Dynamics of the trp Operon
... * Cluster of genes controlled by a single (?) feedback regulatory mechanism. ...
... * Cluster of genes controlled by a single (?) feedback regulatory mechanism. ...
Rabbit anti-Estrogen Receptor-β
... Estrogen receptor (ER) is a member of the steroid-receptor family. Unlike protein growth factors that bind to receptors on the cell surface and activate signal-transduction cascades to influence gene expression, the steroid hormones bind to intracellular receptors, which then bind to DNA and regulat ...
... Estrogen receptor (ER) is a member of the steroid-receptor family. Unlike protein growth factors that bind to receptors on the cell surface and activate signal-transduction cascades to influence gene expression, the steroid hormones bind to intracellular receptors, which then bind to DNA and regulat ...
DNA, RNA, Protein Synthesis
... tRNA molecules • Each tRNA molecule has an anticodon that is complementary to a codon on mRNA coding for a certain amino acid (so most amino acids have more than one tRNA that will code for them) • The tRNA will then retrieve that amino acid and bring it to the ribosome for protein assembly ...
... tRNA molecules • Each tRNA molecule has an anticodon that is complementary to a codon on mRNA coding for a certain amino acid (so most amino acids have more than one tRNA that will code for them) • The tRNA will then retrieve that amino acid and bring it to the ribosome for protein assembly ...
[Business Communication]
... message to specify • Not all DNA is expressed as proteins or structural RNA ...
... message to specify • Not all DNA is expressed as proteins or structural RNA ...
From Gene to Protein
... codon on mRNA, the A site of the the bond between the tRNA in and the other components of ribosome accepts a protein called the P site and the last amino the assembly dissociate. a release factor instead of tRNA. acid of the polypeptide chain. The polypeptide is thus freed from the ribosome. Figure ...
... codon on mRNA, the A site of the the bond between the tRNA in and the other components of ribosome accepts a protein called the P site and the last amino the assembly dissociate. a release factor instead of tRNA. acid of the polypeptide chain. The polypeptide is thus freed from the ribosome. Figure ...
DNA Structure and Sequencing - SP14
... The size of the genome in one of the most well-studied prokaryotes, E.coli, is 4.6 million base pairs (approximately 1.1 mm, if cut and stretched out). So how does this t inside a small bacterial cell? The DNA is twisted by what is known as supercoiling. Supercoiling means that DNA is either under- ...
... The size of the genome in one of the most well-studied prokaryotes, E.coli, is 4.6 million base pairs (approximately 1.1 mm, if cut and stretched out). So how does this t inside a small bacterial cell? The DNA is twisted by what is known as supercoiling. Supercoiling means that DNA is either under- ...
I. GENETIC APPARATUS OF HUMAN CELL – SUPPORT OF
... extend over hundreds of kilobases (kb). Individual regions of genes are defined by specific sequence features. One of the most prominent features of human genes is the presence of distinct segments, some of them responsible for protein-coding information (exons) and others separating such coding seq ...
... extend over hundreds of kilobases (kb). Individual regions of genes are defined by specific sequence features. One of the most prominent features of human genes is the presence of distinct segments, some of them responsible for protein-coding information (exons) and others separating such coding seq ...
Exam 2
... shown that chi structures generally have two pairs of equal length arms (as shown below). Explain why chi structures exhibit this particular symmetry. Homologous recombination is an exchange of DNA between similar or identical molecules of DNA, such as homologous chromosomes. This symmetry arises be ...
... shown that chi structures generally have two pairs of equal length arms (as shown below). Explain why chi structures exhibit this particular symmetry. Homologous recombination is an exchange of DNA between similar or identical molecules of DNA, such as homologous chromosomes. This symmetry arises be ...
What is a Genome? - Mainlab Bioinformatics
... • Refresh your knowledge of basic genomic concepts and terminology • Understand conceptually the different areas of genomic research • Know the basic tools of genomics ...
... • Refresh your knowledge of basic genomic concepts and terminology • Understand conceptually the different areas of genomic research • Know the basic tools of genomics ...
DNA Replication
... empty. In this step, the second amino acid (AA2), carried to the ribosome by a specific tRNA (as an AA2 – tRNA complex) and specified by the next codon of the mRNA, binds to the A site. b) Peptide bond formation. In this step the amino acid fMet dissociates from the fMettRNA complex and forms a pept ...
... empty. In this step, the second amino acid (AA2), carried to the ribosome by a specific tRNA (as an AA2 – tRNA complex) and specified by the next codon of the mRNA, binds to the A site. b) Peptide bond formation. In this step the amino acid fMet dissociates from the fMettRNA complex and forms a pept ...
How are animal proteins made from DNA?
... • A part of the DNA double helix within the nucleus is ________, cut by _______, and then copied onto a new ______ ______, called mRNA. This process is called ___________.” • Once the DNA is transcribed, the single strand moves from the ______ to a ________ in the __________ of the cell. Thus the na ...
... • A part of the DNA double helix within the nucleus is ________, cut by _______, and then copied onto a new ______ ______, called mRNA. This process is called ___________.” • Once the DNA is transcribed, the single strand moves from the ______ to a ________ in the __________ of the cell. Thus the na ...
