Nanoscale microscopy technique allows scientists to
... translated into proteins when needed. AcX can be modified to anchor either proteins or With the new system, it should be possible to RNA to the gel. In the Nature Biotechnology study, determine exactly which RNA molecules are the researchers used it to anchor proteins, and they located near the syna ...
... translated into proteins when needed. AcX can be modified to anchor either proteins or With the new system, it should be possible to RNA to the gel. In the Nature Biotechnology study, determine exactly which RNA molecules are the researchers used it to anchor proteins, and they located near the syna ...
Open questions - in brief: Beyond -omics, missing organisms
... graph or two, like the collection below, to slightly longer contributions, the first two of which are also published this month [2,3]. We will publish these short contri butions regularly during the year, to reflect the interests and preoccupations of our Editorial Board and perhaps stimulate answe ...
... graph or two, like the collection below, to slightly longer contributions, the first two of which are also published this month [2,3]. We will publish these short contri butions regularly during the year, to reflect the interests and preoccupations of our Editorial Board and perhaps stimulate answe ...
Positive Strand RNA Viruses
... – Viral RNA polymerase (replicase) – Certain Host proteins VPg may act as a primer for RNA synthesis, this would explain why it is at the 5' end of all newly synthesized RNA molecules New minus sense strands serve as template for new plus sense strands Again, poliovirus RNA polymerase and VPg are ne ...
... – Viral RNA polymerase (replicase) – Certain Host proteins VPg may act as a primer for RNA synthesis, this would explain why it is at the 5' end of all newly synthesized RNA molecules New minus sense strands serve as template for new plus sense strands Again, poliovirus RNA polymerase and VPg are ne ...
Jalview Homework
... 4. Start Jalview and Choose “File””Input Alignment from…””Textbox”. 5. Paste the sequences into the window that pops up and press the “New Window” button. 6. You should see all of the sequences stacked on top of each other in the window that pops up. Go to the “Web Service” option of the window an ...
... 4. Start Jalview and Choose “File””Input Alignment from…””Textbox”. 5. Paste the sequences into the window that pops up and press the “New Window” button. 6. You should see all of the sequences stacked on top of each other in the window that pops up. Go to the “Web Service” option of the window an ...
2. Where does translation take place
... 5. What is the role of ribosomes in protein production? 6. Below you’ll be given an mRNA codon. Write down the tRNA anticodon and the corresponding amino acid that the codon codes for. You will need the handout Genetic Code. mRNA codon tRNA anticodon Amino acid (AA) UAC CGU AUG UUC AAA AUU AAC CCA ...
... 5. What is the role of ribosomes in protein production? 6. Below you’ll be given an mRNA codon. Write down the tRNA anticodon and the corresponding amino acid that the codon codes for. You will need the handout Genetic Code. mRNA codon tRNA anticodon Amino acid (AA) UAC CGU AUG UUC AAA AUU AAC CCA ...
Slide 1
... • RNA polymerase I is terminated by a mechanism that requires a polymerase-specific termination factor, which binds downstream of the transcription unit • RNA polymerase II is terminated in a region 0.5-2 kb beyond the poly(A) addition site, and termination is coupled to the process that cleaves and ...
... • RNA polymerase I is terminated by a mechanism that requires a polymerase-specific termination factor, which binds downstream of the transcription unit • RNA polymerase II is terminated in a region 0.5-2 kb beyond the poly(A) addition site, and termination is coupled to the process that cleaves and ...
Lecture 12: Enzyme Catalysis Topics: Catalytic Strategies Steps in a
... Allosteric enzymes use changes in conformation to switch between different states which have different levels of activity. Binding of allosteric effectors can control the switch between states, and thereby increase or decrease the enzyme activity to exert control over biological processes. Key Conce ...
... Allosteric enzymes use changes in conformation to switch between different states which have different levels of activity. Binding of allosteric effectors can control the switch between states, and thereby increase or decrease the enzyme activity to exert control over biological processes. Key Conce ...
SIP - Leaf-like rest streams - 20150317
... ambition of the present research line to address this issue in close collaboration with industrial partners. The chemical applications studied so far are mostly based on the hydrolysis of the proteins into amino acids followed by fractionation and separation. However, this procedure also implies tha ...
... ambition of the present research line to address this issue in close collaboration with industrial partners. The chemical applications studied so far are mostly based on the hydrolysis of the proteins into amino acids followed by fractionation and separation. However, this procedure also implies tha ...
Protein - PBworks
... Protein is an energy supplying nutrient made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. The nitrogen is what makes it different from carbohydrates and fats. Proteins are formed from the combining of 20 different amino acids into different combinations and patterns. There are at least 30,000 differ ...
... Protein is an energy supplying nutrient made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. The nitrogen is what makes it different from carbohydrates and fats. Proteins are formed from the combining of 20 different amino acids into different combinations and patterns. There are at least 30,000 differ ...
Name: Protein Synthesis PRICE DNA DNA contains ______
... • Copies DNA & leaves through __________ pores • Contains the Nitrogen Bases A, G, C, ____ ( no T ) • Carries the information for a ___________ protein • Made up of 500 to 1000 nucleotides long • Sequence of ____ bases called codon • AUG – methionine or start ________ • UAA, UAG, or UGA – ______ cod ...
