Anhydrous copper (II) sulfate: an efficient catalyst for the liquid
... the years' but is still not completely understood. Our interest in the synthesis of substituted tetrahydropyrans and deoxy ~ u g a r s ~prompted ...
... the years' but is still not completely understood. Our interest in the synthesis of substituted tetrahydropyrans and deoxy ~ u g a r s ~prompted ...
CHEM 109A CLAS Alkenes and Reactions of
... 1. Determine the # of C atoms in the longest continuous chain (parent chain) that CONTAINS the double bond – Watch for branches! a. Use a prefix for # of double bonds (EX. diene for 2) b. A # is not needed to denote position of double bond in ring, b/c ring is numbered so that double bond is on C #1 ...
... 1. Determine the # of C atoms in the longest continuous chain (parent chain) that CONTAINS the double bond – Watch for branches! a. Use a prefix for # of double bonds (EX. diene for 2) b. A # is not needed to denote position of double bond in ring, b/c ring is numbered so that double bond is on C #1 ...
alcohols, alkyl halides, and nucleophilic substitutions
... separately. What structural change correlates with reactivity? Assuming this to be an SN1 reaction (see scheme in part B), and that the reaction is faster for more stable cation intermediates, indicate the order of stability of all the carbon cations formed from each alcohol. Examine the cations and ...
... separately. What structural change correlates with reactivity? Assuming this to be an SN1 reaction (see scheme in part B), and that the reaction is faster for more stable cation intermediates, indicate the order of stability of all the carbon cations formed from each alcohol. Examine the cations and ...
Alcohols I Reading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10
... a metal atom (C–M, M=Li, Na, K, Mg). The C–M bond is polarized so that most of the electron density resides on carbon, since it is the more electronegative atom of the pair. This makes carbon a good nucleophile (and also a good base). Grignard reagents are organomagnesium compounds formed from alkyl ...
... a metal atom (C–M, M=Li, Na, K, Mg). The C–M bond is polarized so that most of the electron density resides on carbon, since it is the more electronegative atom of the pair. This makes carbon a good nucleophile (and also a good base). Grignard reagents are organomagnesium compounds formed from alkyl ...
... amphipathic molecules consisting of one or several units of sugar head group connected via an ether bond with hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain. They have good emulsification activity and wetting properties. Furthermore, the sugar head group could ionize with no charge. Thus, they have potential use as ...
Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry
... Indicators of a Chemical Reaction – evidence of a chemical reaction a. Evolution of heat and light (simultaneously) b. Production of a gas (bubbles, odor change) c. Formation of a precipitate (solid, cloudy) d. Color change (not introduced by an outside source such as dye or ink) Characteristics of ...
... Indicators of a Chemical Reaction – evidence of a chemical reaction a. Evolution of heat and light (simultaneously) b. Production of a gas (bubbles, odor change) c. Formation of a precipitate (solid, cloudy) d. Color change (not introduced by an outside source such as dye or ink) Characteristics of ...
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY/ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of acetylene (C2H2) form its elements: 2C + H2 Section C ...
... Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of acetylene (C2H2) form its elements: 2C + H2 Section C ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... in the fume hoods. These chemicals are toxic and will harm the environment if not disposed of properly. • Do not eat, drink, or apply the chemicals to skin. Many of these chemicals are highly corrosive and in addition to being toxic, they will burn your skin and muscle tissue. Ouch! • If any of the ...
... in the fume hoods. These chemicals are toxic and will harm the environment if not disposed of properly. • Do not eat, drink, or apply the chemicals to skin. Many of these chemicals are highly corrosive and in addition to being toxic, they will burn your skin and muscle tissue. Ouch! • If any of the ...
19.19 Summary
... Lithium aluminum hydride reduces esters to alcohols. Two alcohols are formed; the acyl group is reduced to the primary alcohol. ...
... Lithium aluminum hydride reduces esters to alcohols. Two alcohols are formed; the acyl group is reduced to the primary alcohol. ...
Organic Chemistry
... This ‘C’ has only 1 other carbon bonded to it R-OH (where R=rest of the molecule/branch) ...
... This ‘C’ has only 1 other carbon bonded to it R-OH (where R=rest of the molecule/branch) ...
Chapter 10 for 301
... There cannot be any acidic protons in the solvent, as the Grignard is such a strong base. There cannot be any pi bonds in the solvent as those are sites of reactivity that the Grignard will attack. From here on, I will use Grignard to refer to both Grignard reagents and organolithiums, as they ...
