V - s3.amazonaws.com
... • The output voltage V of this circuit is proportional to the sum of the two input currents I1 and I2. • This circuit could be useful in audio applications or in instrumentation. • The output of this circuit would probably be connected to an amplifier. ECE201 Lect-10 ...
... • The output voltage V of this circuit is proportional to the sum of the two input currents I1 and I2. • This circuit could be useful in audio applications or in instrumentation. • The output of this circuit would probably be connected to an amplifier. ECE201 Lect-10 ...
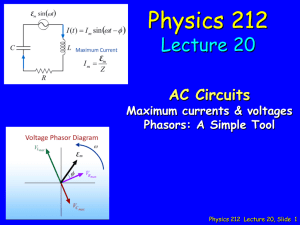
Lecture 2
... physical structure of the npn transistor are given in Fig. 1. We will analyze in the lectures only npn transistors. The only difference between the npn and pnp transistors is in their static states: the static state of the pnp transistors is reverse to that of the npn ones because of their opposite ...
... physical structure of the npn transistor are given in Fig. 1. We will analyze in the lectures only npn transistors. The only difference between the npn and pnp transistors is in their static states: the static state of the pnp transistors is reverse to that of the npn ones because of their opposite ...
Ch. 18 PP - Lemon Bay High School
... paths for current because the components are connected across common points or junctions • Lights wired in parallel have more than one path for current. Parallel circuits do not require all elements to conduct. ...
... paths for current because the components are connected across common points or junctions • Lights wired in parallel have more than one path for current. Parallel circuits do not require all elements to conduct. ...
AND8020/D Termination of ECL Devices with EF (Emitter Follower) OUTPUT Structure
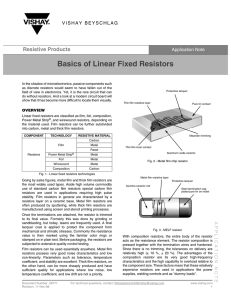
... operating region under all operating conditions. A minimum continuous current occurs for the most negative VOL, therefore the VTT supply must remain more negative than the worst case VOLmin and always sink current. Standard VTT is 2.0 V below VCC supply. A parallel resistor, Rt, matching the control ...
... operating region under all operating conditions. A minimum continuous current occurs for the most negative VOL, therefore the VTT supply must remain more negative than the worst case VOLmin and always sink current. Standard VTT is 2.0 V below VCC supply. A parallel resistor, Rt, matching the control ...
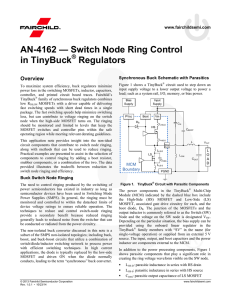
Analog Circuit Design in Nanoscale CMOS Technologies
... highly scaled devices. The second part of the paper focuses on ...
... highly scaled devices. The second part of the paper focuses on ...
Design of a proper set-up for low current
... This case is similar to the shunt ammeter but with a buffer amplifier between the shunt resistance and the operational amplifier. This case is used when the current measured is really low and the input bias current can be around the same range of the desired measured values. For that reason, a speci ...
... This case is similar to the shunt ammeter but with a buffer amplifier between the shunt resistance and the operational amplifier. This case is used when the current measured is really low and the input bias current can be around the same range of the desired measured values. For that reason, a speci ...
electrical measurement laboratory
... 2. What are other methods to measure a DC voltages? Explain their operation and compare with the simple “voltmeter” measurement method. 3. Is there a method to measure the current of a circuit without cutting the current carrying line? Explain the method(s) briefly. ...
... 2. What are other methods to measure a DC voltages? Explain their operation and compare with the simple “voltmeter” measurement method. 3. Is there a method to measure the current of a circuit without cutting the current carrying line? Explain the method(s) briefly. ...
Electronics Tutorial about the Types of Resistors The Different Types
... out the energy lost. When used in DC circuits the potential difference, also known as a resistors voltage drop, is measured across the terminals as the circuit current flows through the resistor. Most resistors are linear devices that produce a voltage drop across themselves when an electrical curre ...
... out the energy lost. When used in DC circuits the potential difference, also known as a resistors voltage drop, is measured across the terminals as the circuit current flows through the resistor. Most resistors are linear devices that produce a voltage drop across themselves when an electrical curre ...
chapter 4 – evolution of electronics in modern society
... Copper is the most commonly used conducting metal in electrical or electronics industry. It has 29 electrons that orbit around the nucleus in four electron shells. An electron is a negatively charged particle in an atom. In conductive materials, electrons can jump from atom to atom. To start the ele ...
... Copper is the most commonly used conducting metal in electrical or electronics industry. It has 29 electrons that orbit around the nucleus in four electron shells. An electron is a negatively charged particle in an atom. In conductive materials, electrons can jump from atom to atom. To start the ele ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.