Heterogeneous catalysis on chitosan
... The interactions of chitosan with metal ions have been abundantly described [2,58]. Three mechanisms are usually cited for the interpretation of metal sorption on chitosan material: (a) metal chelation, (b) electrostatic attraction (or ion exchange), and (c) formation of ion pairs. Though ion pair f ...
... The interactions of chitosan with metal ions have been abundantly described [2,58]. Three mechanisms are usually cited for the interpretation of metal sorption on chitosan material: (a) metal chelation, (b) electrostatic attraction (or ion exchange), and (c) formation of ion pairs. Though ion pair f ...
Co-production of furfural and easily hydrolysable residue from
... When the highest furfural yield was obtained, CSF values were 1.8, 2.6, and −0.45, respectively, for FeCl3-, HCl-, and AlCl3-catalyzed reaction systems. In comparison, the CSF value applied for acid-assisted lignocellulose pretreatment varied from 1.0 to 2.0.30,32 Although CSF for FeCl3-catalzyed fu ...
... When the highest furfural yield was obtained, CSF values were 1.8, 2.6, and −0.45, respectively, for FeCl3-, HCl-, and AlCl3-catalyzed reaction systems. In comparison, the CSF value applied for acid-assisted lignocellulose pretreatment varied from 1.0 to 2.0.30,32 Although CSF for FeCl3-catalzyed fu ...
Non Flory-Schulz ethene oligomerization with titanium
... the rationalization of previous knowledge and theoretical background (when possible)5. ...
... the rationalization of previous knowledge and theoretical background (when possible)5. ...
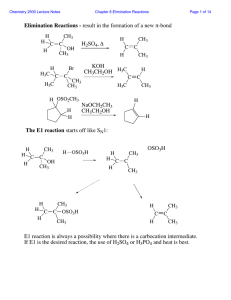
lec-3- 211( Elim+ Re..
... Oxidation is the beginning of the deterioration process. Think of how a slice of apple turns brown when exposed to air. Oxidation leads to the formation of free radicals which are unstable molecules in the body that have one unpaired electron. They can cause oxidation and damage to the cells. This ...
... Oxidation is the beginning of the deterioration process. Think of how a slice of apple turns brown when exposed to air. Oxidation leads to the formation of free radicals which are unstable molecules in the body that have one unpaired electron. They can cause oxidation and damage to the cells. This ...
Alcools
... Alcohols are noticeably less volatile; their melting points are greater and they are more water soluble than the corresponding hydrocarbons having similar molecular weights. These differences are due to the OH group which renders a certain polarity to the molecule. The result is an important intermo ...
... Alcohols are noticeably less volatile; their melting points are greater and they are more water soluble than the corresponding hydrocarbons having similar molecular weights. These differences are due to the OH group which renders a certain polarity to the molecule. The result is an important intermo ...
Ch. 6 - Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Professor William Tam received his B.Sc. at the University of Hong Kong in 1990 and his Ph.D. at the University of Toronto (Canada) in 1995. He was an NSERC postdoctoral fellow at the Imperial College (UK) and at Harvard University (USA). He joined the Department of Chemistry at the University of Gu ...
... Professor William Tam received his B.Sc. at the University of Hong Kong in 1990 and his Ph.D. at the University of Toronto (Canada) in 1995. He was an NSERC postdoctoral fellow at the Imperial College (UK) and at Harvard University (USA). He joined the Department of Chemistry at the University of Gu ...
Chem Soc Rev
... processes that satisfy the principles of green chemistry.8,9 In particular, it is highly desirable to develop new catalytic oxidation processes to replace the current energetically inefficient and/or environmentally unfriendly multi-step reactions. The catalytic oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or k ...
... processes that satisfy the principles of green chemistry.8,9 In particular, it is highly desirable to develop new catalytic oxidation processes to replace the current energetically inefficient and/or environmentally unfriendly multi-step reactions. The catalytic oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or k ...
Lecture8
... The ligand substitution occurs exclusively cis to the phosphine. N-oxides (R = Me or Et) is commonly used instead of heat or UV-irradiation to remove CO ligands in order to speed up dissociative substitution reactions. ...
... The ligand substitution occurs exclusively cis to the phosphine. N-oxides (R = Me or Et) is commonly used instead of heat or UV-irradiation to remove CO ligands in order to speed up dissociative substitution reactions. ...
The story of V
... The polymer chain propagation will tend to terminate. Radicals are unstable, and eventually they are going to find a way to become paired without generating a new radical. Then the chain reaction will come to a halt. This happens in several ways. The simplest way is that the radical sites of two gro ...
... The polymer chain propagation will tend to terminate. Radicals are unstable, and eventually they are going to find a way to become paired without generating a new radical. Then the chain reaction will come to a halt. This happens in several ways. The simplest way is that the radical sites of two gro ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.