Darwin`s Explanation: Natural Selection
... • What did Darwin conclude from his observations? – life forms can & do change…. but, questioned how this change occurred… •“answers” pointed to evolution or “descent with modification” –needed to test ideas before explaining how or why such changes happen ...
... • What did Darwin conclude from his observations? – life forms can & do change…. but, questioned how this change occurred… •“answers” pointed to evolution or “descent with modification” –needed to test ideas before explaining how or why such changes happen ...
What is an Evolutionary Algorithm?
... • Chromosomes contain genes, which are in (usually fixed) positions called loci (sing. locus) and have a value (allele) In order to find the global optimum, every feasible solution must be represented in genotype space ...
... • Chromosomes contain genes, which are in (usually fixed) positions called loci (sing. locus) and have a value (allele) In order to find the global optimum, every feasible solution must be represented in genotype space ...
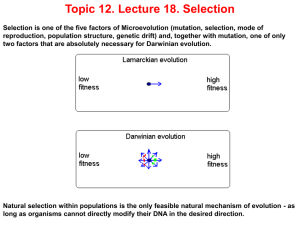
L18Selection
... Genetic load is the difference between w max and W, when fitness is measured in the units of wmax. Variance of relative fitness is the variance of f(w), when fitness is measured in the units of W. Of course, V[f(w/W)] is easier to measure than L - in the first case we need to compare fitnesses to th ...
... Genetic load is the difference between w max and W, when fitness is measured in the units of wmax. Variance of relative fitness is the variance of f(w), when fitness is measured in the units of W. Of course, V[f(w/W)] is easier to measure than L - in the first case we need to compare fitnesses to th ...
IB Biology Year 2 / IHS ALTERING ALLELE FREQUENCIES KEY
... Description and, if appropriate, names of different types ...
... Description and, if appropriate, names of different types ...
Answers - WordPress.com
... SECTION 1. GENETIC VARIATION WITHIN POPULATIONS 1. genetic variation 2. A wide range of phenotypes increases the likelihood that some individuals will have traits that allow them to survive in new environmental conditions. 3. gene pool 4. the combined alleles of all individuals in a population 5. al ...
... SECTION 1. GENETIC VARIATION WITHIN POPULATIONS 1. genetic variation 2. A wide range of phenotypes increases the likelihood that some individuals will have traits that allow them to survive in new environmental conditions. 3. gene pool 4. the combined alleles of all individuals in a population 5. al ...
Evolutionary Anthropology
... across cell membranes → thick and sticky mucus Heterozygotes are carriers, but do not have disease ...
... across cell membranes → thick and sticky mucus Heterozygotes are carriers, but do not have disease ...
Artificial Selection Algorithm - International Journal of Computer
... differential reproduction of organisms with certain traits is attributed to improved survival or reproductive ability. As opposed to artificial selection, in which humans favor specific traits, in natural selection the environment acts as a sieve ...
... differential reproduction of organisms with certain traits is attributed to improved survival or reproductive ability. As opposed to artificial selection, in which humans favor specific traits, in natural selection the environment acts as a sieve ...
Modes of selection: directional, balancing and disruptive RR Rr rr
... increasing the marginal fitness of each allele as it becomes rarer. There are two principal mechanisms: -- heterozygote advantage (with fixed genotypic fitnesses) -- negative frequency dependence (with varying genotypic fitnesses) Disruptive selection favors fixation, like directional selection, but ...
... increasing the marginal fitness of each allele as it becomes rarer. There are two principal mechanisms: -- heterozygote advantage (with fixed genotypic fitnesses) -- negative frequency dependence (with varying genotypic fitnesses) Disruptive selection favors fixation, like directional selection, but ...
Biological Altruism
... sufficiently closed related relatives. The proof of Hamilton's rule relies on certain non-trivial assumptions; see Frank (1998), Grafen (1985) or Michod (1982) for details. Though Hamilton himself did not use the term, his idea quickly became known as ‘kin selection’, for obvious reasons. Kin select ...
... sufficiently closed related relatives. The proof of Hamilton's rule relies on certain non-trivial assumptions; see Frank (1998), Grafen (1985) or Michod (1982) for details. Though Hamilton himself did not use the term, his idea quickly became known as ‘kin selection’, for obvious reasons. Kin select ...
Multifactorial Traits - An-Najah National University
... It can be a powerful agent of change because members of two different populations may exchange genetic material. Sometimes gene flow is obvious, as when an animal moves from one place to another. Other important kinds of gene flow are not as obvious. These subtler movements include the drift ...
... It can be a powerful agent of change because members of two different populations may exchange genetic material. Sometimes gene flow is obvious, as when an animal moves from one place to another. Other important kinds of gene flow are not as obvious. These subtler movements include the drift ...
lecture 02 - selection on the gene, genome, trait and phenotype
... - an adaptation is a trait that makes you better suited to your ecological niche, and increases your fitness Alleles or allele combinations, and the traits they produce, determine fitness of an individual: # of offspring that survive to reproduce - if you live forever but produce no offspring, your ...
... - an adaptation is a trait that makes you better suited to your ecological niche, and increases your fitness Alleles or allele combinations, and the traits they produce, determine fitness of an individual: # of offspring that survive to reproduce - if you live forever but produce no offspring, your ...
Computational Insights and the Theory of Evolution
... landscapes of this form • Unless peak > 2 plateau, in sexual reproduction the plateau will dominate and the peaks will become extinct • In asexual reproduction, the peaks will always dominate and the plateau will ...
... landscapes of this form • Unless peak > 2 plateau, in sexual reproduction the plateau will dominate and the peaks will become extinct • In asexual reproduction, the peaks will always dominate and the plateau will ...