... There cannot be any acidic protons in the solvent, as the Grignard is such a strong base. There cannot be any pi bonds in the solvent as those are sites of reactivity that the Grignard will attack. From here on, I will use Grignard to refer to both Grignard reagents and organolithiums, as they ...
Organic chemistry: introduction
... that might break and where the electrons are going if the bond does break. Is the particle being attacked saturated or not? If it is saturated, there is not much room for the incoming electrons and the reaction will have a high activation energy. This means it will go slowly. If the particle being a ...
... that might break and where the electrons are going if the bond does break. Is the particle being attacked saturated or not? If it is saturated, there is not much room for the incoming electrons and the reaction will have a high activation energy. This means it will go slowly. If the particle being a ...
CHEM 2414
... counter-clockwise) that affords the second substituent the lower possible location number. 4. If several substituents are present on the ring, they are listed in alphabetical order. Location numbers are assigned to the substituents so that one of them is at carbon #1 and the other locations have the ...
... counter-clockwise) that affords the second substituent the lower possible location number. 4. If several substituents are present on the ring, they are listed in alphabetical order. Location numbers are assigned to the substituents so that one of them is at carbon #1 and the other locations have the ...
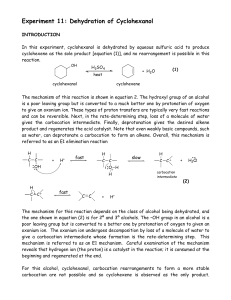
Chapter 9
... • Entropy favors product formation in dehydration since one molecule of reactant forms two molecules of product. • Enthalpy favors reactants, since the two bonds broken in the reactant are stronger than the and bonds formed in the products. Figure 9.6 ...
... • Entropy favors product formation in dehydration since one molecule of reactant forms two molecules of product. • Enthalpy favors reactants, since the two bonds broken in the reactant are stronger than the and bonds formed in the products. Figure 9.6 ...
this PDF file
... corresponding carbonyl compound was accomplished by the procedure reported in earlier papers. [9, 10]. The above procedure may be carried out on 1-100 g scales without any problem. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION TMAFC was used for the oxidation of some alcohols and polycyclic arenes under microwave irradiat ...
... corresponding carbonyl compound was accomplished by the procedure reported in earlier papers. [9, 10]. The above procedure may be carried out on 1-100 g scales without any problem. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION TMAFC was used for the oxidation of some alcohols and polycyclic arenes under microwave irradiat ...
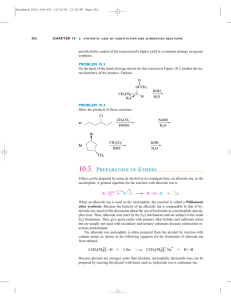
Types of reactions you know:
... Practicing Reactions: --A helpful resource is the companion website for the 6th edition of your textbook. Google “McMurrray Organic Chem” and it should be the first hit. I will also have a link on the SI website to the website. The “organic interactive” problems in each chapter are extremely helpfu ...
... Practicing Reactions: --A helpful resource is the companion website for the 6th edition of your textbook. Google “McMurrray Organic Chem” and it should be the first hit. I will also have a link on the SI website to the website. The “organic interactive” problems in each chapter are extremely helpfu ...
Chapter 4:Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions:
... expected products. Refer to the solubility rules to determine if solid forms. (D-D) double displacement: AB + CD AD + CB A double displacement reaction starts with two ionic compounds in which the ions exchange to produce new balanced ionic compounds. Always write the cation before the anion and v ...
... expected products. Refer to the solubility rules to determine if solid forms. (D-D) double displacement: AB + CD AD + CB A double displacement reaction starts with two ionic compounds in which the ions exchange to produce new balanced ionic compounds. Always write the cation before the anion and v ...
1. What is a Chemical Reaction?
... • A chemical reaction is the process by which atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances(s) with new chemical and physical properties. • A chemical reaction is another name for a chemical change. • When substances chemically react, observations can be made that provi ...
... • A chemical reaction is the process by which atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances(s) with new chemical and physical properties. • A chemical reaction is another name for a chemical change. • When substances chemically react, observations can be made that provi ...
Document
... To predict products of SR reactions, create a new compound with the lone metal ion and the anion from the reactanct compound. The cation from the reacctant compound becomes a lone element on the product side. ...
... To predict products of SR reactions, create a new compound with the lone metal ion and the anion from the reactanct compound. The cation from the reacctant compound becomes a lone element on the product side. ...
+ H 2 O(g)
... Balance the reaction. Describe the chemical process represented by this reaction. Write the name of each single reactant and product. ...
... Balance the reaction. Describe the chemical process represented by this reaction. Write the name of each single reactant and product. ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.