talk_UPR_nano - Columbia University
... We use microarrays to track the changes in mRNA levels of stressed cells in comparison to untreated cells. DTT Each bar is one gene. Arrays for 1 hour and 3 hours are consistent (r = 0.85). ...
... We use microarrays to track the changes in mRNA levels of stressed cells in comparison to untreated cells. DTT Each bar is one gene. Arrays for 1 hour and 3 hours are consistent (r = 0.85). ...
Transcriptional regulatory roles of G
... G-quadruplexes (G4s) are four-stranded DNA secondary structures involved in a diverse range of biological processes. Although the anti-cancer potential of G4s in oncogene promoters has been extensively investigated, the functions of promoter G4s in non-cancer-related genes are not known. We have exp ...
... G-quadruplexes (G4s) are four-stranded DNA secondary structures involved in a diverse range of biological processes. Although the anti-cancer potential of G4s in oncogene promoters has been extensively investigated, the functions of promoter G4s in non-cancer-related genes are not known. We have exp ...
Genetic Engineering
... separates pieces of DNA based on size (after being cut up with restriction enzymes) Different people will have different banding patterns. Related individuals will have similar patterns. ...
... separates pieces of DNA based on size (after being cut up with restriction enzymes) Different people will have different banding patterns. Related individuals will have similar patterns. ...
Gene Section ATF1 (activating transcription factor 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Characterised by the translocation t(12;22)(q13;q12). Hybrid/Mutated gene 5' EWSR1- 3' ATF1. Abnormal protein The chimaeric protein is composed of the N-terminal domain of EWS linked to the bZIP domain of ATF-1. Oncogenesis Binds to ATF sites present in cAMP-responsive promoters via the ATF1 bZIP do ...
... Characterised by the translocation t(12;22)(q13;q12). Hybrid/Mutated gene 5' EWSR1- 3' ATF1. Abnormal protein The chimaeric protein is composed of the N-terminal domain of EWS linked to the bZIP domain of ATF-1. Oncogenesis Binds to ATF sites present in cAMP-responsive promoters via the ATF1 bZIP do ...
Lesson 2
... The genetic code is a set of “rules” by which the information in mRNA is translated into proteins. A codon is made of three nucleotide bases (triplet) and it may translate into: • an amino acid, • a “start” signal (which is always the amino acid Met), or • a “stop” signal (no amino acid) http://www ...
... The genetic code is a set of “rules” by which the information in mRNA is translated into proteins. A codon is made of three nucleotide bases (triplet) and it may translate into: • an amino acid, • a “start” signal (which is always the amino acid Met), or • a “stop” signal (no amino acid) http://www ...
Why teach a course in bioinformatics?
... protein. The altered protein may not function properly. ...
... protein. The altered protein may not function properly. ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated ...
... licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated ...
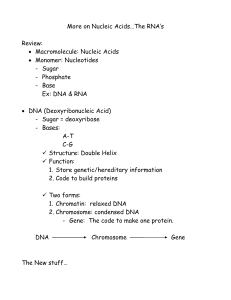
Notes: More on Nucleic Acids
... o A – U (uracil) [There is no T (thymine)] 3 types of RNA: 1. rRNA: [“r” = ribosomal] - structure: ball-like structure with specific “grooves” on the surface, for… - function: synthesize amino acids in to a protein 2. mRNA: [“m” = messenger] - structure: single straight chain of nucleotides - func ...
... o A – U (uracil) [There is no T (thymine)] 3 types of RNA: 1. rRNA: [“r” = ribosomal] - structure: ball-like structure with specific “grooves” on the surface, for… - function: synthesize amino acids in to a protein 2. mRNA: [“m” = messenger] - structure: single straight chain of nucleotides - func ...
The Nature of Genes The Nature of Genes
... • Introns are spliced out of pre-mRNAs to produce the mature mRNA that is translated. • Alternative splicing recognizes different splice sites in different tissue types. • The mature mRNAs in each tissue possess different exons, resulting in different polypeptide products from the same gene. ...
... • Introns are spliced out of pre-mRNAs to produce the mature mRNA that is translated. • Alternative splicing recognizes different splice sites in different tissue types. • The mature mRNAs in each tissue possess different exons, resulting in different polypeptide products from the same gene. ...
