Trans-activation and DNA-binding properties of
... encoding proteins which share homology in their DNA-binding domain (3—8). This DNA-binding domain is closely related to that of the nuclear proteins known as the high mobility group (HMG) proteins. The HMG-box DNA-binding domain is -80 amino acids and contains highly conserved proline, aromatic and ...
... encoding proteins which share homology in their DNA-binding domain (3—8). This DNA-binding domain is closely related to that of the nuclear proteins known as the high mobility group (HMG) proteins. The HMG-box DNA-binding domain is -80 amino acids and contains highly conserved proline, aromatic and ...
Todd Eckdahl - Davidson College
... Minor Groove Binding Drugs Anti-tumor properties Conformational change in the 3D structure of DNA Prior Knowledge of MGBD/DNA interaction As models for minor groove binding proteins ...
... Minor Groove Binding Drugs Anti-tumor properties Conformational change in the 3D structure of DNA Prior Knowledge of MGBD/DNA interaction As models for minor groove binding proteins ...
Gene Regulation
... • General transcription factors are essential for the transcription of all protein-coding genes • In eukaryotes, high levels of transcription of particular genes depend on control elements interacting with specific transcription factors ...
... • General transcription factors are essential for the transcription of all protein-coding genes • In eukaryotes, high levels of transcription of particular genes depend on control elements interacting with specific transcription factors ...
Transcription and Translation ppt
... actually attach to the correct protein. The anticodon( tRNA) binds by complimentary base pairing to the nucleotides of the codon. Example: if the codon on a mRNA is UUU, a tRNA with an AAA anticodon will bind to it. The ribosome links adjacent amino acids with a peptide bond, causing the amino a ...
... actually attach to the correct protein. The anticodon( tRNA) binds by complimentary base pairing to the nucleotides of the codon. Example: if the codon on a mRNA is UUU, a tRNA with an AAA anticodon will bind to it. The ribosome links adjacent amino acids with a peptide bond, causing the amino a ...
Lecture 21 Student Powerpoint
... a. M/G1, G1, S, G2, and M 3. Four different treatments used to synchronize cells a. All gave similar results 4. Results from Spellman et al., 1998; Cho et al., 1998 ...
... a. M/G1, G1, S, G2, and M 3. Four different treatments used to synchronize cells a. All gave similar results 4. Results from Spellman et al., 1998; Cho et al., 1998 ...
File
... • Takes place in the nucleus. • A specific gene of DNA is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase. • The instructions for making a protein are transferred from the nucleus to the ribosome. ...
... • Takes place in the nucleus. • A specific gene of DNA is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase. • The instructions for making a protein are transferred from the nucleus to the ribosome. ...
Chapter 17.
... determined mRNA–amino acid match added fabricated mRNA to test tube of ribosomes, tRNA & amino acids ...
... determined mRNA–amino acid match added fabricated mRNA to test tube of ribosomes, tRNA & amino acids ...
Taxonomy of Life • Three domains: Eukaryotes, Bacteria (Eubacteria
... sequences that control when the gene is expressed. Most (but not all) genes are contained on one chromosome. Other nonstandard arrangements are overlapping and interleaved genes. • An RNA gene is the region on the chromosome that codes for one ncRNA. • A gene that is expressed is being actively used ...
... sequences that control when the gene is expressed. Most (but not all) genes are contained on one chromosome. Other nonstandard arrangements are overlapping and interleaved genes. • An RNA gene is the region on the chromosome that codes for one ncRNA. • A gene that is expressed is being actively used ...
HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase
... The dsDNA bound to the RT (2HMI) has a hybrid structure. The five base-pairs near the polymerase active site have a conformation similar to A-form DNA, while the nine basepairs towards the RNase active site have a conformation similar to B-form DNA. There is a significant bend involving the four ba ...
... The dsDNA bound to the RT (2HMI) has a hybrid structure. The five base-pairs near the polymerase active site have a conformation similar to A-form DNA, while the nine basepairs towards the RNase active site have a conformation similar to B-form DNA. There is a significant bend involving the four ba ...
Document
... result in the production of unusual proteins as introns may still be present in some of the RNAs, and code for additional amino acids or aberrant terminations. c) Normally, a cell only exports mature or fully processed mRNA out of the nucleus. However, we learned in lecture that HIV can co-opt the c ...
... result in the production of unusual proteins as introns may still be present in some of the RNAs, and code for additional amino acids or aberrant terminations. c) Normally, a cell only exports mature or fully processed mRNA out of the nucleus. However, we learned in lecture that HIV can co-opt the c ...
Review Sheet : DNA, RNA & Protein Synthesis
... •Use the base pairing rules to correctly match the nitrogen bases together. ...
... •Use the base pairing rules to correctly match the nitrogen bases together. ...
Types of RNA: mRNA, rRNA and tRNA - Progetto e
... Types of RNA In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, there are three main types of RNA – messenger RNA or mRNA, ribosomal or rRNA, and transfer RNA or tRNA. These 3 types of RNA are discussed below. Messenger RNA (mRNA) mRNA accounts for just 5% of the total RNA in the cell. mRNA is the most heterogeneo ...
... Types of RNA In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, there are three main types of RNA – messenger RNA or mRNA, ribosomal or rRNA, and transfer RNA or tRNA. These 3 types of RNA are discussed below. Messenger RNA (mRNA) mRNA accounts for just 5% of the total RNA in the cell. mRNA is the most heterogeneo ...
Operon
... the lacZ gene is replaced with the gene of interest and IPTG is then used to induce gene expression. ...
... the lacZ gene is replaced with the gene of interest and IPTG is then used to induce gene expression. ...
