NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS - A
... Optical isomers are often found together in a mixture in equal quantities. The opposite effect they have on the rotation of plane polarised light will thus result in no overall rotation. An equimolar mixture of two optical isomers will thus have no effect on plane polarised light and is thus not opt ...
... Optical isomers are often found together in a mixture in equal quantities. The opposite effect they have on the rotation of plane polarised light will thus result in no overall rotation. An equimolar mixture of two optical isomers will thus have no effect on plane polarised light and is thus not opt ...
4.04 Nomenclature and Isomerism in Organic Chemistry
... Optical isomers are often found together in a mixture in equal quantities. The opposite effect they have on the rotation of plane polarised light will thus result in no overall rotation. An equimolar mixture of two optical isomers will thus have no effect on plane polarised light and is thus not opt ...
... Optical isomers are often found together in a mixture in equal quantities. The opposite effect they have on the rotation of plane polarised light will thus result in no overall rotation. An equimolar mixture of two optical isomers will thus have no effect on plane polarised light and is thus not opt ...
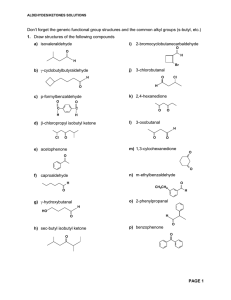
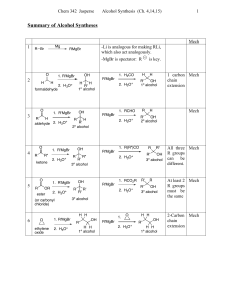
Aldehydes/Ketones Solutions
... mechanisms required but show all reagents and intermediate products formed. More than one step may be necessary a) O O C H ...
... mechanisms required but show all reagents and intermediate products formed. More than one step may be necessary a) O O C H ...
Complexes Of 5,7,7,12,14,14 - European Scientific Journal
... five coordinated square pyramidal complexes. The complexes cis-[Cd(teta)(NO3)](NO3) and cis-[Cd(tet-b)(NO3)](NO3) underwent axial ligand substitution and anion exchange reaction with KCNS to produce [Cd(teta)(SCN)](SCN) and [Cd(tet-b)(SCN)](SCN) respectively. The square pyramidal complex [CdLI](ClO4 ...
... five coordinated square pyramidal complexes. The complexes cis-[Cd(teta)(NO3)](NO3) and cis-[Cd(tet-b)(NO3)](NO3) underwent axial ligand substitution and anion exchange reaction with KCNS to produce [Cd(teta)(SCN)](SCN) and [Cd(tet-b)(SCN)](SCN) respectively. The square pyramidal complex [CdLI](ClO4 ...
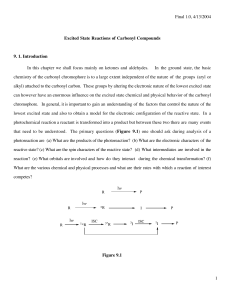
Investigating the Dearomative Rearrangement of Biaryl Phosphine- Ligated Pd(II) Complexes
... connectivity that allows for the loss of HBr and rearomatization to occur. Taken together, these reports suggest that the lower ring of biaryl phosphine ligands may not be innocent in the reactivity and decomposition pathways of catalytic intermediates. Reactions wherein a transition metal-bound are ...
... connectivity that allows for the loss of HBr and rearomatization to occur. Taken together, these reports suggest that the lower ring of biaryl phosphine ligands may not be innocent in the reactivity and decomposition pathways of catalytic intermediates. Reactions wherein a transition metal-bound are ...
Organic Chemistry
... Hydrogenation of alkenes occurs in the presence of a metal catalyst, a syn addition process. The two hydrogen atoms add to the same face of the double bond. Furthermore, if one side is more hindered than the other, addition is stereoselective for the less hindered side. Hydrogenation is exothermic, ...
... Hydrogenation of alkenes occurs in the presence of a metal catalyst, a syn addition process. The two hydrogen atoms add to the same face of the double bond. Furthermore, if one side is more hindered than the other, addition is stereoselective for the less hindered side. Hydrogenation is exothermic, ...
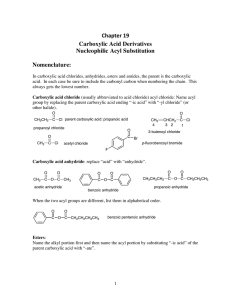
Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl
... For thioesters: Sulfur is a third row element, like chlorine, and so it is considerably larger than oxygen. The C-S bond is relatively long and this makes for poor overlap of the lone pair 3p orbital and the π-orbital of the carbonyl. But thioesters are less reactive than acid chlorides and anhydrid ...
