Ch. 23 HW_Populations
... # of A and a alleles. 2. If you know phenotypes, then use “aa” to find q2, and then q. (p = 1-q) 3. To find out if population is evolving, calculate p2 + 2pq + q2. If in equilibrium, it should = 1. If it DOES NOT = 1, then the population is evolving! ...
... # of A and a alleles. 2. If you know phenotypes, then use “aa” to find q2, and then q. (p = 1-q) 3. To find out if population is evolving, calculate p2 + 2pq + q2. If in equilibrium, it should = 1. If it DOES NOT = 1, then the population is evolving! ...
7.1 Solutions File
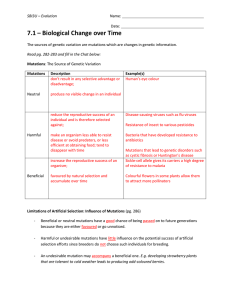
... The sources of genetic variation are mutations which are changes in genetic information. Read pg. 282-283 and fill in the Chat below: Mutations: The Source of Genetic Variation Mutations ...
... The sources of genetic variation are mutations which are changes in genetic information. Read pg. 282-283 and fill in the Chat below: Mutations: The Source of Genetic Variation Mutations ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... c. Mutations occur at such a high rate that they promote major changes in the gene pool from one generation to the next. d. Mutations are insignificant when considering evolution of a large population. e. Mutations are of greater importance in larger populations than in smaller populations. Answer: ...
... c. Mutations occur at such a high rate that they promote major changes in the gene pool from one generation to the next. d. Mutations are insignificant when considering evolution of a large population. e. Mutations are of greater importance in larger populations than in smaller populations. Answer: ...
C) Geographic Isolation
... • 5. The genes carried by all members of a particular population make up that population’s _____________ ___________. ...
... • 5. The genes carried by all members of a particular population make up that population’s _____________ ___________. ...
Genetic Algorithms
... In nature the evolution of species is a successful and robust method for ensuring that biological systems survive in their environment It can be seen as a search problem, in which the survival of solutions is determined by a form of natural selection ...
... In nature the evolution of species is a successful and robust method for ensuring that biological systems survive in their environment It can be seen as a search problem, in which the survival of solutions is determined by a form of natural selection ...
LG and SC 2017 10 genetics
... SC21 I can explain the following: evolution, natural selection, species, variation, isolation, biodiversity SC22 I can explain the processes involved in natural selection including variation, isolation, adaptation and selection. SC23 I can recognise that biodiversity is a result of evolutionary proc ...
... SC21 I can explain the following: evolution, natural selection, species, variation, isolation, biodiversity SC22 I can explain the processes involved in natural selection including variation, isolation, adaptation and selection. SC23 I can recognise that biodiversity is a result of evolutionary proc ...
STAAR REVIEW—GENETICS, NATURAL SELECTION
... Dominant: Alleles in which the traits always show up—They mask other traits; Represented with a capital letter (ex: T=hitchhikers thumb) Recessive: Alleles in which the traits are masked by dominant alleles—They only show up if paired with another recessive allele (ex: t=regular thumb) Homozyg ...
... Dominant: Alleles in which the traits always show up—They mask other traits; Represented with a capital letter (ex: T=hitchhikers thumb) Recessive: Alleles in which the traits are masked by dominant alleles—They only show up if paired with another recessive allele (ex: t=regular thumb) Homozyg ...
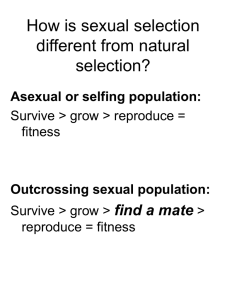
Sexual selection
... more exaggerated, even if the trait has no adaptive value, and the correlated female preference also ...
... more exaggerated, even if the trait has no adaptive value, and the correlated female preference also ...
Natural Selection and Culture - Department of Environmental
... We define culture as informationac- acquire culturaltraits, use the acquired disciplines to reconsider the consequences of inheritanceof acquiredvaria- quiredby imitatingor learningfrom oth- informationto guide behavior,andact as tion. Social scientists (Campbell 1965, er individualsand able to affe ...
... We define culture as informationac- acquire culturaltraits, use the acquired disciplines to reconsider the consequences of inheritanceof acquiredvaria- quiredby imitatingor learningfrom oth- informationto guide behavior,andact as tion. Social scientists (Campbell 1965, er individualsand able to affe ...
Lecture 12 notes
... Co‐opting structures from one function to another is known as exaptation (don’t need a new structure to arise, can simply modify an existing one) Feathers are another example—their original purpose may not have been for flight, but rather for attracting mates or thermoregulation ‐‐new studies ha ...
