Organometallic Chemistry
... • Reactions of crotylmetal (2-butenylmetal) reagents with carbonyl substrates provide access to acyclic stereo- and enantioselective syntheses of β-methyl homoallylic alcohols. ...
... • Reactions of crotylmetal (2-butenylmetal) reagents with carbonyl substrates provide access to acyclic stereo- and enantioselective syntheses of β-methyl homoallylic alcohols. ...
Document
... The formation of carbon-carbon bonds is one of the most widely studied areas in organic synthesis. One class of carbon-carbon bond forming reactions involves the nucleophilic addition of vinyl or allyl organometallics to aldhydes, yielding allylic or homoallylic alcohols. The stereochemical unpredic ...
... The formation of carbon-carbon bonds is one of the most widely studied areas in organic synthesis. One class of carbon-carbon bond forming reactions involves the nucleophilic addition of vinyl or allyl organometallics to aldhydes, yielding allylic or homoallylic alcohols. The stereochemical unpredic ...
CHMY_271_practice_exam_3
... 11. (6 pt) If the following alkyl halide were to undergo elimination, predict the major product in each case, and explain your answer. You do not need to draw out the mechanism, but knowing the mechanism will help you to predict reasonable products. Br ...
... 11. (6 pt) If the following alkyl halide were to undergo elimination, predict the major product in each case, and explain your answer. You do not need to draw out the mechanism, but knowing the mechanism will help you to predict reasonable products. Br ...
A-level Paper 2 Practice Paper 6 - A
... When the initial concentration of C is 4.55 × 10–2 mol dm–3 and the initial concentration of D is 1.70 × 10–2 mol dm–3, the initial rate of reaction is 6.64 × 10–5 mol dm–3 s–1. Calculate the value of the rate constant at this temperature and deduce its units. Calculation ........................... ...
... When the initial concentration of C is 4.55 × 10–2 mol dm–3 and the initial concentration of D is 1.70 × 10–2 mol dm–3, the initial rate of reaction is 6.64 × 10–5 mol dm–3 s–1. Calculate the value of the rate constant at this temperature and deduce its units. Calculation ........................... ...
131 Learning Objectives
... Name organic compounds with carbon-heteroatom single bonds (oxygen, halogens, sulfur) Identify 1°, 2°, 3° alcohols and alkyl halides Predict the products or reactants for following reactions: Alcohol dehydration Alcohol oxidation Sulfur oxidation Sulfur reduction Chapter 15: The 3-D Shape of M ...
... Name organic compounds with carbon-heteroatom single bonds (oxygen, halogens, sulfur) Identify 1°, 2°, 3° alcohols and alkyl halides Predict the products or reactants for following reactions: Alcohol dehydration Alcohol oxidation Sulfur oxidation Sulfur reduction Chapter 15: The 3-D Shape of M ...
a. Rank by acidity. The most acidic compound is 1, wh
... Of the following reactions that generate glycols, one reacts with periodic acid as shown above, while the second does not react with the periodic acid. Draw the structures obtained for each of these reactions. Assume proper work-up for each step. (12 points) O ...
... Of the following reactions that generate glycols, one reacts with periodic acid as shown above, while the second does not react with the periodic acid. Draw the structures obtained for each of these reactions. Assume proper work-up for each step. (12 points) O ...
Final Exam Review Sheet Chemistry 110a/1998
... cation, and anion using a resonance and molecular orbital argument. How does the allylic radical compare in stability to 3°, 2°, and 1°? How about the allylic cation, in this regard? The pKa of an allylic hydrogen is 41: how can you use this value to say that the allylic anion is more stable than th ...
... cation, and anion using a resonance and molecular orbital argument. How does the allylic radical compare in stability to 3°, 2°, and 1°? How about the allylic cation, in this regard? The pKa of an allylic hydrogen is 41: how can you use this value to say that the allylic anion is more stable than th ...
Macromolecules
... II. 7. Lipids are defined by their ___________________. They do not dissolve in polar solvents like _______________. Lipids are ________-________________. _________, _____________, ____________ and the __________ are all lipids. What is their function? One group, the ____________________ are the maj ...
