Organic Chemistry Unit Test
... 1. We did two labs involving esters. In the first, we made a series of esters. In the second, we made two polyesters. Describe at least 3 ‘real world’ uses that you could imagine for the products of either of these labs based on your observations and data table. (3 marks) ...
... 1. We did two labs involving esters. In the first, we made a series of esters. In the second, we made two polyesters. Describe at least 3 ‘real world’ uses that you could imagine for the products of either of these labs based on your observations and data table. (3 marks) ...
LIMITING REACTANT LAB
... a. Be able to name a simple compound from its formula. b. Be able to derive a compound’s formula from its name. c. It never hurts to know your polyatomic ions. See Table 9.3 on page 257 of the text. d. If you want a refresher, there’s a pencast on this material. Questions will be similar to the D2 Q ...
... a. Be able to name a simple compound from its formula. b. Be able to derive a compound’s formula from its name. c. It never hurts to know your polyatomic ions. See Table 9.3 on page 257 of the text. d. If you want a refresher, there’s a pencast on this material. Questions will be similar to the D2 Q ...
Organic Reactions
... ∆H can be obtained by using bond dissociation energies (D) –Table 5.3 gives D values at standard temperature and pressure (∆Ho) ∆H = sum of D of bonds broken – sum of D of bonds formed ...
... ∆H can be obtained by using bond dissociation energies (D) –Table 5.3 gives D values at standard temperature and pressure (∆Ho) ∆H = sum of D of bonds broken – sum of D of bonds formed ...
Polymerization of Olefins: An Outlook After 50
... coordination site empty. A β-hydrogen atom of the ethyl group of a second complex unit may occupy this site. Subsequent transfer of this hydrogen to the other ethyl group would lead to the formation of ethane and ethylene, as has been observed experimentally. As a consequence the titanium is reduced ...
... coordination site empty. A β-hydrogen atom of the ethyl group of a second complex unit may occupy this site. Subsequent transfer of this hydrogen to the other ethyl group would lead to the formation of ethane and ethylene, as has been observed experimentally. As a consequence the titanium is reduced ...
Notes
... Substitution Reactions ‐ A substitution reaction occurs when a saturated hydrocarbon (alkane) or aromatic reacts with a diatomic halide molecule (like Br2, Cl2, F2, I2) ‐ The products of a substitution reaction are a organic halide and a hydrogen halide molecule ‐ Carbon‐hydrogen bonds in the hydr ...
... Substitution Reactions ‐ A substitution reaction occurs when a saturated hydrocarbon (alkane) or aromatic reacts with a diatomic halide molecule (like Br2, Cl2, F2, I2) ‐ The products of a substitution reaction are a organic halide and a hydrogen halide molecule ‐ Carbon‐hydrogen bonds in the hydr ...
Chemical reactions
... NA H2 + NA Cl2 = 2 NA HCl The second signification of the chemical equation is: that 1 mole of hydrogen reacts with 1 mole of chlorine to obtain 2 moles of hydrochloric acid. ...
... NA H2 + NA Cl2 = 2 NA HCl The second signification of the chemical equation is: that 1 mole of hydrogen reacts with 1 mole of chlorine to obtain 2 moles of hydrochloric acid. ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... ________ 20. The complete combustion of octane (C8H18) would: a. require 25 O2(g). c. produce 18 H2O(g). b. produce 16 CO2(g). d. all of the above ________ 21. Double-replacement reactions are generally driven by the formation of: a. a precipitate. c. water. b. a gaseous product. d. all of the above ...
... ________ 20. The complete combustion of octane (C8H18) would: a. require 25 O2(g). c. produce 18 H2O(g). b. produce 16 CO2(g). d. all of the above ________ 21. Double-replacement reactions are generally driven by the formation of: a. a precipitate. c. water. b. a gaseous product. d. all of the above ...
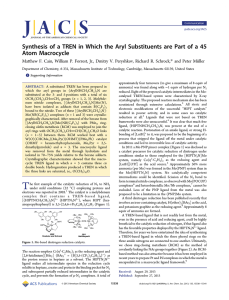
Synthesis of a TREN in Which the Aryl Substituents are... Atom Macrocycle ̈ller *
... data are all consistent with formation of 8c from structurally characterized c,c,c-6c. Apparently three cis CC bonds between C5 and C6 in each link in c,c,c-6c provide enough rigidity to allow it to be crystallized readily. The reaction between c,c,c-6c and (NMe2)3MoN (1.75 equiv) in C6D6 at 50 °C ...
... data are all consistent with formation of 8c from structurally characterized c,c,c-6c. Apparently three cis CC bonds between C5 and C6 in each link in c,c,c-6c provide enough rigidity to allow it to be crystallized readily. The reaction between c,c,c-6c and (NMe2)3MoN (1.75 equiv) in C6D6 at 50 °C ...
Formative 3.5 2014
... (ii) Amino acids can form polymers because at each end of the molecule is a functional group that can react with a functional group from neighbouring molecules. (b) To be able to form enantiomers a molecule must have a chiral atom – one to which four different groups are attached. This enables the f ...
... (ii) Amino acids can form polymers because at each end of the molecule is a functional group that can react with a functional group from neighbouring molecules. (b) To be able to form enantiomers a molecule must have a chiral atom – one to which four different groups are attached. This enables the f ...
Problem Set: Empirical and Molecular Formulas
... 3. Ammonia, NH3, is used throughout the world as a fertilizer. To manufacture ammonia, nitrogen, N2, is combined with hydrogen, H2, in a synthesis reaction. a) Write a balanced chemical equation for the formation of ammonia. b) If 92.7 kg N2 and 265.8 kg H2 are used, which is the limiting reactant? ...
... 3. Ammonia, NH3, is used throughout the world as a fertilizer. To manufacture ammonia, nitrogen, N2, is combined with hydrogen, H2, in a synthesis reaction. a) Write a balanced chemical equation for the formation of ammonia. b) If 92.7 kg N2 and 265.8 kg H2 are used, which is the limiting reactant? ...
Synthesis and reactions of silicon containing cyclic a
... 2). It turns out that the order and nature of reagents added are critical for the outcome of this catalytic reaction. Vollhardt group reported that slow addition of a solution containing dialkyne and catalyst in BTMSA to a refluxing solution of catalyst in BTMSA is essential for the success of the re ...
... 2). It turns out that the order and nature of reagents added are critical for the outcome of this catalytic reaction. Vollhardt group reported that slow addition of a solution containing dialkyne and catalyst in BTMSA to a refluxing solution of catalyst in BTMSA is essential for the success of the re ...
4 • Reactions In Aqueous Solution
... equation for the reaction of washing soda, Na2CO3 and vinegar, HC2H3O2. ...
... equation for the reaction of washing soda, Na2CO3 and vinegar, HC2H3O2. ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.