... Co‐opting structures from one function to another is known as exaptation (don’t need a new structure to arise, can simply modify an existing one) Feathers are another example—their original purpose may not have been for flight, but rather for attracting mates or thermoregulation ‐‐new studies ha ...
The Evolution of Populations
... • Often many compromises ex: human knee is amazing in function, but often weak in structure ...
... • Often many compromises ex: human knee is amazing in function, but often weak in structure ...
Evolution Lecture Part 2
... • 2. Evolution is limited by historical constraints (bats, birds from walking) • 3. Adaptations are often compromises • 4. Chance, natural (founders effect does not ensure fit alleles in new pop) selection,and the environment interact ...
... • 2. Evolution is limited by historical constraints (bats, birds from walking) • 3. Adaptations are often compromises • 4. Chance, natural (founders effect does not ensure fit alleles in new pop) selection,and the environment interact ...
Evolution for Bio. I Powerpoint
... Modern Interpretation – DNA mutations and genetic recombination through meiosis and fertilization cause variations within populations ...
... Modern Interpretation – DNA mutations and genetic recombination through meiosis and fertilization cause variations within populations ...
Unit3Day6
... (bone cracking is difficult; competition is intense) Selection may favor aggressive mothers ...
... (bone cracking is difficult; competition is intense) Selection may favor aggressive mothers ...
Microevolution PPT
... • Bottleneck effect – The change in allele frequency in a population due to chance following a sharp reduction in the population size. • Founder effect – When a small portion of a population migrates to another area, starting a new population. ...
... • Bottleneck effect – The change in allele frequency in a population due to chance following a sharp reduction in the population size. • Founder effect – When a small portion of a population migrates to another area, starting a new population. ...
COURSE LAYOUT GENERAL SCHOOL FOOD, BIOTECHNOLOGY
... Be able to comprehend the mechanisms of Evolution in phenotypic and molecular level and classify the species according to their phenotypic and molecular homology. ...
... Be able to comprehend the mechanisms of Evolution in phenotypic and molecular level and classify the species according to their phenotypic and molecular homology. ...
Answer Key Chapter 13
... 12. A population of bacteria contains no members with resistance to penicillin. Several generations pass with the bacteria reproducing. A researcher adds penicillin to the population of bacteria and discovers a few bacteria remain after the application of the antibiotic. Assume no new bacteria wer ...
... 12. A population of bacteria contains no members with resistance to penicillin. Several generations pass with the bacteria reproducing. A researcher adds penicillin to the population of bacteria and discovers a few bacteria remain after the application of the antibiotic. Assume no new bacteria wer ...
Bio101 Midterm II Study Guide 10/25/10
... Where does Meiosis fit in? How does genetics play a role in fitness? Do all organisms born have the same likelihood of survival? Is the survival of an individual likely to be based upon its traits? What is the gene pool? How does it relate to evolution? Other than Natural Selection, what processes c ...
... Where does Meiosis fit in? How does genetics play a role in fitness? Do all organisms born have the same likelihood of survival? Is the survival of an individual likely to be based upon its traits? What is the gene pool? How does it relate to evolution? Other than Natural Selection, what processes c ...
Chapter 9 Maintenance of Genetic Diversity
... diversity differs between large and small populations. Selection has a major impact in large populations. However, its impacts are greatly reduced in small populations where genetic drift has an increasingly important role. ...
... diversity differs between large and small populations. Selection has a major impact in large populations. However, its impacts are greatly reduced in small populations where genetic drift has an increasingly important role. ...
Group selection

Group selection is a proposed mechanism of evolution in which natural selection is imagined to act at the level of the group, instead of at the more conventional level of the individual.Early authors such as V. C. Wynne-Edwards and Konrad Lorenz argued that the behavior of animals could affect their survival and reproduction as groups.From the mid 1960s, evolutionary biologists such as John Maynard Smith argued that natural selection acted primarily at the level of the individual. They argued on the basis of mathematical models that individuals would not altruistically sacrifice fitness for the sake of a group. They persuaded the majority of biologists that group selection did not occur, other than in special situations such as the haplodiploid social insects like honeybees (in the Hymenoptera), where kin selection was possible.In 1994 David Sloan Wilson and Elliott Sober argued for multi-level selection, including group selection, on the grounds that groups, like individuals, could compete. In 2010 three authors including E. O. Wilson, known for his work on ants, again revisited the arguments for group selection, provoking a strong rebuttal from a large group of evolutionary biologists. As of yet, there is no clear consensus among biologists regarding the importance of group selection.