Year 12 Unit 1b - Moulsham High School
... Name or give chemical formulae for suitable reagents for carrying out this conversion. .......................................... mixed with ............................................................ ...
... Name or give chemical formulae for suitable reagents for carrying out this conversion. .......................................... mixed with ............................................................ ...
File
... The bit ending in –yl comes from the alcohol that has formed it and is next to the single bonded oxygen. The reaction is reversible. The reaction is quite slow and needs heating under reflux, (often for several hours or days). Low yields (50% ish) are achieved. An acid catalyst (H2SO4) is needed. ...
... The bit ending in –yl comes from the alcohol that has formed it and is next to the single bonded oxygen. The reaction is reversible. The reaction is quite slow and needs heating under reflux, (often for several hours or days). Low yields (50% ish) are achieved. An acid catalyst (H2SO4) is needed. ...
chem 217 intermediate chemistry ii assignment #5 3/9/00 due: 3/23/00
... The differences are due to the fact that carbonyl groups of ketones and esters are less electronwithdrawing that those of aldehydes because alkyl (ketone) and alkoxy (ester) groups are electron donating thus counteracting the electron-withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group. Thus, ketones and ester ...
... The differences are due to the fact that carbonyl groups of ketones and esters are less electronwithdrawing that those of aldehydes because alkyl (ketone) and alkoxy (ester) groups are electron donating thus counteracting the electron-withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group. Thus, ketones and ester ...
Slide 1
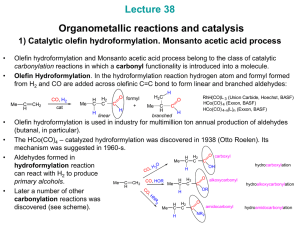
... decomposition. becomes stronger Bulkier PR3 favor greater linear / branched becomes more hydride-like H aldehyde ratios ( up to 8 : 1). CO Finally, more hydride-like Co-H promotes aldehyde OC Co hydrogenation to alcohols: CO ...
... decomposition. becomes stronger Bulkier PR3 favor greater linear / branched becomes more hydride-like H aldehyde ratios ( up to 8 : 1). CO Finally, more hydride-like Co-H promotes aldehyde OC Co hydrogenation to alcohols: CO ...
Laboratory 21: Properties of Alkanes, Alkenes, and Alkynes
... to different physical and chemical properties. ...
... to different physical and chemical properties. ...
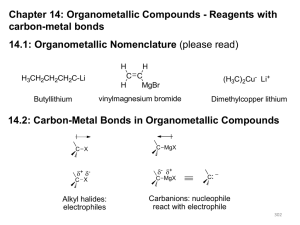
Organometallic Compounds - Reagents
... to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of progressively simpler structures along the pathway which ultimately leads to simple or commercially available starting mat ...
... to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of progressively simpler structures along the pathway which ultimately leads to simple or commercially available starting mat ...
Synthesis of the hexoses
... For a, c, e, and g, l=Pummerer reaction, P=DIBAL, J=deprotection. a: 1 (9O%), 2 @l%), 3 (90810).C: 1 (%%6),2 @5%), 3 (90%). e: 1 (87%), 2 (81%), 3 (84%). g: I (71%), 2 (77%), 3 (61%). For b, d, f, and h, l=Pummerer reaction, Z=WCQ/MeOH, ...
... For a, c, e, and g, l=Pummerer reaction, P=DIBAL, J=deprotection. a: 1 (9O%), 2 @l%), 3 (90810).C: 1 (%%6),2 @5%), 3 (90%). e: 1 (87%), 2 (81%), 3 (84%). g: I (71%), 2 (77%), 3 (61%). For b, d, f, and h, l=Pummerer reaction, Z=WCQ/MeOH, ...
Reductive Coupling Reactions of Nitrones and Imines
... Reductive coupling is generally thought to proceed by a single-electron transfer (SET) from a reducing reagent to either the carbonyl compound or the C=N component, forming a radical anion. This relatively stable species then undergoes addition to the coupling partner followed by a second SET and pr ...
... Reductive coupling is generally thought to proceed by a single-electron transfer (SET) from a reducing reagent to either the carbonyl compound or the C=N component, forming a radical anion. This relatively stable species then undergoes addition to the coupling partner followed by a second SET and pr ...
Enzymatic synthesis of sialic acid derivative by immobilized lipase
... anhydrides, fatty acid methyl esters, and triacylglycerols with different chain lengths as acyl donors on yield was investigated. Nonanoic anhydride showed the best performance of all the nonanoyl samples in the esterification reaction, producing an 87.7% yield (1.3-fold increase with respect to nona ...
... anhydrides, fatty acid methyl esters, and triacylglycerols with different chain lengths as acyl donors on yield was investigated. Nonanoic anhydride showed the best performance of all the nonanoyl samples in the esterification reaction, producing an 87.7% yield (1.3-fold increase with respect to nona ...
Microsoft Word
... and two different carbon ligands. It is well known that sulfoxides participate as neighbouring groups in a number of reactions. Sulfoxide group participation in halohydrin formation from cyclic and simple acyclic olefins has been demonstrated, but its potential to produce highly functionalized produ ...
... and two different carbon ligands. It is well known that sulfoxides participate as neighbouring groups in a number of reactions. Sulfoxide group participation in halohydrin formation from cyclic and simple acyclic olefins has been demonstrated, but its potential to produce highly functionalized produ ...
Reaction of orthoesters with alcohols in the presence of acidic
... Claisen-Johnson orthoester rearrangement1 is an important C-C bond forming reaction, which yields vinylic esters. This reaction being heat promoted is generally low yielding. The poor conversion is usually attributed to the inactivation of the catalyst or decomposition of the orthoester and to compe ...
