Worksheet Chapter 5.1
... over time is called biological evolution. There are four primary mechanisms of biological evolution. Mutations are accidental changes in an organism’s ...
... over time is called biological evolution. There are four primary mechanisms of biological evolution. Mutations are accidental changes in an organism’s ...
Document
... three. Create a phylogenetic tree to represent the relationship between these species. ...
... three. Create a phylogenetic tree to represent the relationship between these species. ...
part - MOCKSTER.NET!
... There are 6 main points to Darwin's theory. Match the term with the definition… Competition one trait is more favorable, so is favored Overproduction these come about from mutations and may or may not be helpful Variation over time, one species may become several Adaptations there is naturally varie ...
... There are 6 main points to Darwin's theory. Match the term with the definition… Competition one trait is more favorable, so is favored Overproduction these come about from mutations and may or may not be helpful Variation over time, one species may become several Adaptations there is naturally varie ...
Evolution - Hannah E. Styron
... England polluted the air with tons of soot which coated the trees. This caused dark colored moths to increase in population and the light colored moths to decline because dark colored moths were more suited for survival. ...
... England polluted the air with tons of soot which coated the trees. This caused dark colored moths to increase in population and the light colored moths to decline because dark colored moths were more suited for survival. ...
15.2 PDQ - Biology with Radjewski
... 2. Explain, “natural selection acts on individuals, but populations evolve” • Changes that occur are developmental in a single organism over the course of a life cycle. • After breeding populations will evolve ...
... 2. Explain, “natural selection acts on individuals, but populations evolve” • Changes that occur are developmental in a single organism over the course of a life cycle. • After breeding populations will evolve ...
Activity 1 -Natural selection and genetics
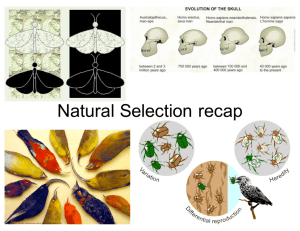
... Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace (1858). Natural selection is the gradual, nonrandom process by which biological traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It will occur if three conditions are met: 1. Heredity: Indiv ...
... Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace (1858). Natural selection is the gradual, nonrandom process by which biological traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It will occur if three conditions are met: 1. Heredity: Indiv ...
here - WordPress.com
... Both versions of adaptationism have been resoundingly rejected by modern evolutionary biologists. Due to their intuitive appeal, constant policing is required on this front, especially in the social sciences. - Darwinian evolution: the primary mechanism to explain most or all adaptation (i.e. match ...
... Both versions of adaptationism have been resoundingly rejected by modern evolutionary biologists. Due to their intuitive appeal, constant policing is required on this front, especially in the social sciences. - Darwinian evolution: the primary mechanism to explain most or all adaptation (i.e. match ...
Natural Selection Intro
... The variation exists BEFORE competition to survive happens (e.g. the competing to survive does not CREATE new genetic variants, it just makes them more likely to survive and reproduce than others) ...
... The variation exists BEFORE competition to survive happens (e.g. the competing to survive does not CREATE new genetic variants, it just makes them more likely to survive and reproduce than others) ...
Lecture 2
... Fitness of AA, if 80% in first generation and 40% in second generation. Natural, shuffling of existing genes, occurring with meiosis and sexual reproduction. One of the five conditions to maintain Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Principle that the frequency of a gene / allele does not change over time ( ...
... Fitness of AA, if 80% in first generation and 40% in second generation. Natural, shuffling of existing genes, occurring with meiosis and sexual reproduction. One of the five conditions to maintain Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Principle that the frequency of a gene / allele does not change over time ( ...
Phenotype Genotype and the Environment
... The environment doesn’t “see” recessive alleles. They are hidden, but still passed on. ...
... The environment doesn’t “see” recessive alleles. They are hidden, but still passed on. ...
Natural Selection
... a. Some individuals are more “fit” for the environment or for life in general ex. Resistance to disease ...
... a. Some individuals are more “fit” for the environment or for life in general ex. Resistance to disease ...
