Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... genomes allows one to narrow the search for human transcription factor binding sites by beginning with conserved regions of the genome • In addition, it is easier to search for cis-regulatory modules (CRMs), which contain several transcription factor binding sites ...
... genomes allows one to narrow the search for human transcription factor binding sites by beginning with conserved regions of the genome • In addition, it is easier to search for cis-regulatory modules (CRMs), which contain several transcription factor binding sites ...
Answers to the Study Guide for C12 Molecular Genetics Labeled
... Inversion – part of the chromosome breaks off and inverts, flips and reattached to the chromosome. Point mutation – can be an insertion of one base or a deletion of one base. Translocation – is when part of one chromosome breaks off and reattaches to another chromosome. The two chromosomes are not h ...
... Inversion – part of the chromosome breaks off and inverts, flips and reattached to the chromosome. Point mutation – can be an insertion of one base or a deletion of one base. Translocation – is when part of one chromosome breaks off and reattaches to another chromosome. The two chromosomes are not h ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation - CK
... patterns of regulatory elements are common to all genes, regardless of the cells in which they occur. An example is the TATA box, so named because it has a core sequence of TATAAA. This is a regulatory element that is part of the promoter of most eukaryotic genes. A number of regulatory proteins bin ...
... patterns of regulatory elements are common to all genes, regardless of the cells in which they occur. An example is the TATA box, so named because it has a core sequence of TATAAA. This is a regulatory element that is part of the promoter of most eukaryotic genes. A number of regulatory proteins bin ...
Chapter 19 - mrswehri.com
... complex assembles on the promoter sequence. RNA polymerase II proceeds to transcribe the gene making premRNA. Transcription factors are proteins that assist RNA polymerase II to initiate transcription. ...
... complex assembles on the promoter sequence. RNA polymerase II proceeds to transcribe the gene making premRNA. Transcription factors are proteins that assist RNA polymerase II to initiate transcription. ...
DNA, and in some cases RNA, is the primary source of heritable
... operator - region can block the action of the RNA polymerase if the region is occupied by a repressor protein structural genes - contain DNA sequences that code for several related enzymes that direct the production of some particular end product regulatory genes - produces proteins that either (1) ...
... operator - region can block the action of the RNA polymerase if the region is occupied by a repressor protein structural genes - contain DNA sequences that code for several related enzymes that direct the production of some particular end product regulatory genes - produces proteins that either (1) ...
One copy from each parent Each parent passes on a “mixed copy”
... Molecular Cell Biology: Components of the Central Dogma Protein Translation ...
... Molecular Cell Biology: Components of the Central Dogma Protein Translation ...
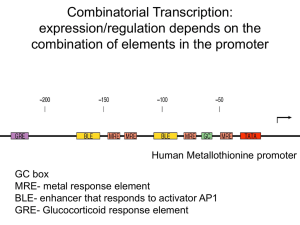
Combinatorial Transcription: expression/regulation depends on the
... Figure 3 Mechanism of insulator effect on enhancer function. (a) Diagram of two genes, X and Y, located within a chromosomal domain defined by two insulator sequences (ins) and their associated proteins (ibp). Enhancers located between the two genes (en1and en2) can activate transcription from the ...
... Figure 3 Mechanism of insulator effect on enhancer function. (a) Diagram of two genes, X and Y, located within a chromosomal domain defined by two insulator sequences (ins) and their associated proteins (ibp). Enhancers located between the two genes (en1and en2) can activate transcription from the ...
PPT
... Figure 6: A Schematic showing the principle behind agglomerative and divisive clustering. The colour code represents the log2 (expression ratio), where red represents up-regulation, green represents down-regulation, and black representing no change in expression. In aggregative clustering, genes tha ...
... Figure 6: A Schematic showing the principle behind agglomerative and divisive clustering. The colour code represents the log2 (expression ratio), where red represents up-regulation, green represents down-regulation, and black representing no change in expression. In aggregative clustering, genes tha ...
The four types of nucleotides in DNA are Adenine, Thymine
... B) Transfer RNA reads the information stored in mRNA and uses it to synthesize a protein C) Transfer RNA carries information from genes into the ribosome for protein synthesis D) Transfer RNA analyzes a protein in order to create an exact duplicate ...
... B) Transfer RNA reads the information stored in mRNA and uses it to synthesize a protein C) Transfer RNA carries information from genes into the ribosome for protein synthesis D) Transfer RNA analyzes a protein in order to create an exact duplicate ...
