So…….what is natural Selection?
... Principles of Natural Selection I. Allele variation due to mutation (may alter function of protein) II. Some alleles enhance reproductive success III. Beneficial alleles more likely to survive IV. Allele frequency change through natural selection ...
... Principles of Natural Selection I. Allele variation due to mutation (may alter function of protein) II. Some alleles enhance reproductive success III. Beneficial alleles more likely to survive IV. Allele frequency change through natural selection ...
Chapter 7 Questions
... differences. Biotic factors are alive. They require a source of energy and use energy. They are influences of other living organisms on survival of a particular species. 2. Define biological fitness. What role does fitness play in selection? Biological fitness is the relative reproductive success of ...
... differences. Biotic factors are alive. They require a source of energy and use energy. They are influences of other living organisms on survival of a particular species. 2. Define biological fitness. What role does fitness play in selection? Biological fitness is the relative reproductive success of ...
Review for Final: Chap 16: Evolulution of Populations
... random occurences in a small population may change the relative frequency of an allele by chance ...
... random occurences in a small population may change the relative frequency of an allele by chance ...
Ch 8 Notes
... Directional selection favors increases or decreases in the mean of a trait Stabilizing selection favors average values of a trait Long-term studies reveal fluctuation in the direction and strength of natural selection ...
... Directional selection favors increases or decreases in the mean of a trait Stabilizing selection favors average values of a trait Long-term studies reveal fluctuation in the direction and strength of natural selection ...
CP Chapter 5 - Madeira City Schools
... 9. What is the difference between a generalist and a specialist? List some characteristics of each. ...
... 9. What is the difference between a generalist and a specialist? List some characteristics of each. ...
ch12kinquizkey
... • A) is called Fisher’s Fundamental Theorum • B) is called Hamilton’s rule • C) describes the conditions under which a gene affecting social behavior will experience positive selection • D) only applies in animals that live in social groups where each one knows the relatedness to each other • E) B a ...
... • A) is called Fisher’s Fundamental Theorum • B) is called Hamilton’s rule • C) describes the conditions under which a gene affecting social behavior will experience positive selection • D) only applies in animals that live in social groups where each one knows the relatedness to each other • E) B a ...
2 How Populations Evolve
... Genes, Populations and Evolution Explain how evolution in populations is related to a change in allele frequencies. List the five conditions necessary to maintain Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Apply the Hardy-Weinberg principle to estimate equilibrium genotype frequencies. Describe the agents of evolu ...
... Genes, Populations and Evolution Explain how evolution in populations is related to a change in allele frequencies. List the five conditions necessary to maintain Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Apply the Hardy-Weinberg principle to estimate equilibrium genotype frequencies. Describe the agents of evolu ...
10.3 Theory of Natural Selection
... and limited resources. • Darwin proposed that adaptations arose over many generations. • Natural selection is when individuals that have inherited beneficial adaptations produce more offspring ...
... and limited resources. • Darwin proposed that adaptations arose over many generations. • Natural selection is when individuals that have inherited beneficial adaptations produce more offspring ...
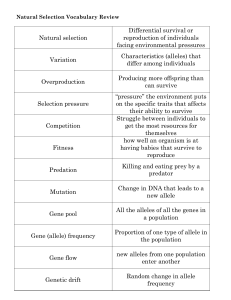
Natural selection Differential survival or reproduction of individuals
... Natural Selection Vocabulary Review ...
... Natural Selection Vocabulary Review ...
Theory of Natural Selection Power Notes
... Heritability – Natural Selection can only act on traits that already exist. Traits must be heritable in order to be passed down ...
... Heritability – Natural Selection can only act on traits that already exist. Traits must be heritable in order to be passed down ...
NATURAL SELECTION IN A NUTSHELL
... As populations of living things expand, generation by generation, they will inevitably run into limits: limits on food, space or the right kind of habitat These natural pressures limit or determine which individuals are able to survive and reproduce Not all individuals in a population are exac ...
... As populations of living things expand, generation by generation, they will inevitably run into limits: limits on food, space or the right kind of habitat These natural pressures limit or determine which individuals are able to survive and reproduce Not all individuals in a population are exac ...
Kin Selection Definition Otherwise known as inclusive fitness theory
... another case of people (or animals) providing care for closely related kin who carry shared genetic material. History and Modern Usage The theory of kin selection is widely regarded as the most important theoretical development in evolutionary thinking since Darwin, as it proposes a mechanism that e ...
... another case of people (or animals) providing care for closely related kin who carry shared genetic material. History and Modern Usage The theory of kin selection is widely regarded as the most important theoretical development in evolutionary thinking since Darwin, as it proposes a mechanism that e ...
Guided Notes2: Mechanisms of Evolution:
... 9. Stablizing selection favors the _______________________ individuals in a population. 10.Directional selection favors one extreme version of a ___________________ or the other extreme version. 11.In ___________________ selection, both extreme versions of a phenotype are selected. 12.______________ ...
... 9. Stablizing selection favors the _______________________ individuals in a population. 10.Directional selection favors one extreme version of a ___________________ or the other extreme version. 11.In ___________________ selection, both extreme versions of a phenotype are selected. 12.______________ ...
