Conflict & cooperation
... Sterile workers in social insects: give up all reproduction for the benefit of their mother queen. How can such behaviour be selected? ...
... Sterile workers in social insects: give up all reproduction for the benefit of their mother queen. How can such behaviour be selected? ...
Teacher Guide
... This lesson takes a step away from programming and returns to using simulation as a teaching tool. Though the students touched on the importance of chance events in the previous lesson when talking about small populations, this activity should bring the role of random events in population dynamics i ...
... This lesson takes a step away from programming and returns to using simulation as a teaching tool. Though the students touched on the importance of chance events in the previous lesson when talking about small populations, this activity should bring the role of random events in population dynamics i ...
Dracula and Darwin" session from the FEAR course
... The medium? (writing, the stage) Modes and periods? ...
... The medium? (writing, the stage) Modes and periods? ...
Natural selection on the molecular level
... Genetic drift is a random process, but its rate is equal over long time ...
... Genetic drift is a random process, but its rate is equal over long time ...
What causes Evolution?
... variation, this produces homozygous recessives at many loci in your offspring 3. If a significant proportion of mutations are deleterious, these will be expressed... A greater proportion of your offspring will have lower fitness than offspring from outcrosses-> Inbreeding Depression ...
... variation, this produces homozygous recessives at many loci in your offspring 3. If a significant proportion of mutations are deleterious, these will be expressed... A greater proportion of your offspring will have lower fitness than offspring from outcrosses-> Inbreeding Depression ...
What drives evolution?
... because it is not observable or testable. Misconception: Most scientists no longer believe Darwin's ...
... because it is not observable or testable. Misconception: Most scientists no longer believe Darwin's ...
Population Genetics
... malaria agent to medications are examples of directional selection. c. The gradual increase in the size of the modern horse, Equus, correlates with a change in the environment from forest-like conditions to grassland conditions. 2. Stabilizing selection occurs when extreme phenotypes are eliminated ...
... malaria agent to medications are examples of directional selection. c. The gradual increase in the size of the modern horse, Equus, correlates with a change in the environment from forest-like conditions to grassland conditions. 2. Stabilizing selection occurs when extreme phenotypes are eliminated ...
HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE NSPIRED - Education TI
... Students sometimes get confused about the idea of “survival of the fittest.” If there is not an objective difference between the probabilities that two animals will survive to reproduce, then we don’t see natural selection. This simulation should remind students that many mutations don’t make a diff ...
... Students sometimes get confused about the idea of “survival of the fittest.” If there is not an objective difference between the probabilities that two animals will survive to reproduce, then we don’t see natural selection. This simulation should remind students that many mutations don’t make a diff ...
02 Microevolution Changing Allelic Frequencies
... – Chance in the context of mutations causing new genetic variations – Sorting in the context of natural selection favoring some alleles over others • This favoring process causes the outcome of natural selection to be anything but random! • Natural Selection consistently increases the frequencies of ...
... – Chance in the context of mutations causing new genetic variations – Sorting in the context of natural selection favoring some alleles over others • This favoring process causes the outcome of natural selection to be anything but random! • Natural Selection consistently increases the frequencies of ...
02 Microevolution Changing Allelic Frequencies [1]
... – Chance in the context of mutations causing new genetic variations – Sorting in the context of natural selection favoring some alleles over others • This favoring process causes the outcome of natural selection to be anything but random! • Natural Selection consistently increases the frequencies of ...
... – Chance in the context of mutations causing new genetic variations – Sorting in the context of natural selection favoring some alleles over others • This favoring process causes the outcome of natural selection to be anything but random! • Natural Selection consistently increases the frequencies of ...
EXAM 4-Fall2005con respuestas.doc
... 23) Strong evidence for the close relatedness of vertebrates is A) they all have legs. B) their means of reproduction. C) the similarity of their embryological stages. D) they all evolved from fish. E) they all possess DNA. Answer: C 24) The many different breeds of domestic dog were produced by A) ...
... 23) Strong evidence for the close relatedness of vertebrates is A) they all have legs. B) their means of reproduction. C) the similarity of their embryological stages. D) they all evolved from fish. E) they all possess DNA. Answer: C 24) The many different breeds of domestic dog were produced by A) ...
Adaptation and Evolution
... What happens? If we repeat this for many generations, we find that the system reaches equilibrium: a point at which allele frequencies no longer change. This is called Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. In other words, allele frequencies will not change unless something happens. ...
... What happens? If we repeat this for many generations, we find that the system reaches equilibrium: a point at which allele frequencies no longer change. This is called Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. In other words, allele frequencies will not change unless something happens. ...
Allele Frequencies: Changing
... Whenever one allele changes into another; introducing a new allele • We covered the causes of mutations already: – Spontaneous – Radiation, chemical or etc induced ...
