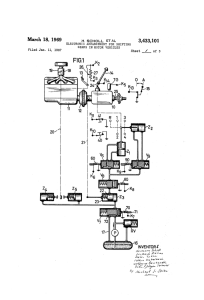
Electronic arrangement for shifting gears in motor vehicles
... their operative state, the pump P circulates the oil freely. value of the output voltage, voltage supply means for ener The electromagnetic valve V7 is operated by applying an gizing the switching circuits, voltage stabilizing means con actuating voltage to the terminal K-; of the coil 70. When nect ...
... their operative state, the pump P circulates the oil freely. value of the output voltage, voltage supply means for ener The electromagnetic valve V7 is operated by applying an gizing the switching circuits, voltage stabilizing means con actuating voltage to the terminal K-; of the coil 70. When nect ...
basics_of_branch_cir..
... • Over-current. For any current above its current rating it will trip according to its circuit breaker time-current characteristic. • Hazardous arcing. For arcing at current levels of about 75 amperes and above, the AFCI will trip. Commercially available AFCIs will actually operate at some level bel ...
... • Over-current. For any current above its current rating it will trip according to its circuit breaker time-current characteristic. • Hazardous arcing. For arcing at current levels of about 75 amperes and above, the AFCI will trip. Commercially available AFCIs will actually operate at some level bel ...
The Current Generators of Proportional to Absolute Temperature
... (3) High accuracy of BGR signals For (1), the demand for low power VLSI increases, the power consumption of start-up circuits of BGR will make the power consumption of overall BGR not be scaled down [5]. A simple power-on-reset (POR) circuit will be introduced to replace the start-up circuit to make ...
... (3) High accuracy of BGR signals For (1), the demand for low power VLSI increases, the power consumption of start-up circuits of BGR will make the power consumption of overall BGR not be scaled down [5]. A simple power-on-reset (POR) circuit will be introduced to replace the start-up circuit to make ...
THE PATCH-CLAMP TECHNIQUE EXPLAINED AND EXERCISED
... our opinion, mastering ERC-circuits should have the highest priority for obtaining measurement skills. The earlier chapters of the present book are particularly devoted to providing the basics of bioelectricity to the beginning student and attempts to fill the gap between basic physical theory and m ...
... our opinion, mastering ERC-circuits should have the highest priority for obtaining measurement skills. The earlier chapters of the present book are particularly devoted to providing the basics of bioelectricity to the beginning student and attempts to fill the gap between basic physical theory and m ...
1. Introduction - About the journal
... implemented using positive second-generation current conveyors (CCII+). The principle of the first oscillator is based on a conventional Wien-bridge network. However, this implementation suffers from the use of a floating capacitor, which can be unacceptable in the case of on-chip integration. This ...
... implemented using positive second-generation current conveyors (CCII+). The principle of the first oscillator is based on a conventional Wien-bridge network. However, this implementation suffers from the use of a floating capacitor, which can be unacceptable in the case of on-chip integration. This ...
Out-of-Step Protection for Generators
... The operation of the scheme is simple and straightforward. Figure 6 shows the relay characteristics and an assumed impedance locus (F-K). Proper operation of the scheme depends upon the impedance locus entering the offset mho unit and crossing both blinder characteristics. By the time the impedance ...
... The operation of the scheme is simple and straightforward. Figure 6 shows the relay characteristics and an assumed impedance locus (F-K). Proper operation of the scheme depends upon the impedance locus entering the offset mho unit and crossing both blinder characteristics. By the time the impedance ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.