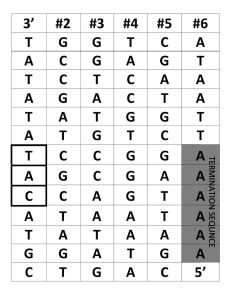
Wed 12-2 Computers Lab (40 points if all correct or 0 if not) Open up
... RNA is transcribed from DNA by enzymes called RNA polymerases and is generally further processed by other enzymes. RNA is central to protein synthesis. Here, a type of RNA called messenger RNA carries information from DNA to structures called ribosomes. These ribosomes are made from proteins and rib ...
... RNA is transcribed from DNA by enzymes called RNA polymerases and is generally further processed by other enzymes. RNA is central to protein synthesis. Here, a type of RNA called messenger RNA carries information from DNA to structures called ribosomes. These ribosomes are made from proteins and rib ...
No Slide Title
... 1) In Bacteria transcription and translation are initially coupled • RNA polymerase quits if ribosomes lag too much • Recent studies show that ribosomes continue translating once mRNA is complete; i.e after transcription is done ...
... 1) In Bacteria transcription and translation are initially coupled • RNA polymerase quits if ribosomes lag too much • Recent studies show that ribosomes continue translating once mRNA is complete; i.e after transcription is done ...
Transcription lesson
... RNA polymerase will continue along the DNA strand until a terminator sequence is encountered. After this, the RNA polymerase molecule separates from the DNA strand AND the new RNA molecule dissociates as well. the RNA is now called mRNA for messanger RNA ...
... RNA polymerase will continue along the DNA strand until a terminator sequence is encountered. After this, the RNA polymerase molecule separates from the DNA strand AND the new RNA molecule dissociates as well. the RNA is now called mRNA for messanger RNA ...
Student Activity PDF - TI Education
... DNA is the blueprint of life, but how does a long piece of DNA control the activity of a cell? DNA is transcribed into RNA, which can be translated into the proteins that drive the activity in a cell. This is the Central Dogma of biology: DNA RNA Protein In this lesson, you will explore transcri ...
... DNA is the blueprint of life, but how does a long piece of DNA control the activity of a cell? DNA is transcribed into RNA, which can be translated into the proteins that drive the activity in a cell. This is the Central Dogma of biology: DNA RNA Protein In this lesson, you will explore transcri ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • These are position- and orientationindependent DNA elements that stimulate or depress, respectively, transcription of associated genes • Are often tissue-specific in that they rely on tissue-specific DNA-binding proteins for their activities • Some DNA elements can act either as enhancer or silenc ...
... • These are position- and orientationindependent DNA elements that stimulate or depress, respectively, transcription of associated genes • Are often tissue-specific in that they rely on tissue-specific DNA-binding proteins for their activities • Some DNA elements can act either as enhancer or silenc ...
Transcriptional regulatory network underlying connective tissue
... mesenchymal explant cultures overexpressing each of the transcription factors. Wholetranscriptome sequencing revealed that the transcription factors share common regulatory functions and positively regulate biological processes related to signal transduction, cell communication and biological adhesi ...
... mesenchymal explant cultures overexpressing each of the transcription factors. Wholetranscriptome sequencing revealed that the transcription factors share common regulatory functions and positively regulate biological processes related to signal transduction, cell communication and biological adhesi ...
Chapter 14
... • Results when DNA regions (called transposable elements) move form one location to another in the same DNA molecule of different one ...
... • Results when DNA regions (called transposable elements) move form one location to another in the same DNA molecule of different one ...
Welcome to Our Microbial Genetics Class
... Global regulatory systems are so complex that a specialized nomenclature is used to describe the various kinds. Perhaps the most basic type is the regulon. A regulon is a collection of genes or operons that is controlled by a common regulatory protein. Usually the operons are associated with a sing ...
... Global regulatory systems are so complex that a specialized nomenclature is used to describe the various kinds. Perhaps the most basic type is the regulon. A regulon is a collection of genes or operons that is controlled by a common regulatory protein. Usually the operons are associated with a sing ...
Central Dogma of Biology - Marengo Community Middle School
... Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein: an overview • Genes provide the instructions for making specific proteins. • The bridge between DNA and protein synthesis is RNA. • RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and sub ...
... Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein: an overview • Genes provide the instructions for making specific proteins. • The bridge between DNA and protein synthesis is RNA. • RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and sub ...
Supporting Information S1: 1. Establishment of hSMP30 transcription
... cooled to room temp and was reverse transcribed at 42ºC for 1hour using primer extension system (Promega, USA) according to manufacturer’s instruction. The same primer was used for the sequencing reactions of cloned SMP30 promoter containing exon 1. Sequencing reactions and primer extension product ...
... cooled to room temp and was reverse transcribed at 42ºC for 1hour using primer extension system (Promega, USA) according to manufacturer’s instruction. The same primer was used for the sequencing reactions of cloned SMP30 promoter containing exon 1. Sequencing reactions and primer extension product ...
Transcription
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation | Principles of Biology from Nature
... multiple genes. How does it go about orchestrating this complex process? Regulation of gene expression involves many different mechanisms. In prokaryotes, regulatory mechanisms are generally simpler than those found in eukaryotes. Prokaryotic regulation is often dependent on the type and quantity of ...