... Whenever one allele changes into another; introducing a new allele • We covered the causes of mutations already: – Spontaneous – Radiation, chemical or etc induced ...
CH 23: The Evolution of Populations Terms: Population genetics: is
... 13. Distinguish between the bottleneck effect and the founder effect.:: FOUNDER EFFEFT: When a few individuals become isolated from a larger population whose gene pool differs from the source population. BOTTLENECK EFFECT: a sudden change in the environment, such as a fire or flood may drastically ...
... 13. Distinguish between the bottleneck effect and the founder effect.:: FOUNDER EFFEFT: When a few individuals become isolated from a larger population whose gene pool differs from the source population. BOTTLENECK EFFECT: a sudden change in the environment, such as a fire or flood may drastically ...
Allele Frequencies: Changing
... Whenever one allele changes into another; introducing a new allele • We covered the causes of mutations already: – Spontaneous – Radiation, chemical or etc induced ...
... Whenever one allele changes into another; introducing a new allele • We covered the causes of mutations already: – Spontaneous – Radiation, chemical or etc induced ...
Hardy-Weinberg Equation Notes
... WARM UP 1. Calculate the R and r frequency for the handedness trait in the human population, which is about 8% left-handed (the recessive trait). ...
... WARM UP 1. Calculate the R and r frequency for the handedness trait in the human population, which is about 8% left-handed (the recessive trait). ...
Important questions from the unit genetics and
... Answer: Convergent evolution When more than one adaptive radiation occurs in an isolated geographical area, the phenomenon is called convergent evolution. The best example for convergent evolution is the case of Australian marsupials. A number of marsupial animals evolved from a single stock but the ...
... Answer: Convergent evolution When more than one adaptive radiation occurs in an isolated geographical area, the phenomenon is called convergent evolution. The best example for convergent evolution is the case of Australian marsupials. A number of marsupial animals evolved from a single stock but the ...
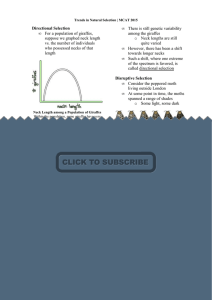
Directional Selection • For a population of giraffes, suppose we
... programmed to lay a given number of eggs might look like this: ...
... programmed to lay a given number of eggs might look like this: ...
Dvouúrovňová evoluční optimalizace regulátorů
... the gene and on its context. If a chromosome is crossed at random point, it is very probable that the context of the genes in second part will change. This way crossover causes destruction of the phenotype, because the newly added parts code different phenotype than in the original individual. This ...
... the gene and on its context. If a chromosome is crossed at random point, it is very probable that the context of the genes in second part will change. This way crossover causes destruction of the phenotype, because the newly added parts code different phenotype than in the original individual. This ...
Evolutionary Algorithms
... For the survivor selection after offspring creation, different possibilities arise for the selection source: – survivor selection only from the offspring P 0: P (t + 1) = select_population(µ, P 0, f ) (comma selection) – survivor selection from the offspring P 0 and the current generation P (t): P ( ...
... For the survivor selection after offspring creation, different possibilities arise for the selection source: – survivor selection only from the offspring P 0: P (t + 1) = select_population(µ, P 0, f ) (comma selection) – survivor selection from the offspring P 0 and the current generation P (t): P ( ...
We found evidence for rapid evolution in grassland species at both a
... Our results show selection for monoculture and mixture types ocurred. Plants with a selection history in mixtures performed better than plants with a selection history in monoculture A and showed higher between species variation B in newly assembled mixtures. ...
... Our results show selection for monoculture and mixture types ocurred. Plants with a selection history in mixtures performed better than plants with a selection history in monoculture A and showed higher between species variation B in newly assembled mixtures. ...
Group selection

Group selection is a proposed mechanism of evolution in which natural selection is imagined to act at the level of the group, instead of at the more conventional level of the individual.Early authors such as V. C. Wynne-Edwards and Konrad Lorenz argued that the behavior of animals could affect their survival and reproduction as groups.From the mid 1960s, evolutionary biologists such as John Maynard Smith argued that natural selection acted primarily at the level of the individual. They argued on the basis of mathematical models that individuals would not altruistically sacrifice fitness for the sake of a group. They persuaded the majority of biologists that group selection did not occur, other than in special situations such as the haplodiploid social insects like honeybees (in the Hymenoptera), where kin selection was possible.In 1994 David Sloan Wilson and Elliott Sober argued for multi-level selection, including group selection, on the grounds that groups, like individuals, could compete. In 2010 three authors including E. O. Wilson, known for his work on ants, again revisited the arguments for group selection, provoking a strong rebuttal from a large group of evolutionary biologists. As of yet, there is no clear consensus among biologists regarding the importance of group selection.








![02 Microevolution Changing Allelic Frequencies [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008308188_1-924385fb013df68d17fede3a117a87f4-300x300.png)