Natural Selection Bio.3.4.2 Explain how natural selection influences
... Bio.3.4.2 Explain how natural selection influences the changes in species over time • Develop a cause and effect model for the process of natural selection: Species have the potential to increase in numbers exponentially. Populations are genetically variable due to mutations and genetic recombin ...
... Bio.3.4.2 Explain how natural selection influences the changes in species over time • Develop a cause and effect model for the process of natural selection: Species have the potential to increase in numbers exponentially. Populations are genetically variable due to mutations and genetic recombin ...
Genetic Change - Minneota Public Schools
... a. the movement of alleles into and out of a population 2. gene flow b. one of the most powerful agents of genetic change 3. nonrandom mating c. eliminates individuals with average phenotype values 4. genetic drift d. a change in allele frequency because of random occurrences 5. mutation e. the stat ...
... a. the movement of alleles into and out of a population 2. gene flow b. one of the most powerful agents of genetic change 3. nonrandom mating c. eliminates individuals with average phenotype values 4. genetic drift d. a change in allele frequency because of random occurrences 5. mutation e. the stat ...
Directed Reading 17.2 - Blair Community Schools
... _____ 1. genetic equilibrium a. the movement of alleles into and out of a population _____ 2. gene flow b. one of the most powerful agents of genetic change _____ 3. nonrandom mating c. eliminates individuals with average phenotype values _____ 4. genetic drift d. a change in allele frequency becaus ...
... _____ 1. genetic equilibrium a. the movement of alleles into and out of a population _____ 2. gene flow b. one of the most powerful agents of genetic change _____ 3. nonrandom mating c. eliminates individuals with average phenotype values _____ 4. genetic drift d. a change in allele frequency becaus ...
Evolution Bingo Review KEY
... 2. Structures/limbs that are different in structure but similar in function (bat wing and butterfly wing) are known as ___ ANALAGOUS _ structures. 3. Evolution occurs as a result of __ NATURAL SELECTION _ (2 words). 4. The 5 conditions of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are: a. Large _POPULATION__. b. Ra ...
... 2. Structures/limbs that are different in structure but similar in function (bat wing and butterfly wing) are known as ___ ANALAGOUS _ structures. 3. Evolution occurs as a result of __ NATURAL SELECTION _ (2 words). 4. The 5 conditions of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are: a. Large _POPULATION__. b. Ra ...
Natural Selection and Evolution
... individuals with some traits over individuals with alternative traits ...
... individuals with some traits over individuals with alternative traits ...
File
... Population has experienced a “bottleneck” and certain alleles may be over-represented ...
... Population has experienced a “bottleneck” and certain alleles may be over-represented ...
View PDF
... c) Benefit is meiotic recombination. d) Benefit is short term – generation to generation time scale (here and now). Q: Does Evolution fashion “perfect” organisms? A: NO! a) Limited by historical constraints – modifying what came before, not from scratch. Descent with modification from ancestral for ...
... c) Benefit is meiotic recombination. d) Benefit is short term – generation to generation time scale (here and now). Q: Does Evolution fashion “perfect” organisms? A: NO! a) Limited by historical constraints – modifying what came before, not from scratch. Descent with modification from ancestral for ...
DISRUPTING GENETIC EQUILIBRIUM
... Organisms best suited to their environment live to reproduce and pass on their genes Acts on a phenotype Varying types of selection ...
... Organisms best suited to their environment live to reproduce and pass on their genes Acts on a phenotype Varying types of selection ...
Biology -Evolution OEQs
... Evolution is the change in a species over a period of time. Discuss 3 factors that affect the evolutionary process. Explain in detail. What would happen if organisms were not able to adapt to their environment? ...
... Evolution is the change in a species over a period of time. Discuss 3 factors that affect the evolutionary process. Explain in detail. What would happen if organisms were not able to adapt to their environment? ...
Misconceptions About Natural Selection
... Misconceptions about Natural Selection Because natural selection can produce amazing adaptations, it's tempting to think of it as an all-powerful force, urging organisms on, constantly pushing them in the direction of progress — but this is not what natural selection is like at all. First, natural s ...
... Misconceptions about Natural Selection Because natural selection can produce amazing adaptations, it's tempting to think of it as an all-powerful force, urging organisms on, constantly pushing them in the direction of progress — but this is not what natural selection is like at all. First, natural s ...
Group selection

Group selection is a proposed mechanism of evolution in which natural selection is imagined to act at the level of the group, instead of at the more conventional level of the individual.Early authors such as V. C. Wynne-Edwards and Konrad Lorenz argued that the behavior of animals could affect their survival and reproduction as groups.From the mid 1960s, evolutionary biologists such as John Maynard Smith argued that natural selection acted primarily at the level of the individual. They argued on the basis of mathematical models that individuals would not altruistically sacrifice fitness for the sake of a group. They persuaded the majority of biologists that group selection did not occur, other than in special situations such as the haplodiploid social insects like honeybees (in the Hymenoptera), where kin selection was possible.In 1994 David Sloan Wilson and Elliott Sober argued for multi-level selection, including group selection, on the grounds that groups, like individuals, could compete. In 2010 three authors including E. O. Wilson, known for his work on ants, again revisited the arguments for group selection, provoking a strong rebuttal from a large group of evolutionary biologists. As of yet, there is no clear consensus among biologists regarding the importance of group selection.