... multiple genes. How does it go about orchestrating this complex process? Regulation of gene expression involves many different mechanisms. In prokaryotes, regulatory mechanisms are generally simpler than those found in eukaryotes. Prokaryotic regulation is often dependent on the type and quantity of ...
TUTORIAL FIGURES: Basic Molecular Biology
... Figure 5: RNA processing. The DNA segment corresponding to a gene (top) consists of coding regions called exons and these regions are interrupted with intervening non-coding regions called introns (blue). During transcription the whole segment of DNA corresponding to the gene is copied to RNA. An RN ...
... Figure 5: RNA processing. The DNA segment corresponding to a gene (top) consists of coding regions called exons and these regions are interrupted with intervening non-coding regions called introns (blue). During transcription the whole segment of DNA corresponding to the gene is copied to RNA. An RN ...
Transcription in Bacteria
... During initial transcription, RNA polymerase produces and releases short RNA transcripts of less then ten ribonucleotides (abortive synthesis) before escaping the promoter (promotor clearance). It is not clear why RNA polymerase must undergo this period of abortive initiation before achieving escape ...
... During initial transcription, RNA polymerase produces and releases short RNA transcripts of less then ten ribonucleotides (abortive synthesis) before escaping the promoter (promotor clearance). It is not clear why RNA polymerase must undergo this period of abortive initiation before achieving escape ...
Chapter 9 Expressing Genetic Information Learning Targets
... What does the structure determine. 9.3 RNA Synthesis I can describe RNA Polymerase What happens during transcription Where transcription takes place How do the RNA nucleotides pair with DNA The three stages of transcription 9.4 RNA Processing I can describe Eukaryotes vs Prokaryotes ...
... What does the structure determine. 9.3 RNA Synthesis I can describe RNA Polymerase What happens during transcription Where transcription takes place How do the RNA nucleotides pair with DNA The three stages of transcription 9.4 RNA Processing I can describe Eukaryotes vs Prokaryotes ...
Slide 1
... the start of the target genes. 3. DNA Polymerase replicates the DNA using complementary base pairing. 4. This cycle is repeated many times, until there are thousands of copies – enough to amplify even tiny samples found at a crime scene! ...
... the start of the target genes. 3. DNA Polymerase replicates the DNA using complementary base pairing. 4. This cycle is repeated many times, until there are thousands of copies – enough to amplify even tiny samples found at a crime scene! ...
Slide 1
... LTR-retroelements can contribute to tissue-specific splicing variants Positions of LTR-retroelements present in Wx gene in different ...
... LTR-retroelements can contribute to tissue-specific splicing variants Positions of LTR-retroelements present in Wx gene in different ...
Slides
... Quantitatively characterize interactions of network elements; Predict the function of genes in biological networks. ...
... Quantitatively characterize interactions of network elements; Predict the function of genes in biological networks. ...
Introduction to Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology II Losiana
... has passed into protein it cannot get out again. The transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein, may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid, is impossible. Information means here the precise determination of ...
... has passed into protein it cannot get out again. The transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein, may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid, is impossible. Information means here the precise determination of ...
Lecture 2
... 5.4 Catabolite repression A diauxic growth curve results when two sugars are present –e.g. Glucose is used first followed by other sugars such as lactose or xylose. Glucose has been shown to block the expression of a number of operons controlling the catabolism of particular sugars such as lact ...
... 5.4 Catabolite repression A diauxic growth curve results when two sugars are present –e.g. Glucose is used first followed by other sugars such as lactose or xylose. Glucose has been shown to block the expression of a number of operons controlling the catabolism of particular sugars such as lact ...
Reverse Transcription - St. Michael`s Hospital
... activities: as a RNA‐dependent DNA polymerase, a DNA‐dependent DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H. Many commercially available kits, such as Super Script® III (Invitrogen/Life Technologies) have specifically engineered enzymes that possess reduced RNase H activity and provide increased thermal sta ...
... activities: as a RNA‐dependent DNA polymerase, a DNA‐dependent DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H. Many commercially available kits, such as Super Script® III (Invitrogen/Life Technologies) have specifically engineered enzymes that possess reduced RNase H activity and provide increased thermal sta ...
notes for mondays lab
... cellular proteins by splitting them into smaller peptides and amino acids 3. Buffer AL: a cell lysis solution that breaks open cell and nuclear membranes 4. Ethanol: used to precipitate DNA from the extracted material 5. Buffer AW1 and AW2: solutions that wash the DNA attached in the column membrane ...
... cellular proteins by splitting them into smaller peptides and amino acids 3. Buffer AL: a cell lysis solution that breaks open cell and nuclear membranes 4. Ethanol: used to precipitate DNA from the extracted material 5. Buffer AW1 and AW2: solutions that wash the DNA attached in the column membrane ...
슬라이드 1
... ▶ WRKY (pronounced‘worky’) proteins, a large family of transcriptional regulators that has to date only been found in plants. ▶ The WRKY domain is defined by the conserved amino acidsequence WRKYGQK at its N-terminal end, together with a novel zinc-finger-like motif ▶ Many WRKY proteins having a reg ...
... ▶ WRKY (pronounced‘worky’) proteins, a large family of transcriptional regulators that has to date only been found in plants. ▶ The WRKY domain is defined by the conserved amino acidsequence WRKYGQK at its N-terminal end, together with a novel zinc-finger-like motif ▶ Many WRKY proteins having a reg ...