Design and evaluation of a low thermal electromotive
... Measurements were not made at 1, 10, and 100 MÙ, with the active-arm bridge since previous measurements made with the Wheatstone bridge determined that differences between channels were less than 1 X 10-6 for resistances <100 MÙ. Figure 4 shows the relative difference between measurements made with ...
... Measurements were not made at 1, 10, and 100 MÙ, with the active-arm bridge since previous measurements made with the Wheatstone bridge determined that differences between channels were less than 1 X 10-6 for resistances <100 MÙ. Figure 4 shows the relative difference between measurements made with ...
to this file.
... Note the menu items and icons. To familiarize yourself with these, place your mouse pointer over each in turn. As you do, a text box opens to tell you what the selected item’s function is. After you have familiarized yourself with these, review the PSpice information in Appendix A of the text, start ...
... Note the menu items and icons. To familiarize yourself with these, place your mouse pointer over each in turn. As you do, a text box opens to tell you what the selected item’s function is. After you have familiarized yourself with these, review the PSpice information in Appendix A of the text, start ...
Harmonic/State Model Order Reduction of Nonlinear Networks
... applications in the power systems area [13]-[18]. An additional application proposed in this paper is the MOR of nonlinear networks involving harmonic dynamics. In power systems, nonlinear loads act as frequency converters. The generated frequencies penetrate a network and produce waveform distortio ...
... applications in the power systems area [13]-[18]. An additional application proposed in this paper is the MOR of nonlinear networks involving harmonic dynamics. In power systems, nonlinear loads act as frequency converters. The generated frequencies penetrate a network and produce waveform distortio ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... • If the current is the same throughout the circuit, what is used by the lamp to produce the thermal and light energy? • Recall that power, the rate at which electric energy is converted, is represented by P = IV. • Thus, if there is a potential difference, or voltage drop, across the lamp, then ele ...
... • If the current is the same throughout the circuit, what is used by the lamp to produce the thermal and light energy? • Recall that power, the rate at which electric energy is converted, is represented by P = IV. • Thus, if there is a potential difference, or voltage drop, across the lamp, then ele ...
12 Multimeter - Fluke Meter Repair Fluke Networks Repair
... Do not use the meter if the meter or test leads look damaged, or if you suspect that the meter is not operating properly. Turn off power to the circuit under test before cutting, unsoldering, or breaking the circuit. Small amounts of current can be dangerous. Do not apply more than 600 V rms between ...
... Do not use the meter if the meter or test leads look damaged, or if you suspect that the meter is not operating properly. Turn off power to the circuit under test before cutting, unsoldering, or breaking the circuit. Small amounts of current can be dangerous. Do not apply more than 600 V rms between ...
E1.1 Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet 1
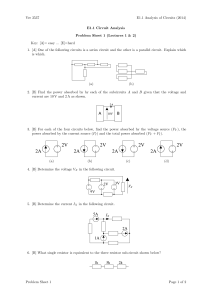
... value is 470 Ω. Show how, by combining two resistors in each case, it is possible to make networks whose equivalent resistance is (a) 3 kΩ, (b) 4 kΩ and (c) as close as possible to 3.5 kΩ. Determine is the worst case percentage error that might arise if, instead of combining resistors, you just pick ...
... value is 470 Ω. Show how, by combining two resistors in each case, it is possible to make networks whose equivalent resistance is (a) 3 kΩ, (b) 4 kΩ and (c) as close as possible to 3.5 kΩ. Determine is the worst case percentage error that might arise if, instead of combining resistors, you just pick ...
- SlideBoom
... simulation and verify the simulated results are the same as the calculated values. Were the values the same? Yes/No. If no, why? 3.Construct the circuit above on the breadboard. Connect the circuit’s input to the power supply and set it to +10 V. Use the handheld DMM to adjust the supply to +10 V. U ...
... simulation and verify the simulated results are the same as the calculated values. Were the values the same? Yes/No. If no, why? 3.Construct the circuit above on the breadboard. Connect the circuit’s input to the power supply and set it to +10 V. Use the handheld DMM to adjust the supply to +10 V. U ...
Basic Concepts
... While the two circuits are identical in terms of voltages and currents at the output terminals, there is one difference between the two circuits. With no load connected, the Norton circuit still dissipates power! ...
... While the two circuits are identical in terms of voltages and currents at the output terminals, there is one difference between the two circuits. With no load connected, the Norton circuit still dissipates power! ...
doctor - Shodhganga
... behavior of the transformer core under transient condition in ferroresonant circuit needs different approach then that in steady condition(2,3,4,7) The analysis of transformer core is very much desirable in transient simulation studies such as harmonic oscillations, self excitation, ferrroresonance ...
... behavior of the transformer core under transient condition in ferroresonant circuit needs different approach then that in steady condition(2,3,4,7) The analysis of transformer core is very much desirable in transient simulation studies such as harmonic oscillations, self excitation, ferrroresonance ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.