... Claisen-Johnson orthoester rearrangement1 is an important C-C bond forming reaction, which yields vinylic esters. This reaction being heat promoted is generally low yielding. The poor conversion is usually attributed to the inactivation of the catalyst or decomposition of the orthoester and to compe ...
Microsoft Word - Open Access Repository of Indian Theses
... of benzene sulfonic acid 46 in presence of formic acid which furnished compound 47, and it was converted to Boc-imine compound 48 by using K2CO3. Proline catalysed manich was performed between benzyl protected α-oxy aldehyde 49 and Boc-imine 48 to give compound 50. Two carbon Wittig reaction provide ...
... of benzene sulfonic acid 46 in presence of formic acid which furnished compound 47, and it was converted to Boc-imine compound 48 by using K2CO3. Proline catalysed manich was performed between benzyl protected α-oxy aldehyde 49 and Boc-imine 48 to give compound 50. Two carbon Wittig reaction provide ...
Exam Name___________________________________
... 19) Typically, amides will hydrolyze under __________ conditions than esters. A) milder B) stronger C) more saline D) more dilute E) less vigorous ...
... 19) Typically, amides will hydrolyze under __________ conditions than esters. A) milder B) stronger C) more saline D) more dilute E) less vigorous ...
Synthetic Applications of Zinc Borohydride
... amino acids by sodium in ethanol.25 Subsequently, LiAlH426 and NaBH427 were used for the reduction of esters. Moreover, reduction of amino acids directly to the amino alcohols was accomplished using LiAlH428 or BMS in the presence of BF3 • Et2O.29 Metal borohydrides do not reduce amino acids; howeve ...
... amino acids by sodium in ethanol.25 Subsequently, LiAlH426 and NaBH427 were used for the reduction of esters. Moreover, reduction of amino acids directly to the amino alcohols was accomplished using LiAlH428 or BMS in the presence of BF3 • Et2O.29 Metal borohydrides do not reduce amino acids; howeve ...
Chapter 10 Outline: Alcohols
... Alcohol Reactions. Provide correct organic product(s) and the mechanism for the following reactions. If stereochemistry pertains, ensure it is clearly demonstrated. If there is more than one product, then circle the major product. OH H3PO4, heat ...
... Alcohol Reactions. Provide correct organic product(s) and the mechanism for the following reactions. If stereochemistry pertains, ensure it is clearly demonstrated. If there is more than one product, then circle the major product. OH H3PO4, heat ...
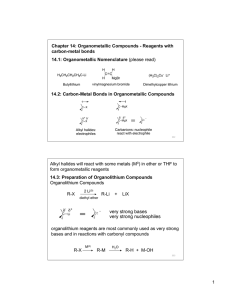
Grignard Reagents
... to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of progressively simpler structures along the pathway which ultimately leads to simple or commercially available starting mat ...
... to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of progressively simpler structures along the pathway which ultimately leads to simple or commercially available starting mat ...
Alkenes—The Products of Elimination
... • The reaction is concerted—all bonds are broken and formed in a single step. ...
... • The reaction is concerted—all bonds are broken and formed in a single step. ...
Chapter 16: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides
... The ether oxygen is sp3-hybridized and tetrahedral. In general, the C-O bonds of ethers have low reactivity. 16.3: Physical Properties of Ethers the O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Cr ...
... The ether oxygen is sp3-hybridized and tetrahedral. In general, the C-O bonds of ethers have low reactivity. 16.3: Physical Properties of Ethers the O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Cr ...
Compounds Containing a C=O (Carbonyl) Group
... an aldehyde or ketone by treatment with aqueous acid. Because this reaction is also an equilibrium process, it is ...
... an aldehyde or ketone by treatment with aqueous acid. Because this reaction is also an equilibrium process, it is ...
16 Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes
... Primary alcohols (1o) easily oxidize to form aldehydes with can then oxidize to form carboxylic acids. Secondary alcohols (2o) oxidize to ketones. Tertiary alcohols (3o) do not oxidize. Oxidation of alcohols or aldehydes requires an oxidizing agent that itself will get reduced. A common oxidizing ag ...
... Primary alcohols (1o) easily oxidize to form aldehydes with can then oxidize to form carboxylic acids. Secondary alcohols (2o) oxidize to ketones. Tertiary alcohols (3o) do not oxidize. Oxidation of alcohols or aldehydes requires an oxidizing agent that itself will get reduced. A common oxidizing ag ...
Abstracts - Thieme Verlag
... an amine. Alkynes undergo very efficient hydroalkoxyesterifications of the type extensively studied in alkene carbonylation chemistry, but in this case giving unsaturated esters and seemingly by a different mechanism that allows for a wider range of reaction pathways. In this chapter, examples are p ...
... an amine. Alkynes undergo very efficient hydroalkoxyesterifications of the type extensively studied in alkene carbonylation chemistry, but in this case giving unsaturated esters and seemingly by a different mechanism that allows for a wider range of reaction pathways. In this chapter, examples are p ...
Solutions (DOC format, upgraded July 20)
... 5. The work W done on gas during cooling and compression stages can be found from equation ...
... 5. The work W done on gas during cooling and compression stages can be found from equation ...
Problem 5. The Second Law of thermodynamics
... 5. The work W done on gas during cooling and compression stages can be found from equation ...
... 5. The work W done on gas during cooling and compression stages can be found from equation ...
Problem 5. The Second Law of thermodynamics
... 5. The work W done on gas during cooling and compression stages can be found from equation ...
... 5. The work W done on gas during cooling and compression stages can be found from equation ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.