Chapter 11 Circuits
... 22. In which circuit is the current furnished by the battery the greatest? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 23. In which circuit is the equivalent resistance connected to the battery the greatest? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 24. Which circuit dissipates the least power? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 25. The power diss ...
... 22. In which circuit is the current furnished by the battery the greatest? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 23. In which circuit is the equivalent resistance connected to the battery the greatest? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 24. Which circuit dissipates the least power? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 25. The power diss ...
Equipment Life Extension and Modernization of Generator
... to prove these capabilities. The only way to prove this capability is by high power testing with the synthetic test method, where two separate sources are used: one to provide the required short-circuit current and the other to produce the required transient recovery voltage. These circuits were ori ...
... to prove these capabilities. The only way to prove this capability is by high power testing with the synthetic test method, where two separate sources are used: one to provide the required short-circuit current and the other to produce the required transient recovery voltage. These circuits were ori ...
SN74LVC1G11-Q1, Single 3-Input Positive
... changes to its semiconductor products and services per JESD46, latest issue, and to discontinue any product or service per JESD48, latest issue. Buyers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All semiconduct ...
... changes to its semiconductor products and services per JESD46, latest issue, and to discontinue any product or service per JESD48, latest issue. Buyers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All semiconduct ...
BDTIC
... The complete gate resistor consists of the internal gate resistor together with an external gate resistor and due to that, a part of the IGBT drive power losses will be dissipated directly in the PCB, whereas the other part of the losses will be dissipated externally to the ambient air. The ratio of ...
... The complete gate resistor consists of the internal gate resistor together with an external gate resistor and due to that, a part of the IGBT drive power losses will be dissipated directly in the PCB, whereas the other part of the losses will be dissipated externally to the ambient air. The ratio of ...
Industrial Electricity 1: Domains and Competencies
... Describe how Ohms law is used to calculate values of an electrical circuit. Describe how Krichhoffs is used for the calculation of values in an electrical circuit. Define power and give its units of measurement State a formula for calculating the total power used in an electrical circuit State Kirch ...
... Describe how Ohms law is used to calculate values of an electrical circuit. Describe how Krichhoffs is used for the calculation of values in an electrical circuit. Define power and give its units of measurement State a formula for calculating the total power used in an electrical circuit State Kirch ...
Chapter 5 Using Sources and Stimuli
... and H elements. You can use these controlled elements in Star-Hspice to model both MOS and bipolar transistors, tunnel diodes, SCRs, as well as analog functions such as operational amplifiers, summers, comparators, voltage controlled oscillators, modulators, and switched capacitor circuits. The cont ...
... and H elements. You can use these controlled elements in Star-Hspice to model both MOS and bipolar transistors, tunnel diodes, SCRs, as well as analog functions such as operational amplifiers, summers, comparators, voltage controlled oscillators, modulators, and switched capacitor circuits. The cont ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

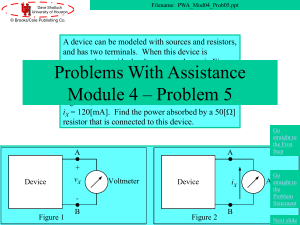
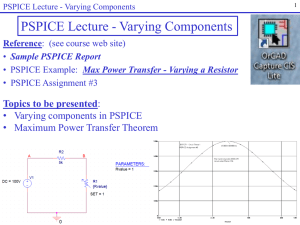
A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.