I2C Bus Pullup Resistor Calculation
... I2C communication standard is the mostly widely used inter-chip communication standard in today’s electronic systems. It is an open-drain/open-collector communication standard which implies integrated circuits (IC’s) with different voltage supply rails can be connected for communication. Pullup resi ...
... I2C communication standard is the mostly widely used inter-chip communication standard in today’s electronic systems. It is an open-drain/open-collector communication standard which implies integrated circuits (IC’s) with different voltage supply rails can be connected for communication. Pullup resi ...
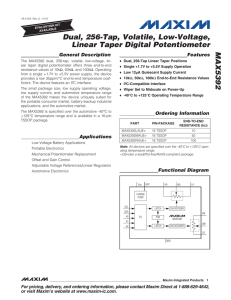
Dual, 256-Tap, Volatile, Low-Voltage, Linear Taper Digital Potentiometer MAX5392 General Description Features
... The MAX5392 dual, 256-tap, volatile, low-voltage linear taper digital potentiometer offers three end-to-end resistance values of 10kI, 50kI, and 100kI. The potentiometer consists of 255 fixed resistors in series between terminals H_ and L_. The potentiometer wiper, W_, is programmable to access any ...
... The MAX5392 dual, 256-tap, volatile, low-voltage linear taper digital potentiometer offers three end-to-end resistance values of 10kI, 50kI, and 100kI. The potentiometer consists of 255 fixed resistors in series between terminals H_ and L_. The potentiometer wiper, W_, is programmable to access any ...
NOTES Tech Std H Applied Electronics
... (temperature in o C) or to allow something to happen at a predetermined level (e.g. switching ON the central heating at 20 °C). Changes in the resistance of an input transducer must be converted to changes in voltage before the signal can be processed. This is normally done by using a voltage divide ...
... (temperature in o C) or to allow something to happen at a predetermined level (e.g. switching ON the central heating at 20 °C). Changes in the resistance of an input transducer must be converted to changes in voltage before the signal can be processed. This is normally done by using a voltage divide ...
TD-5 Timing Relay
... the relay. Because of its slow dropout characteristic, a contact of the TX relay is connected externally around the contact of the initiating relay. This maintains voltage to the timing module of the relay if the contact of the initiating relay bounces. Discrete components (a resistor and diode in D ...
... the relay. Because of its slow dropout characteristic, a contact of the TX relay is connected externally around the contact of the initiating relay. This maintains voltage to the timing module of the relay if the contact of the initiating relay bounces. Discrete components (a resistor and diode in D ...
80 Series V User Manual
... voltage, as marked on the Meter, between the terminals or between any terminal and earth ground. Never operate the Meter with the cover removed or the case open. Use caution when working with voltages above 30 V ac rms, 42 V ac peak, or 60 V dc. These voltages pose a shock hazard. Use only the repla ...
... voltage, as marked on the Meter, between the terminals or between any terminal and earth ground. Never operate the Meter with the cover removed or the case open. Use caution when working with voltages above 30 V ac rms, 42 V ac peak, or 60 V dc. These voltages pose a shock hazard. Use only the repla ...
document
... and BEM meshes, and to join the associated resistance networks based on proximity of the FEM nodes and, say, the center of gravity of the BEM panels. That is, each BEM panel is associated with the closest FEM node. The FEM/BEM combination produces a combined resistance network, of which the FEM part ...
... and BEM meshes, and to join the associated resistance networks based on proximity of the FEM nodes and, say, the center of gravity of the BEM panels. That is, each BEM panel is associated with the closest FEM node. The FEM/BEM combination produces a combined resistance network, of which the FEM part ...
Power System Analysis Prof. A. K. Sinha Department of Electrical
... Whereas, we know that the resistance of most of the equipments and power system are much smaller than the reactance. So, basically when a fault occurs it will be the reactive current, which will be flowing. That is the current that we get, when the fault occurs will be something like this. So, if o ...
... Whereas, we know that the resistance of most of the equipments and power system are much smaller than the reactance. So, basically when a fault occurs it will be the reactive current, which will be flowing. That is the current that we get, when the fault occurs will be something like this. So, if o ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.