... • Copies DNA & leaves through __________ pores • Contains the Nitrogen Bases A, G, C, ____ ( no T ) • Carries the information for a ___________ protein • Made up of 500 to 1000 nucleotides long • Sequence of ____ bases called codon • AUG – methionine or start ________ • UAA, UAG, or UGA – ______ cod ...
some molecular basics
... downregulated) as the binding partner for ENaC. Nedd4 [19] contains a C2 domain, 3 (or 4 in the human) WW domains, and a ubiquitin-ligase HECT (homology to the E6-AP C terminus) domain (Fig. 1). ENaC–Nedd4 interaction is mediated by the WW domains of Nedd4 which bind to the PY motifs of a, b and g E ...
... downregulated) as the binding partner for ENaC. Nedd4 [19] contains a C2 domain, 3 (or 4 in the human) WW domains, and a ubiquitin-ligase HECT (homology to the E6-AP C terminus) domain (Fig. 1). ENaC–Nedd4 interaction is mediated by the WW domains of Nedd4 which bind to the PY motifs of a, b and g E ...
Material Safety Data Sheet
... Stability/Incompatibility: Stable. See enclosed data sheet for product-specific storage information. Hazardous Decomposition: None known. FIRST AID MEASURES Eye Contact: Check for contact lenses and remove if present. Flush eyes with large volumes of water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical atten ...
... Stability/Incompatibility: Stable. See enclosed data sheet for product-specific storage information. Hazardous Decomposition: None known. FIRST AID MEASURES Eye Contact: Check for contact lenses and remove if present. Flush eyes with large volumes of water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical atten ...
Flexibility of a polypeptide chain
... and frequently exhibit similar functions, these combinations are called motifs or supersecondary structures For instance, a helix-turn-helix motif, often found in DNA-binding proteins some polypeptide chains fold into 2 or more compact globular units or regions that are connected by flexible regions ...
... and frequently exhibit similar functions, these combinations are called motifs or supersecondary structures For instance, a helix-turn-helix motif, often found in DNA-binding proteins some polypeptide chains fold into 2 or more compact globular units or regions that are connected by flexible regions ...
Lecture
... Examples: Keratin is the protein of hair, horns, feathers, and other skin appendages. Insects and spiders use silk fibers to make their cocoons and webs, respectively. Collagen and elastin proteins provide a fibrous framework in animal connective tissues. ...
... Examples: Keratin is the protein of hair, horns, feathers, and other skin appendages. Insects and spiders use silk fibers to make their cocoons and webs, respectively. Collagen and elastin proteins provide a fibrous framework in animal connective tissues. ...
Positive Strand RNA Viruses
... – Viral RNA polymerase (replicase) – Certain Host proteins VPg may act as a primer for RNA synthesis, this would explain why it is at the 5' end of all newly synthesized RNA molecules New minus sense strands serve as template for new plus sense strands Again, poliovirus RNA polymerase and VPg are ne ...
... – Viral RNA polymerase (replicase) – Certain Host proteins VPg may act as a primer for RNA synthesis, this would explain why it is at the 5' end of all newly synthesized RNA molecules New minus sense strands serve as template for new plus sense strands Again, poliovirus RNA polymerase and VPg are ne ...
Macromolecules - Georgetown ISD
... 3. Carbon has how many electrons in its outer energy shell? 4. Carbon can form up to ______ covalent bonds with other atoms (elements) 5. Elements that carbon usually bonds with: _____, _____, _____, or _____. Example: ___________________ 6. Macromolecules are also called ___________________. 7. Mad ...
... 3. Carbon has how many electrons in its outer energy shell? 4. Carbon can form up to ______ covalent bonds with other atoms (elements) 5. Elements that carbon usually bonds with: _____, _____, _____, or _____. Example: ___________________ 6. Macromolecules are also called ___________________. 7. Mad ...
Cas_ProteinsFinal
... Kunin, V., Sorek, R., Hugenholtz, P. (2007) Evolutionary conservation of sequence and secondary structures in CRISPR repeats. Genome Biology.http://genomebiology.com/2007/8/4/R61. ...
... Kunin, V., Sorek, R., Hugenholtz, P. (2007) Evolutionary conservation of sequence and secondary structures in CRISPR repeats. Genome Biology.http://genomebiology.com/2007/8/4/R61. ...
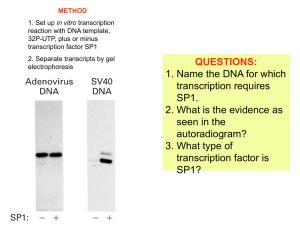
Key to Exam 2
... conjunction with gel electrophoresis to identify specific proteins or subunits recognized by antibodies. Many times the two methods will provide the same information about a protein and can be used interchangeably. In other situations one of the methods will work better or be more appropriate. For e ...
... conjunction with gel electrophoresis to identify specific proteins or subunits recognized by antibodies. Many times the two methods will provide the same information about a protein and can be used interchangeably. In other situations one of the methods will work better or be more appropriate. For e ...
Protein Synthesis
... mRNA: A U G C C U C A C G A G C G U G C G C U A U G A Codons and anticodons consist of 3 nucleotides. How many codons are on the above mRNA strand? 8 Now mRNA can take it’s copy of the DNA code to the ribosome ...
... mRNA: A U G C C U C A C G A G C G U G C G C U A U G A Codons and anticodons consist of 3 nucleotides. How many codons are on the above mRNA strand? 8 Now mRNA can take it’s copy of the DNA code to the ribosome ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.