Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013
... (ii) Link the structure of enantiomers to a physical property that can be used to distinguish them from non-optically active molecules. ...
... (ii) Link the structure of enantiomers to a physical property that can be used to distinguish them from non-optically active molecules. ...
Page 1 - WordPress.com
... Draw the repeating unit of the polyamide formed by the reaction of propanedioic acid with hexane-1,6-diamine.(2) In terms of the intermolecular forces between the polymer chains, explain why polyamides can be made into fibres suitable for use in sewing and weaving, whereas polyalkenes usually produc ...
... Draw the repeating unit of the polyamide formed by the reaction of propanedioic acid with hexane-1,6-diamine.(2) In terms of the intermolecular forces between the polymer chains, explain why polyamides can be made into fibres suitable for use in sewing and weaving, whereas polyalkenes usually produc ...
Enzymological basis of nitrogen fixation
... vivo activity would be only ca 40% dinitrogen reduction with a 3 H2/N2 ratio. Substrate reduction by MoFe-P requires Fe-P as the electron source with ATP hydrolysis; other reducing agents are able to reduce the MoFe-P cluster but do not drive substrate reduction. ATP hydrolysis requires both compone ...
... vivo activity would be only ca 40% dinitrogen reduction with a 3 H2/N2 ratio. Substrate reduction by MoFe-P requires Fe-P as the electron source with ATP hydrolysis; other reducing agents are able to reduce the MoFe-P cluster but do not drive substrate reduction. ATP hydrolysis requires both compone ...
Document
... Carbohydrates can be defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, acids, their simple derivatives and their polymers having acetal type linkages. They may be classified according to their degree of polymerization and may be divided into three principal groups, namely sugars, oligosaccharide ...
... Carbohydrates can be defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, acids, their simple derivatives and their polymers having acetal type linkages. They may be classified according to their degree of polymerization and may be divided into three principal groups, namely sugars, oligosaccharide ...
what are acyl chlorides?
... This is an easy way of producing an ester from an alcohol because it happens at room temperature, and is irreversible. Making an ester from an alcohol and a carboxylic acid (the usual alternative method) needs heat, a catalyst and is reversible - so that it is difficult to get a 100% conversion. ...
... This is an easy way of producing an ester from an alcohol because it happens at room temperature, and is irreversible. Making an ester from an alcohol and a carboxylic acid (the usual alternative method) needs heat, a catalyst and is reversible - so that it is difficult to get a 100% conversion. ...
Naming Aldehydes & Ketones
... Biochemical Oxidation of Aldehydes • When our cells ‘burn’ carbohydrates, they take advantage of the aldehyde reactivity. • The aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid and is eventually converted to carbon dioxide, which is then exhaled. • This stepwise oxidation provides some of the energy neces ...
... Biochemical Oxidation of Aldehydes • When our cells ‘burn’ carbohydrates, they take advantage of the aldehyde reactivity. • The aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid and is eventually converted to carbon dioxide, which is then exhaled. • This stepwise oxidation provides some of the energy neces ...
Aldehydes and Ketones - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Reduction of aldes and kets to alcohols O R-C-H + H2 –Pt/Pd R-C-OH RCHO + H2 –Pt/Pd RCH2OH O O R-C-R + H2 –Pt/Pd R-C-R RCOR + H2 –Pt/Pd RCHOHR ...
... Reduction of aldes and kets to alcohols O R-C-H + H2 –Pt/Pd R-C-OH RCHO + H2 –Pt/Pd RCH2OH O O R-C-R + H2 –Pt/Pd R-C-R RCOR + H2 –Pt/Pd RCHOHR ...
Chapter 12 Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
... CH3CH2CH2OH in the following conditions: A. H+, heat ...
... CH3CH2CH2OH in the following conditions: A. H+, heat ...