RECONSTRUCTING A “UNIVERSAL TREE”
... eg. chloroplast & cyanobacterial sequences are more similar than either is to nuclear homologue…. ...
... eg. chloroplast & cyanobacterial sequences are more similar than either is to nuclear homologue…. ...
Feb 21 Bacteria, DNA Technology, and Cell Communication
... Negative vs. positive regulation (repressors vs. enhancers) Eukaryotic gene regulation—transcription factors Difference btw prokaryote and eukaryote gene regulation DNA technology DNA is redundant main differences due to gene expression Restriction enzymes, sticky ends, DNA ligase (endonuclease) Pa ...
... Negative vs. positive regulation (repressors vs. enhancers) Eukaryotic gene regulation—transcription factors Difference btw prokaryote and eukaryote gene regulation DNA technology DNA is redundant main differences due to gene expression Restriction enzymes, sticky ends, DNA ligase (endonuclease) Pa ...
Allosteric Modulation of DNA by Small Molecules
... interfaces could silence aberrant gene expression pathways. Pyrrole-imidazole polyamides are DNA minor groove binding small molecules that are programmable for a large repertoire of DNA motifs. Py/Im polyamides bind the minor groove of DNA sequence specifically (1), encoded by sideby-side arrangemen ...
... interfaces could silence aberrant gene expression pathways. Pyrrole-imidazole polyamides are DNA minor groove binding small molecules that are programmable for a large repertoire of DNA motifs. Py/Im polyamides bind the minor groove of DNA sequence specifically (1), encoded by sideby-side arrangemen ...
7.2.7 Describe the promoter as an example of non
... gene’s location. It is the binding site of RNA polymerase--the enzyme that constructs mRNA from the DNA template during Transcription. ...
... gene’s location. It is the binding site of RNA polymerase--the enzyme that constructs mRNA from the DNA template during Transcription. ...
Bis2A 9.0 Introduction to Gene Regulation
... pattern of the gene being observed. If the regulatory protein acts (by binding DNA) in a way that increases expression then it is considered an activator. If the regulatory protein acts (by binding DNA) to repress or decrease expression of the gene then it is considered a repressor. Activators and r ...
... pattern of the gene being observed. If the regulatory protein acts (by binding DNA) in a way that increases expression then it is considered an activator. If the regulatory protein acts (by binding DNA) to repress or decrease expression of the gene then it is considered a repressor. Activators and r ...
Programming Gene Expression
... CAP binds with cAMP to forms a dimer. and then stimulates the transcription of lactose- and arabinose-catabolizing genes as sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. The E. coli genome contains many CAP-binding sites in positions appropriate for interactions with RNA polymerase. Thus, an increase in th ...
... CAP binds with cAMP to forms a dimer. and then stimulates the transcription of lactose- and arabinose-catabolizing genes as sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. The E. coli genome contains many CAP-binding sites in positions appropriate for interactions with RNA polymerase. Thus, an increase in th ...
DNA Transcription and Translation
... DNA does not leave the nucleus so a carrier molecule called messanger RNA (mRNA) is used o mRNA carries the genetic message to the ribosomes RNA is different than DNA in a few ways o RNA contains ribose sugar, not deoxyribose RNA has no thymine base (T), instead has uracil (U) RNA is sin ...
... DNA does not leave the nucleus so a carrier molecule called messanger RNA (mRNA) is used o mRNA carries the genetic message to the ribosomes RNA is different than DNA in a few ways o RNA contains ribose sugar, not deoxyribose RNA has no thymine base (T), instead has uracil (U) RNA is sin ...
Transcript Maps
... • trans-acting Referring to DNA sequences encoding diffusible proteins (e.g., transcription activators and repressors) that control genes on the same or different chromosomes. ...
... • trans-acting Referring to DNA sequences encoding diffusible proteins (e.g., transcription activators and repressors) that control genes on the same or different chromosomes. ...
Document
... Growth and division genes of bacteria are regulated genes. Their expression is controlled by the needs of the cell as it responds to its environment with the goal of increasing in mass and dividing. Genes that generally are continuously expressed are constitutive genes (housekeeping genes). Examples ...
... Growth and division genes of bacteria are regulated genes. Their expression is controlled by the needs of the cell as it responds to its environment with the goal of increasing in mass and dividing. Genes that generally are continuously expressed are constitutive genes (housekeeping genes). Examples ...