Ab_initio_predition_tools - Compgenomics2010
... of RBS score ,IMM coding potentials and a score for start codons which is dependent on relative frequency of each possible start codon in the same training set used for RBS determination. • Algorithm used reverse scoring of IMM by scoring all ORF (open reading frames) in reverse ,from the stop codon ...
... of RBS score ,IMM coding potentials and a score for start codons which is dependent on relative frequency of each possible start codon in the same training set used for RBS determination. • Algorithm used reverse scoring of IMM by scoring all ORF (open reading frames) in reverse ,from the stop codon ...
Irreducible complexity: some candid admissions by evolutionists
... researching other topics). For this reason, no inferences should be drawn regarding the extent of irreducible complexity based on this short report. The traditional conception of step-by-step major evolutionary change has the supposed advantage of reasonable probability for each step while suffering ...
... researching other topics). For this reason, no inferences should be drawn regarding the extent of irreducible complexity based on this short report. The traditional conception of step-by-step major evolutionary change has the supposed advantage of reasonable probability for each step while suffering ...
Lecture 9 RNA world and emegence of complexity
... Atoms go in, change, and go out. This process is essential for the survival to the phenomenon. The overall phenomenon is constant (i.e. there is a flame) for as long there is food (oxygen, fuel …). There even can be replication (one fire can light another fire). ...
... Atoms go in, change, and go out. This process is essential for the survival to the phenomenon. The overall phenomenon is constant (i.e. there is a flame) for as long there is food (oxygen, fuel …). There even can be replication (one fire can light another fire). ...
pdf
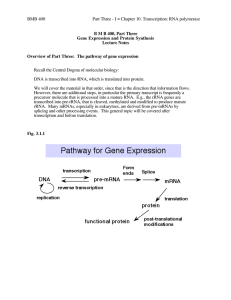
... of transcription. They are required for RNA polymerase to bind avidly and specifically to normal sites for transcription initiation, thereby generating specific transcripts of genes (see Fig. 3.1.14). Other transcription factors are needed for elongation. In living cells, RNA polymerases usually sta ...
... of transcription. They are required for RNA polymerase to bind avidly and specifically to normal sites for transcription initiation, thereby generating specific transcripts of genes (see Fig. 3.1.14). Other transcription factors are needed for elongation. In living cells, RNA polymerases usually sta ...
Non-coding RNAs - Structural Biology Labs
... • Of all RNA, transcribed in higher eukaryotes, 98% are never translated into proteins • Of those 98%, about 50-70% are introns • The rest originate from non-protein genes, including rRNA, tRNA and a vast number of other non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) • Even introns have been shown to contain ncRNAs, for ...
... • Of all RNA, transcribed in higher eukaryotes, 98% are never translated into proteins • Of those 98%, about 50-70% are introns • The rest originate from non-protein genes, including rRNA, tRNA and a vast number of other non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) • Even introns have been shown to contain ncRNAs, for ...
Activity
... In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequences in the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the mRNA carries this information in the form of a code to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis ta ...
... In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequences in the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the mRNA carries this information in the form of a code to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis ta ...
Gene Movement
... 1. Plasmid biology: plasmids are extrachromosomal elements that can replicate independently of the host cell chromosome (generally do not contain any essential genes for the host cell’s survival) plasmids are distinguished from one another in several ways, noted below. -size: from 1 to >100 kb ...
... 1. Plasmid biology: plasmids are extrachromosomal elements that can replicate independently of the host cell chromosome (generally do not contain any essential genes for the host cell’s survival) plasmids are distinguished from one another in several ways, noted below. -size: from 1 to >100 kb ...
Slide 1
... 1) the majority of DNA in the human genome is transcribed into functional molecules RNA, and that these transcripts extensively overlap one another. This broad pattern of transcription challenges the long-standing view that the human genome consists of a relatively small set of discrete genes, along ...
... 1) the majority of DNA in the human genome is transcribed into functional molecules RNA, and that these transcripts extensively overlap one another. This broad pattern of transcription challenges the long-standing view that the human genome consists of a relatively small set of discrete genes, along ...
review: cloning in plasmid vectors
... known as regulated. The basic expression vector contains a replication origin (Ori), a selectable antibiotic-resistance gene, and a strong-regulated promoter. This section uses the lac operon to discuss the means by which the operon regulates and induces the promoter. (2) The lac operon consists of ...
... known as regulated. The basic expression vector contains a replication origin (Ori), a selectable antibiotic-resistance gene, and a strong-regulated promoter. This section uses the lac operon to discuss the means by which the operon regulates and induces the promoter. (2) The lac operon consists of ...
DNA RNA ppt
... •Without lactose, the lac repressor binds to the operator site. •With lactose, the repressor is removed •Once repressor is removed, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter •RNA is transcribed, which is then translated, and becomes the lactase ...
... •Without lactose, the lac repressor binds to the operator site. •With lactose, the repressor is removed •Once repressor is removed, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter •RNA is transcribed, which is then translated, and becomes the lactase ...


![[Business Communication]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013653307_1-657ec703938b15762101dfd9c3e1212f-300x300.png)