... II. 7. Lipids are defined by their ___________________. They do not dissolve in polar solvents like _______________. Lipids are ________-________________. _________, _____________, ____________ and the __________ are all lipids. What is their function? One group, the ____________________ are the maj ...
Lecture 9a - University of California, Los Angeles
... The problem in this reaction is that aldehydes are generally more reactive than ketones which means that both groups would react with the Grignard reagent, albeit with different rates The higher reactivity of the aldehyde is exploited in the formation of the cyclic acetal using 1,3-propanediol ...
... The problem in this reaction is that aldehydes are generally more reactive than ketones which means that both groups would react with the Grignard reagent, albeit with different rates The higher reactivity of the aldehyde is exploited in the formation of the cyclic acetal using 1,3-propanediol ...
Problem Set: Empirical and Molecular Formulas
... 1molAl (OH )3 34.0g HCl needs 24.2 g Al(OH)3 to react completely, 12.0g Al(OH)3 is not enough 3. Ammonia, NH3, is used throughout the world as a fertilizer. To manufacture ammonia, nitrogen, N2, is combined with hydrogen, H2, in a synthesis reaction. a) Write a balanced chemical equation for the for ...
... 1molAl (OH )3 34.0g HCl needs 24.2 g Al(OH)3 to react completely, 12.0g Al(OH)3 is not enough 3. Ammonia, NH3, is used throughout the world as a fertilizer. To manufacture ammonia, nitrogen, N2, is combined with hydrogen, H2, in a synthesis reaction. a) Write a balanced chemical equation for the for ...
File
... 18. Half-life period of a radioactive element is 100 seconds. Calculate the disintegration constant and average life period. How much time will it take for 90% decay? 19. (a) Describe the structure and magnetic behaviour of [Ni(CN)4]2– ion on the basis of valence bond theory. (Atomic No. of Ni = 28) ...
... 18. Half-life period of a radioactive element is 100 seconds. Calculate the disintegration constant and average life period. How much time will it take for 90% decay? 19. (a) Describe the structure and magnetic behaviour of [Ni(CN)4]2– ion on the basis of valence bond theory. (Atomic No. of Ni = 28) ...
Chapter 18 lectures as pdf
... • Thus two sites for nucleophilic attack • Called 1,2 and 1,4 (or conjugate addition) • 1,2 addition is kinetic • Conjugate addition is thermodynamic • Cuprates also do conjugate addition ...
... • Thus two sites for nucleophilic attack • Called 1,2 and 1,4 (or conjugate addition) • 1,2 addition is kinetic • Conjugate addition is thermodynamic • Cuprates also do conjugate addition ...
Chemistry: Spring Semester Lecture Notes - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... -- requires a catalyst (usually a finely-divided _________) to rupture the multiple bond H ...
... -- requires a catalyst (usually a finely-divided _________) to rupture the multiple bond H ...
1. Dehydration Synthesis 2. Fermentation
... remove an H from one hydroxyl and an OH from the other. This becomes water. ...
... remove an H from one hydroxyl and an OH from the other. This becomes water. ...
Nitrogen Compounds
... the reaction is normally carried out in ice. An aliphatic Diazonium salt is very unstable, so only aromatics are used. The lone pairs present in the salt can participate in the benzene ring, making it more stable. More correctly this is due to overlap of p-orbitals in the diazo group with the p-syst ...
... the reaction is normally carried out in ice. An aliphatic Diazonium salt is very unstable, so only aromatics are used. The lone pairs present in the salt can participate in the benzene ring, making it more stable. More correctly this is due to overlap of p-orbitals in the diazo group with the p-syst ...
Chem 130 Fall 2004 Exam 3 Study Guide Chapter 8.1
... Conversion into alkyl halides (with HCl, HBr, SOCl2) Dehydration to form alkene (with H2SO4, concentrated, ∆) Oxidation: Primary alcohol to aldehydes (with PCC) Primary alcohol to carboxylic acids (with CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Secondary alcohol to ketones (with PCC or CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Tertiary alcoho ...