Enolate Chemistry - Institut für Organische Chemie
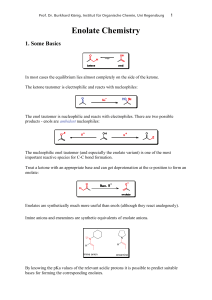
... combined with the steric accessibility of the α-protons, is usually enough to be able to selectively form the kinetic enolate. NOTE: The more substituted enolate is not always the thermodynamically more stable enolate; in some cases steric hindrance can destabilise the more substituted enolate; thus ...
... combined with the steric accessibility of the α-protons, is usually enough to be able to selectively form the kinetic enolate. NOTE: The more substituted enolate is not always the thermodynamically more stable enolate; in some cases steric hindrance can destabilise the more substituted enolate; thus ...
rev2
... 2. Know that aldehydes and ketones are functional isomers (constitutional isomers that involve having different functional groups) 3. Understand why aldehydes and ketones have lower bps than alcohols, but about the same solubility in water as alcohols. 4. Know the chemical properties of aldehydes an ...
... 2. Know that aldehydes and ketones are functional isomers (constitutional isomers that involve having different functional groups) 3. Understand why aldehydes and ketones have lower bps than alcohols, but about the same solubility in water as alcohols. 4. Know the chemical properties of aldehydes an ...
International Indian School Dammam
... (a) Write electrode reactions when a lead storage battery is discharging (b) Galvanized iron pipe does not rust even if the zinc coating is broken. Why? (c) Calculate the Λ0 of NH4OH from the following data: Λ 0 of NaOH = 257.7 Scm2mol-1 Λ 0 of NaCl = 140.6 Scm2mol-1 Λ 0 of NH4 Cl =129.8 Scm2mol-1 ( ...
... (a) Write electrode reactions when a lead storage battery is discharging (b) Galvanized iron pipe does not rust even if the zinc coating is broken. Why? (c) Calculate the Λ0 of NH4OH from the following data: Λ 0 of NaOH = 257.7 Scm2mol-1 Λ 0 of NaCl = 140.6 Scm2mol-1 Λ 0 of NH4 Cl =129.8 Scm2mol-1 ( ...
CHEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 4 April 15, 2003 Name
... (9 pts) Mark as true (T) or false (F) the following statements. Do not explain! • Fischer esterification occurs only in strongly basic conditions; • Amides are less reactive than acid chlorides but more reactive than esters; • Saponification is the process of base-catalyzed hydrolysis of esters; • L ...
... (9 pts) Mark as true (T) or false (F) the following statements. Do not explain! • Fischer esterification occurs only in strongly basic conditions; • Amides are less reactive than acid chlorides but more reactive than esters; • Saponification is the process of base-catalyzed hydrolysis of esters; • L ...
WRL3502.tmp
... General Concepts Alkyl halides are most commonly synthesized from alcohols by replacing the hydroxyl group with a halide substituent. This is an example of nucleophilic aliphatic substitution, which is part of a very important group of reactions. The overall reaction is the same, but the mechanism v ...
... General Concepts Alkyl halides are most commonly synthesized from alcohols by replacing the hydroxyl group with a halide substituent. This is an example of nucleophilic aliphatic substitution, which is part of a very important group of reactions. The overall reaction is the same, but the mechanism v ...
Photocatalytic reduction of aromatic azides to amines using CdS
... to ensure the absence of product formation by direct azide photolysis. Table 1 shows the percentage conversion of azides to their corresponding amines under standard conditions that included 15 min irradiation at 298 K. With solutions that are 6 × 10⫺6 M in nanoparticle and 3.7 × 10⫺3 M azide and me ...
... to ensure the absence of product formation by direct azide photolysis. Table 1 shows the percentage conversion of azides to their corresponding amines under standard conditions that included 15 min irradiation at 298 K. With solutions that are 6 × 10⫺6 M in nanoparticle and 3.7 × 10⫺3 M azide and me ...
evans enolate alkylation
... R The N-acyl oxazolidinones are similar to esters in terms of ability to form enolates, most commonly with LDA or the base that functions as its sodium analogues, NaHMDS. Since these are essentially amides, the enolates are entirely the Z- isomer (using the particular definition for enolates). The m ...