Patentability of essentially biological processes
... (or animals) which are based on crossing and selection steps. It is clear that for patentability a significant step of human intervention is required which takes the process beyond being a process based solely or principally on crossing and selection. In practice, it is likely that a step of genetic ...
... (or animals) which are based on crossing and selection steps. It is clear that for patentability a significant step of human intervention is required which takes the process beyond being a process based solely or principally on crossing and selection. In practice, it is likely that a step of genetic ...
Document
... shuffling of genes alone cannot alter the overall genetic make-up of a population. • The five conditions that are required for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are: 1. A very large population size 2. Isolation from other populations ...
... shuffling of genes alone cannot alter the overall genetic make-up of a population. • The five conditions that are required for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are: 1. A very large population size 2. Isolation from other populations ...
Mrs. Willis Biology Blizzard Bag Days 1-3
... Looking at this karyotype, what would you determine for the future of this fetus. How could this have occurred? What causes down syndrome? What is nondisjunction? How many chromosomes are found in an egg and sperm? What is a pedigree? What does each shape represent? What does a shaded square mean? ...
... Looking at this karyotype, what would you determine for the future of this fetus. How could this have occurred? What causes down syndrome? What is nondisjunction? How many chromosomes are found in an egg and sperm? What is a pedigree? What does each shape represent? What does a shaded square mean? ...
ISCI FINAL EXAM
... table for a trait with perfect dominance and tell what the expected ratio of phenotypes would be. Be able to illustrate how the genes on a homologous pair of DNA strands controls this ratio. 13) Be familiar with the idea of Mendel’s second “law” – the principle of independent sorting. Be able to con ...
... table for a trait with perfect dominance and tell what the expected ratio of phenotypes would be. Be able to illustrate how the genes on a homologous pair of DNA strands controls this ratio. 13) Be familiar with the idea of Mendel’s second “law” – the principle of independent sorting. Be able to con ...
Descent with modification, Fitness as a result of adaptation, and
... most often associated with human evolution, but it is actually a more general term than that would suggest. Simply put, descent with modification means that traits are passed down from generation to generation and sometimes undergo changes or modifications over time These changes may be caused by na ...
... most often associated with human evolution, but it is actually a more general term than that would suggest. Simply put, descent with modification means that traits are passed down from generation to generation and sometimes undergo changes or modifications over time These changes may be caused by na ...
COOPERATION, EVOLUTION OF
... altruism is the most difficult type of cooperation to explain, the evolution of altruism has received by far the most theoretical attention. In fact, many biologists think of altruism as synonymous with cooperation. It is thus important for field ecologists interested in testing theory not to assume ...
... altruism is the most difficult type of cooperation to explain, the evolution of altruism has received by far the most theoretical attention. In fact, many biologists think of altruism as synonymous with cooperation. It is thus important for field ecologists interested in testing theory not to assume ...
VII. Natural Selection - Effingham County Schools
... beneficial traits will more likely survive long enough to reproduce and pass on those beneficial traits. Natural Selection- Works much like artificial selection, but the environment “selects” the best traits. – A. Causes Survival of the fittest! – B. Fitness is a result of adaptation. • Fitness= the ...
... beneficial traits will more likely survive long enough to reproduce and pass on those beneficial traits. Natural Selection- Works much like artificial selection, but the environment “selects” the best traits. – A. Causes Survival of the fittest! – B. Fitness is a result of adaptation. • Fitness= the ...
The role of gradualism and punctuation in cave adaptation
... no clear evidence for stabilizing selection in the sense that both extremes of the distribution are selected against. In sum, the data of Jones, even though preliminary, provide convincing evidence for directional selection. The multivariate techniques used hold exceptional promise not only for the ...
... no clear evidence for stabilizing selection in the sense that both extremes of the distribution are selected against. In sum, the data of Jones, even though preliminary, provide convincing evidence for directional selection. The multivariate techniques used hold exceptional promise not only for the ...
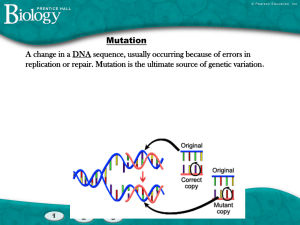
Notes
... A high degree of variability is obviously favourable, as freely giving the materials for selection to work on… Charles Darwin, The Origin of Species, Chap. 1. Darwin was the first person to recognize clearly that evolutionary change over time is the result of processes acting on genetically controll ...
... A high degree of variability is obviously favourable, as freely giving the materials for selection to work on… Charles Darwin, The Origin of Species, Chap. 1. Darwin was the first person to recognize clearly that evolutionary change over time is the result of processes acting on genetically controll ...
Group selection

Group selection is a proposed mechanism of evolution in which natural selection is imagined to act at the level of the group, instead of at the more conventional level of the individual.Early authors such as V. C. Wynne-Edwards and Konrad Lorenz argued that the behavior of animals could affect their survival and reproduction as groups.From the mid 1960s, evolutionary biologists such as John Maynard Smith argued that natural selection acted primarily at the level of the individual. They argued on the basis of mathematical models that individuals would not altruistically sacrifice fitness for the sake of a group. They persuaded the majority of biologists that group selection did not occur, other than in special situations such as the haplodiploid social insects like honeybees (in the Hymenoptera), where kin selection was possible.In 1994 David Sloan Wilson and Elliott Sober argued for multi-level selection, including group selection, on the grounds that groups, like individuals, could compete. In 2010 three authors including E. O. Wilson, known for his work on ants, again revisited the arguments for group selection, provoking a strong rebuttal from a large group of evolutionary biologists. As of yet, there is no clear consensus among biologists regarding the importance of group selection.