... Conversion into alkyl halides (with HCl, HBr, SOCl2) Dehydration to form alkene (with H2SO4, concentrated, ∆) Oxidation: Primary alcohol to aldehydes (with PCC) Primary alcohol to carboxylic acids (with CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Secondary alcohol to ketones (with PCC or CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Tertiary alcoho ...
I (21 points) Complete the following reactions by providing starting
... A. (JOC 2008, ASAP, Hartung) The reagent 2-chloro-bis[menth-1-yloxycarbonyl]-1,3,2dioxaphospholane was shown to be useful in determining the enatiomeric purity of chiral alcohols via 31P NMR. The enatiomerically pure phosphorous reagent reacts with chiral alcohols to form diasteromers as shown below ...
... A. (JOC 2008, ASAP, Hartung) The reagent 2-chloro-bis[menth-1-yloxycarbonyl]-1,3,2dioxaphospholane was shown to be useful in determining the enatiomeric purity of chiral alcohols via 31P NMR. The enatiomerically pure phosphorous reagent reacts with chiral alcohols to form diasteromers as shown below ...
Mechanistic Assignment
... chloroacetyl chloride. The product of that reaction (2) was then reacted with acetic anhydride to give cyclic compound 3 which isomerized to cyclic compound 4. A conjugate addition of HS– followed by reaction with CH3O– opened up the ring to give compound 5. Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of both amide a ...
... chloroacetyl chloride. The product of that reaction (2) was then reacted with acetic anhydride to give cyclic compound 3 which isomerized to cyclic compound 4. A conjugate addition of HS– followed by reaction with CH3O– opened up the ring to give compound 5. Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of both amide a ...
Ch 4/5 Power Point - Carbon/Macromolecules
... – At end of C skeleton aldehyde - ex. proponal – Within C skeleton – ketone – ex. acetone ...
... – At end of C skeleton aldehyde - ex. proponal – Within C skeleton – ketone – ex. acetone ...
Organic Reactions 1
... Condensation is an organic reaction when two molecules combine, usually in the presence of a catalyst, with the elimination of water or some other simple molecule. Catalysts commonly used in condensation reactions include acids and bases. The combination of two identical molecules is known as self-c ...
... Condensation is an organic reaction when two molecules combine, usually in the presence of a catalyst, with the elimination of water or some other simple molecule. Catalysts commonly used in condensation reactions include acids and bases. The combination of two identical molecules is known as self-c ...
Organic Chemistry 1 1st Hour Exam Student ID # Name
... with the molecular formula C5H10 as possible and name each isomer according to the IUPAC nomenclature. You may use the condensed formula to draw the structure if you want. ...
... with the molecular formula C5H10 as possible and name each isomer according to the IUPAC nomenclature. You may use the condensed formula to draw the structure if you want. ...
Workshop 9
... mechanisms are well established. In other cases they may be speculative and are likely to change as more data become available. Mechanisms map the path by which the reactants change into products and the movement of electrons that accompanies this change. They also show how reactants come together, ...
... mechanisms are well established. In other cases they may be speculative and are likely to change as more data become available. Mechanisms map the path by which the reactants change into products and the movement of electrons that accompanies this change. They also show how reactants come together, ...
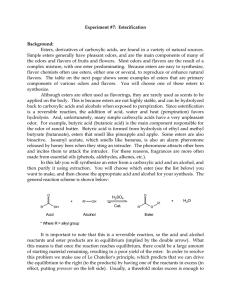
102 Lab 7 Esters Fall05
... made from essential oils (phenols, aldehydes, alkenes, etc.). In this lab you will synthesize an ester from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, and then purify it using extraction. You will choose which ester (see the list below) you want to make, and then choose the appropriate acid and alcohol for y ...
... made from essential oils (phenols, aldehydes, alkenes, etc.). In this lab you will synthesize an ester from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, and then purify it using extraction. You will choose which ester (see the list below) you want to make, and then choose the appropriate acid and alcohol for y ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.