Men Women - iiap.res.in
... multicellular development I believe that natural selection, by acting on the fertile parents, could form a species which should regularly produce neuters… ...
... multicellular development I believe that natural selection, by acting on the fertile parents, could form a species which should regularly produce neuters… ...
Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.”
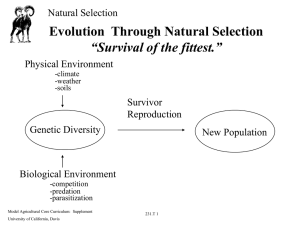
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
Lecture 2
... • At what level does natural selection occur? • Darwin “organismal” • But selection can act at other levels – Genes – Cells – (Organisms) – Groups (social insects) – Species? ...
... • At what level does natural selection occur? • Darwin “organismal” • But selection can act at other levels – Genes – Cells – (Organisms) – Groups (social insects) – Species? ...
The role of positive selection in molecular evolution
... within-locus selective effects Abstract: A key question in population genetics is the extent to which positive selection drives molecular evolution. According to the selectionist viewpoint, evolution at the molecular level occurs by natural selection acting on DNA sequence mutations, with selectivel ...
... within-locus selective effects Abstract: A key question in population genetics is the extent to which positive selection drives molecular evolution. According to the selectionist viewpoint, evolution at the molecular level occurs by natural selection acting on DNA sequence mutations, with selectivel ...
Chapter 10.3 Notes The Theory of Natural Selection **Key Concept
... c. Darwin proposed that adaptations arose over many generations ...
... c. Darwin proposed that adaptations arose over many generations ...
Disruptive selection, also called diversifying selection, is a
... Disruptive selection, also called diversifying selection, is a descriptive term used to describe changes in population genetics that simultaneously favor individuals at both extremes of the distribution. When disruptive selection operates, individuals at the extremes contribute more offspring than t ...
... Disruptive selection, also called diversifying selection, is a descriptive term used to describe changes in population genetics that simultaneously favor individuals at both extremes of the distribution. When disruptive selection operates, individuals at the extremes contribute more offspring than t ...
11 - Group Selection
... adaptations can arise is through natural selection. The effects of such adaptation can be seen at many levels: gene frequencies, frequencies of types of organisms, even populations. ...
... adaptations can arise is through natural selection. The effects of such adaptation can be seen at many levels: gene frequencies, frequencies of types of organisms, even populations. ...
Warm-Up 5/2 and 5/3
... • We saw how natural selection impacts the frequency of alleles for a SINGLE gene trait • What about polygenic traits, where individuals have more than two genes for a trait? ...
... • We saw how natural selection impacts the frequency of alleles for a SINGLE gene trait • What about polygenic traits, where individuals have more than two genes for a trait? ...
HERE
... 1. Where in the world did Darwin’s voyage take him and what did he study along the way? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ...
... 1. Where in the world did Darwin’s voyage take him and what did he study along the way? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ...
Group selection

Group selection is a proposed mechanism of evolution in which natural selection is imagined to act at the level of the group, instead of at the more conventional level of the individual.Early authors such as V. C. Wynne-Edwards and Konrad Lorenz argued that the behavior of animals could affect their survival and reproduction as groups.From the mid 1960s, evolutionary biologists such as John Maynard Smith argued that natural selection acted primarily at the level of the individual. They argued on the basis of mathematical models that individuals would not altruistically sacrifice fitness for the sake of a group. They persuaded the majority of biologists that group selection did not occur, other than in special situations such as the haplodiploid social insects like honeybees (in the Hymenoptera), where kin selection was possible.In 1994 David Sloan Wilson and Elliott Sober argued for multi-level selection, including group selection, on the grounds that groups, like individuals, could compete. In 2010 three authors including E. O. Wilson, known for his work on ants, again revisited the arguments for group selection, provoking a strong rebuttal from a large group of evolutionary biologists. As of yet, there is no clear consensus among biologists regarding the importance of group selection.