Viruses (4)
... • General transcription factors – present in all transcription events • Attaches RNA polymerase to the promoter region • Target the TATA box • Specific Trans. Factors – activators and repressors specific to each cell type (ex. Liver and eye cells), bind to enhancer region on gene. ...
... • General transcription factors – present in all transcription events • Attaches RNA polymerase to the promoter region • Target the TATA box • Specific Trans. Factors – activators and repressors specific to each cell type (ex. Liver and eye cells), bind to enhancer region on gene. ...
Necessary Components for Translation
... • Bases may be inserted, deleted, or mismatched during replication. • Mutations: are permanent changes in DNA. • Any mistakes that cause changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. • Mutations may be either harmful, beneficial, or have no effect on a cell or individual. ...
... • Bases may be inserted, deleted, or mismatched during replication. • Mutations: are permanent changes in DNA. • Any mistakes that cause changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. • Mutations may be either harmful, beneficial, or have no effect on a cell or individual. ...
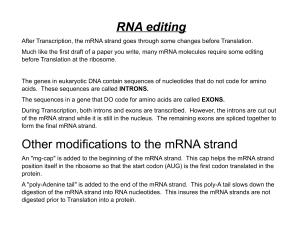
RNA editing Other modifications to the mRNA strand
... After Transcription, the mRNA strand goes through some changes before Translation. Much like the first draft of a paper you write, many mRNA molecules require some editing before Translation at the ribosome. The genes in eukaryotic DNA contain sequences of nucleotides that do not code for amino acid ...
... After Transcription, the mRNA strand goes through some changes before Translation. Much like the first draft of a paper you write, many mRNA molecules require some editing before Translation at the ribosome. The genes in eukaryotic DNA contain sequences of nucleotides that do not code for amino acid ...
Lab 1 Introduction to nucleic acids Structural Properties
... hydrogen bonding and base stacking within the single nucleic acid chain. These regions can form where one part of the RNA chain is complementary to another (RNA secondary structure). • Essential function is to interpret DNA code and direct protein synthesis. ...
... hydrogen bonding and base stacking within the single nucleic acid chain. These regions can form where one part of the RNA chain is complementary to another (RNA secondary structure). • Essential function is to interpret DNA code and direct protein synthesis. ...
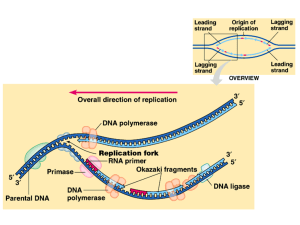
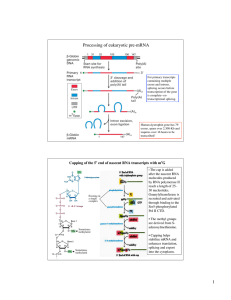
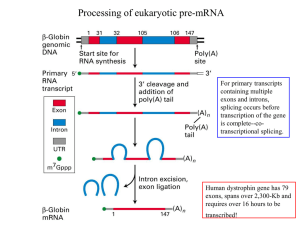
1 Processing of eukaryotic pre-mRNA
... intron. The bound U2AF also helps recruit U2 snRNP to the branch point. The resulting RNAprotein cross-exon recognition complex spans an exon and activates the correct splice sites for RNA splicing and this exon is retained in the final spliced mRNA. If U1 snRNP and/or U2AF are not recruited to the ...
... intron. The bound U2AF also helps recruit U2 snRNP to the branch point. The resulting RNAprotein cross-exon recognition complex spans an exon and activates the correct splice sites for RNA splicing and this exon is retained in the final spliced mRNA. If U1 snRNP and/or U2AF are not recruited to the ...
Powerpoint file - revised
... intron. The bound U2AF also helps recruit U2 snRNP to the branch point. The resulting RNAprotein cross-exon recognition complex spans an exon and activates the correct splice sites for RNA splicing and this exon is retained in the final spliced mRNA. If U1 snRNP and/or U2AF are not recruited to the ...
... intron. The bound U2AF also helps recruit U2 snRNP to the branch point. The resulting RNAprotein cross-exon recognition complex spans an exon and activates the correct splice sites for RNA splicing and this exon is retained in the final spliced mRNA. If U1 snRNP and/or U2AF are not recruited to the ...
Ch. 5A: Transforming Bacteria with Recombinant Plasmids
... The ampicillin plate is old (meaning that the antibiotic is partially degraded) The transformed cells are plated at very high density (meaning that the plate is covered with huge number of cells) The copy number of the plasmid in the cells is so high that beta lactamase is secreted at high ...
... The ampicillin plate is old (meaning that the antibiotic is partially degraded) The transformed cells are plated at very high density (meaning that the plate is covered with huge number of cells) The copy number of the plasmid in the cells is so high that beta lactamase is secreted at high ...
Slide 1
... The ampicillin plate is old (meaning that the antibiotic is partially degraded) The transformed cells are plated at very high density (meaning that the plate is covered with huge number of cells) The copy number of the plasmid in the cells is so high that beta lactamase is secreted at high ...
... The ampicillin plate is old (meaning that the antibiotic is partially degraded) The transformed cells are plated at very high density (meaning that the plate is covered with huge number of cells) The copy number of the plasmid in the cells is so high that beta lactamase is secreted at high ...
Chapt21 Lecture 13ed Pt 2
... 2b. Second stage of elongation. The ribosome has moved to the right and the tRNA polypeptide at the P site is now longer by one amino acid. One tRNA is outgoing and another tRNA is incoming. ...
... 2b. Second stage of elongation. The ribosome has moved to the right and the tRNA polypeptide at the P site is now longer by one amino acid. One tRNA is outgoing and another tRNA is incoming. ...