Ch. 17 - Ltcconline.net
... 2. Distinguish between transcription and translation. 3. Compare where transcription and translation occur in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes. 4. Define codon and explain the relationship between the linear sequence of codons on mRNA and the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. 5. Explain ...
... 2. Distinguish between transcription and translation. 3. Compare where transcription and translation occur in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes. 4. Define codon and explain the relationship between the linear sequence of codons on mRNA and the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. 5. Explain ...
Chapter 12 guided Notes 2
... An operon is a group of genes that operate together. In E. coli, these genes must be turned on so the bacterium can use lactose as food. Therefore, they are called the lac operon. How are lac genes turned off and on? The lac genes are turned off by repressors and turned on by the presence of lactose ...
... An operon is a group of genes that operate together. In E. coli, these genes must be turned on so the bacterium can use lactose as food. Therefore, they are called the lac operon. How are lac genes turned off and on? The lac genes are turned off by repressors and turned on by the presence of lactose ...
Bioinformatics and Personal Health/Intro computer lab
... transcriptional repressors. When the hormone GA is absent the GRAS domain binds transcription factors, inactivating them. When GA is present the DELLA domain binds the protein GID1. This binding causes the DELLA protein to be tagged for degradation (using ubiquitination). With DELLA proteins degrade ...
... transcriptional repressors. When the hormone GA is absent the GRAS domain binds transcription factors, inactivating them. When GA is present the DELLA domain binds the protein GID1. This binding causes the DELLA protein to be tagged for degradation (using ubiquitination). With DELLA proteins degrade ...
Crash Course in Biochemistry
... • Tells where genes start and stop • This still not well understood ...
... • Tells where genes start and stop • This still not well understood ...
Problem Set 8 ——– Answer Key - University of California, Berkeley
... You want to express a human keratin protein, so you need to integrate the human gene into a bacterial plasmid. If you cut out the human keratin gene directly from the human DNA genome and insert it into the plasmid, will the bacteria be able to express this gene for you? If not, why not? What additi ...
... You want to express a human keratin protein, so you need to integrate the human gene into a bacterial plasmid. If you cut out the human keratin gene directly from the human DNA genome and insert it into the plasmid, will the bacteria be able to express this gene for you? If not, why not? What additi ...
Slide ()
... Proposed genetic rearrangement of chromosome 11 in a subset of sporadic parathyroid adenomas. An inversion of DNA sequence near the centromere of chromosome 11 places the 5′-regulatory region of the PTH gene (also on chromosome 11) adjacent to the PRAD1 gene, whose product is involved in cell cycle ...
... Proposed genetic rearrangement of chromosome 11 in a subset of sporadic parathyroid adenomas. An inversion of DNA sequence near the centromere of chromosome 11 places the 5′-regulatory region of the PTH gene (also on chromosome 11) adjacent to the PRAD1 gene, whose product is involved in cell cycle ...
Chapter 15 Gene Regulation Prokaryotic Regulation
... for the biosynthesis of amino acids and other essential macromolecules • If the amino acid tryptophan is present in enough quantity in growth medium for E. coli, then the enzymes necessary for its production are repressed • 5 genes are involved in the trp operon • In the presence of tryptophan, all ...
... for the biosynthesis of amino acids and other essential macromolecules • If the amino acid tryptophan is present in enough quantity in growth medium for E. coli, then the enzymes necessary for its production are repressed • 5 genes are involved in the trp operon • In the presence of tryptophan, all ...
Gene Control
... 4. High trp level in cell : operon repressed a. trp repressor is allosteric 1. binding to trp activates repressor 2. active repressor binds to operator 3. blocks RNA polymerase ...
... 4. High trp level in cell : operon repressed a. trp repressor is allosteric 1. binding to trp activates repressor 2. active repressor binds to operator 3. blocks RNA polymerase ...
Reduction: For and Against Chapter 7
... The law of independent assortment reduced to molecular level ...
... The law of independent assortment reduced to molecular level ...
Promoters
... - based on the E.coli Tn10-encoded tetracycline resistant operon - Tc resistance operon consists of two genes: a) the resistance gene TetA – codes for a membrane protein that exports invaded Tc out of the bacterial cell b) the regulator gene TetR – codes for a dimeric DNA-binding protein In the abse ...
... - based on the E.coli Tn10-encoded tetracycline resistant operon - Tc resistance operon consists of two genes: a) the resistance gene TetA – codes for a membrane protein that exports invaded Tc out of the bacterial cell b) the regulator gene TetR – codes for a dimeric DNA-binding protein In the abse ...