... For thioesters: Sulfur is a third row element, like chlorine, and so it is considerably larger than oxygen. The C-S bond is relatively long and this makes for poor overlap of the lone pair 3p orbital and the π-orbital of the carbonyl. But thioesters are less reactive than acid chlorides and anhydrid ...
Ozone decomposition
... above 105 °C. The gaseous ozone is characterized by different times of half-life, depending on the temperature (Table 1). The ozone structure is resonance stabilized, which is one of the reasons for its resistance against decomposition at low temperatures (Figure 2). In most reactions with inorganic ...
... above 105 °C. The gaseous ozone is characterized by different times of half-life, depending on the temperature (Table 1). The ozone structure is resonance stabilized, which is one of the reasons for its resistance against decomposition at low temperatures (Figure 2). In most reactions with inorganic ...
The Organometallic Chemistry Of Transition Metals
... the interface between classical organic and inorganic chemistry in dealing with the interaction between inorganic metal species and organic molecules. In the related metal–organic compound area, in contrast, the organic fragment is bound only by metal–heteroatom bonds [e.g., Ti(OMe)4 ]. The organome ...
... the interface between classical organic and inorganic chemistry in dealing with the interaction between inorganic metal species and organic molecules. In the related metal–organic compound area, in contrast, the organic fragment is bound only by metal–heteroatom bonds [e.g., Ti(OMe)4 ]. The organome ...
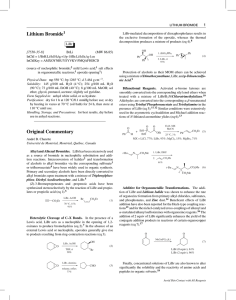
Lithium Bromide Original Commentary
... Weak Lewis Acid. Lithium bromide is used as a mild Lewis acid in a variety of reactions. For example, this reagent was used in the Pictet-Spengler cyclization of a highly functionalized imine (eq 13).33 In this reaction, carbon-carbon bond formation occurs without reaction or loss of stereochemical ...
... Weak Lewis Acid. Lithium bromide is used as a mild Lewis acid in a variety of reactions. For example, this reagent was used in the Pictet-Spengler cyclization of a highly functionalized imine (eq 13).33 In this reaction, carbon-carbon bond formation occurs without reaction or loss of stereochemical ...
Study of η6 - cyclic π-perimeter hydrocarbon ruthenium complexes
... Within the large family of η5 - and η6 -cyclichydrocarbon metal complexes, piano stool complexes of ruthenium are undeniably the most studied classes of complexes. In particular, η6 -arene metal complexes have emerged as versatile intermediates in organic synthesis as a consequence of the ease with ...
... Within the large family of η5 - and η6 -cyclichydrocarbon metal complexes, piano stool complexes of ruthenium are undeniably the most studied classes of complexes. In particular, η6 -arene metal complexes have emerged as versatile intermediates in organic synthesis as a consequence of the ease with ...
SUPPORTED LIGANDS FOR METAL CATALYZED REACTIONS Rocío Marcos Escartín ISBN:
... Homogeneous metal catalysts are composed by a metal complex modified with organic ligands. Although the first non enzymatic asymmetric catalysts known were simple organic molecules,[1] the research regarding catalysis reached full development with metal-based systems, which have been predominant for ...
... Homogeneous metal catalysts are composed by a metal complex modified with organic ligands. Although the first non enzymatic asymmetric catalysts known were simple organic molecules,[1] the research regarding catalysis reached full development with metal-based systems, which have been predominant for ...
Metallocenyl Dendrimers and Their Applications in
... e have investigated the movement of electrons around the peripheries of dendrimers and between their redox termini and electrodes through studies of the electrochemistry of dendrimers presenting metallocenes (and other transition metal sandwich complexes) as terminal groups. Because these compounds ...
... e have investigated the movement of electrons around the peripheries of dendrimers and between their redox termini and electrodes through studies of the electrochemistry of dendrimers presenting metallocenes (and other transition metal sandwich complexes) as terminal groups. Because these compounds ...
History of Organic Chemistry
... Confused, the student tells the naive chemistry-challenged person that the task is impossible. a) Why can=t the student show the structure of C4H10? (2) b) Rephrase the question by changing one word so that the question can be answered, and then answer it. (Keep the flavor of the question - don't ch ...
... Confused, the student tells the naive chemistry-challenged person that the task is impossible. a) Why can=t the student show the structure of C4H10? (2) b) Rephrase the question by changing one word so that the question can be answered, and then answer it. (Keep the flavor of the question - don't ch ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.