
Why Genetic Programming?
... • Early versions of EP applied to the evolution of transition table of finite state machines • One population of solutions, reproduction is by mutation only • Like ES operates on the decision variable of the problem directly (ie Genotype = Phenotype) • Tournament selection of parents – better fitnes ...
... • Early versions of EP applied to the evolution of transition table of finite state machines • One population of solutions, reproduction is by mutation only • Like ES operates on the decision variable of the problem directly (ie Genotype = Phenotype) • Tournament selection of parents – better fitnes ...
Sir R A Fisher and the Evolution of Genetics -RE-S-O-N-A-N-C-E--I
... show that the observed patterns of continuous variation were entirely consistent with Mendelian inheritance. He was also able to consider the effects on these traits of various other modifying factors like dominance, linkage and non-random mating. Moreover, he developed techniques for partitioning t ...
... show that the observed patterns of continuous variation were entirely consistent with Mendelian inheritance. He was also able to consider the effects on these traits of various other modifying factors like dominance, linkage and non-random mating. Moreover, he developed techniques for partitioning t ...
Biology Chapter 10 Review
... 1. Explain why the blending hypothesis was eventually rejected as the method of inheritance? 2. Define trait, loci, gene, allele. 3. Describe Mendel’s particulate hypothesis of inheritance. 4. What does it mean to be true-breeding? 5. What characteristics make pea plants ideal organisms for genetic ...
... 1. Explain why the blending hypothesis was eventually rejected as the method of inheritance? 2. Define trait, loci, gene, allele. 3. Describe Mendel’s particulate hypothesis of inheritance. 4. What does it mean to be true-breeding? 5. What characteristics make pea plants ideal organisms for genetic ...
SFR12_06 Jordan et al GR01.indd
... evolution, individuals became more likely to encounter strangers who were the kin or partners of their partners, but not directly known to them; that is, in-group strangers (Hill et al. 2011). At this point the interaction history with ego could no longer be relied on to estimate the reliability of ...
... evolution, individuals became more likely to encounter strangers who were the kin or partners of their partners, but not directly known to them; that is, in-group strangers (Hill et al. 2011). At this point the interaction history with ego could no longer be relied on to estimate the reliability of ...
Sexual Selection - Cathedral High School
... – just by chance some rare alleles may be at high frequency; others may be missing – skew the gene pool of new population • human populations that started from small group of colonists • example: ...
... – just by chance some rare alleles may be at high frequency; others may be missing – skew the gene pool of new population • human populations that started from small group of colonists • example: ...
Behavioral Adaptations for Survival 1
... • 1) spread in the past because of natural selection and has been maintained by selection to the present…OR… • 2) is currently spreading relative to alternative traits because of natural selection ...
... • 1) spread in the past because of natural selection and has been maintained by selection to the present…OR… • 2) is currently spreading relative to alternative traits because of natural selection ...
Evolution of sElflEss bEhaviour
... the sharp teeth of the tiger, the thick fur of the polar bear and the camouflage of the moth evolved. When the ancestors of polar bears colonised the Arctic, for instance, those with thicker fur would have had a better chance of surviving and producing more offspring than those with thinner fur. Man ...
... the sharp teeth of the tiger, the thick fur of the polar bear and the camouflage of the moth evolved. When the ancestors of polar bears colonised the Arctic, for instance, those with thicker fur would have had a better chance of surviving and producing more offspring than those with thinner fur. Man ...
Natural Selection
... • Natural selection only leads to adaptive evolution. – Better fit between organisms and environment. ...
... • Natural selection only leads to adaptive evolution. – Better fit between organisms and environment. ...
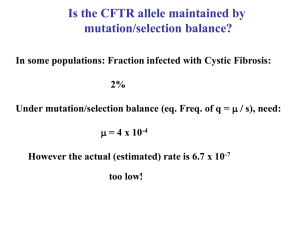
Is the CFTR allele maintained by mutation/selection balance?
... are determined by the same evolutionary process. ...
... are determined by the same evolutionary process. ...
Adaptive evolution without natural selection
... also to behave in the ways that do not meet the needs, it should be possible to make errors. In this case we can say that organic selection – or rather, organic choice made by organisms – is inevitable. Where a population of organisms is facing a shared change of conditions, all organisms in the pop ...
... also to behave in the ways that do not meet the needs, it should be possible to make errors. In this case we can say that organic selection – or rather, organic choice made by organisms – is inevitable. Where a population of organisms is facing a shared change of conditions, all organisms in the pop ...
1. What is Anthropology
... open mouth grin: This is where the mouth is open, the corners of the mouth are drawn back, and the teeth are showing. This display is shown when an individual is threatened by a more dominant individual that it fears pout face: This is where the eyes are opened and the lips are pushed forward ma ...
... open mouth grin: This is where the mouth is open, the corners of the mouth are drawn back, and the teeth are showing. This display is shown when an individual is threatened by a more dominant individual that it fears pout face: This is where the eyes are opened and the lips are pushed forward ma ...
Chapter 23: The Evolution of Populations Populations & Gene Pools
... If the gene pool is to change over time there must be genetic variation: • genetic variation refers to the variety of alleles for a given gene that exist in the population • genetic variation underlies phenotypic variation, and phenotypic variation is what Natural Selection actually acts upon in sel ...
... If the gene pool is to change over time there must be genetic variation: • genetic variation refers to the variety of alleles for a given gene that exist in the population • genetic variation underlies phenotypic variation, and phenotypic variation is what Natural Selection actually acts upon in sel ...
122 [Study Guide] 23-3 How Evolution Occurs
... This allele has a frequency of 0% in laboratory strains of Drosophila collected in the 1930s, before DDT was used. ...
... This allele has a frequency of 0% in laboratory strains of Drosophila collected in the 1930s, before DDT was used. ...
2.4.measuring evolution of populations
... 4. Which of the following is NOT a component of Darwin’s theory of natural selection? A. Mutations cause a significant amount of genetic variation B. Evolution is a slow process that occurs over a long period of time C. Variations among organisms are the basis by which organisms will or will not re ...
... 4. Which of the following is NOT a component of Darwin’s theory of natural selection? A. Mutations cause a significant amount of genetic variation B. Evolution is a slow process that occurs over a long period of time C. Variations among organisms are the basis by which organisms will or will not re ...
Mechanisms for Evolution
... who are more fit for their environment survive and reproduce more often ...
... who are more fit for their environment survive and reproduce more often ...
ppt
... genotypic change, it is important to understand intraspecific variation Note: If all individuals were phenotypically identical, there would be no opportunity for selection Note: If all individuals were genotypically identical, there would be no opportunity for evolution ...
... genotypic change, it is important to understand intraspecific variation Note: If all individuals were phenotypically identical, there would be no opportunity for selection Note: If all individuals were genotypically identical, there would be no opportunity for evolution ...
Nov 28 - Dec 2
... Performance Indicator: H.B.4.C.2 SEP: Analyze data Content: on the variation of traits among individual organisms within a population to explain patterns in the data in the context of transmission of genetic information. ...
... Performance Indicator: H.B.4.C.2 SEP: Analyze data Content: on the variation of traits among individual organisms within a population to explain patterns in the data in the context of transmission of genetic information. ...













![122 [Study Guide] 23-3 How Evolution Occurs](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001074020_1-358b9d8f022104c7e366974b91b777d2-300x300.png)








