CHM 222 Organic Chemistry II
... After completing CHM 222, Organic Chemistry II, the student will be able to: A. Demonstrate an understanding of the structure, nomenclature, reactions, mechanisms and synthesis of the different classes of carbon compounds. B. Describe the characteristics of the different classes of organic compounds ...
... After completing CHM 222, Organic Chemistry II, the student will be able to: A. Demonstrate an understanding of the structure, nomenclature, reactions, mechanisms and synthesis of the different classes of carbon compounds. B. Describe the characteristics of the different classes of organic compounds ...
ethers - WordPress.com
... Nomenclatures, methods nof preparations, properties, reactions and uses ...
... Nomenclatures, methods nof preparations, properties, reactions and uses ...
organic synthesis
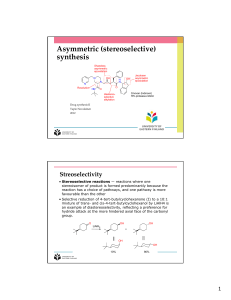
... • one optical isomer usually works better than the other • in some cases the other optical isomer may cause dangerous side effects • laboratory reactions usually produce both optical isomers • naturally occurring reactions usually produce just one optical isomer ...
... • one optical isomer usually works better than the other • in some cases the other optical isomer may cause dangerous side effects • laboratory reactions usually produce both optical isomers • naturally occurring reactions usually produce just one optical isomer ...
Organic Chemistry Practice Test
... 19. In which pair of hydrocarbons does each compound contain only one double bond per molecule? ...
... 19. In which pair of hydrocarbons does each compound contain only one double bond per molecule? ...
Document
... charge may reside with the C2H4 fragment, but with a low probability, since it has a higher ionisation energy than butadiene. If a substituent is present, the charge may remain on the fragment containing this group, depending on the relative ionisation energies of the two products. ...
... charge may reside with the C2H4 fragment, but with a low probability, since it has a higher ionisation energy than butadiene. If a substituent is present, the charge may remain on the fragment containing this group, depending on the relative ionisation energies of the two products. ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.