cellular Decapping Activators by Positive
... hence, the endogenous mRNA turnover is altered [27–29]. This deregulated host mRNA stability is directly related to sfRNA expression and plays an important role in pathogenesis. As found for WNV and DENV, both the HCV and the Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) contain regions that stall and repress ...
... hence, the endogenous mRNA turnover is altered [27–29]. This deregulated host mRNA stability is directly related to sfRNA expression and plays an important role in pathogenesis. As found for WNV and DENV, both the HCV and the Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) contain regions that stall and repress ...
ASH1 by Puf6p–Fun12p/eIF5B interaction and released by CK2 phosphorylation Yingfeng Deng,
... and bud (Long et al. 1997). To test whether Fun12p was also required for the localization of other mRNAs, we examined the localization of IST2 mRNA (Takizawa et al. 2000), which contains putative Puf6p-binding sites at the 3⬘UTR (Gu et al. 2004). IST2 mRNA was found diffusely distributed within the ...
... and bud (Long et al. 1997). To test whether Fun12p was also required for the localization of other mRNAs, we examined the localization of IST2 mRNA (Takizawa et al. 2000), which contains putative Puf6p-binding sites at the 3⬘UTR (Gu et al. 2004). IST2 mRNA was found diffusely distributed within the ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.