... R The N-acyl oxazolidinones are similar to esters in terms of ability to form enolates, most commonly with LDA or the base that functions as its sodium analogues, NaHMDS. Since these are essentially amides, the enolates are entirely the Z- isomer (using the particular definition for enolates). The m ...
Week # 6 Homework doc
... The aldehyde and alcohol approach each other as follows because of the attraction of opposite charges on the polar groups. The reaction is written as an equilibrium because the hemiacetal is unstable and reverts back to the original aldehyde and alcohol. 1. The alcohol oxygen becomes bonded to the c ...
... The aldehyde and alcohol approach each other as follows because of the attraction of opposite charges on the polar groups. The reaction is written as an equilibrium because the hemiacetal is unstable and reverts back to the original aldehyde and alcohol. 1. The alcohol oxygen becomes bonded to the c ...
When 1°, 2°, aromatic amines or aryl amines . (Rand
... a Zwitterion). It is formed by the reaction of on acidic group (-S020H) and a basic group (-NH2) that are part of the same molecule, hence it is also called inner salt. It is interesting to note that its properties are different from that of a typical amine and a sulphonic acid. Such properties are ...
... a Zwitterion). It is formed by the reaction of on acidic group (-S020H) and a basic group (-NH2) that are part of the same molecule, hence it is also called inner salt. It is interesting to note that its properties are different from that of a typical amine and a sulphonic acid. Such properties are ...
X-ray Structure and Reactivity of (η4
... 1H NMR at that temperature over 2 h. However, 7 showed catalytic activity comparable to 1 in the racemization of optically active 1-phenylethanol and in the transfer hydrogenation of acetophenone with 2-propanol. The optical purity of (S)-1-phenylethanol (>99% ee, 0.2 M) in toluene was changed to 45 ...
... 1H NMR at that temperature over 2 h. However, 7 showed catalytic activity comparable to 1 in the racemization of optically active 1-phenylethanol and in the transfer hydrogenation of acetophenone with 2-propanol. The optical purity of (S)-1-phenylethanol (>99% ee, 0.2 M) in toluene was changed to 45 ...
Tech Info - Davis Instruments
... Here, the enolate ion of one compound undergoes nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl carbon of a different compound. Crossed-condensation products are usually undesirable since they result in a mixture of products, and reduce the yield of a desired product. Careful selection of starting materials w ...
... Here, the enolate ion of one compound undergoes nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl carbon of a different compound. Crossed-condensation products are usually undesirable since they result in a mixture of products, and reduce the yield of a desired product. Careful selection of starting materials w ...
Student Worksheet Part 1 Synthesis w/ answers
... 3. The reaction can only happen at higher temperatures, which ties in with (2) and means that removing sample from the reaction vessel essentially quenches (stops) the reaction as soon as it cools below 200°C. 4. Because the reaction is relatively slow, thermodynamic considerations are important, me ...
... 3. The reaction can only happen at higher temperatures, which ties in with (2) and means that removing sample from the reaction vessel essentially quenches (stops) the reaction as soon as it cools below 200°C. 4. Because the reaction is relatively slow, thermodynamic considerations are important, me ...
Solvothermal Synthesis of Polyazomethine Microspheres
... 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-nitrophenyl)-21H,23H-porphine was synthesised according to the previously reported procedure[S2] with a little modified. 4-nitrobenzaldehydewas(10.0 g,66mmol) dissolved in 60 mL nitrobenzene, to which 4.7ml (68mmol) pyrrole was added. Then the above solution was dropped into re ...
... 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-nitrophenyl)-21H,23H-porphine was synthesised according to the previously reported procedure[S2] with a little modified. 4-nitrobenzaldehydewas(10.0 g,66mmol) dissolved in 60 mL nitrobenzene, to which 4.7ml (68mmol) pyrrole was added. Then the above solution was dropped into re ...
Welcome to Class 7
... produced by glucose oxidase to convert a colorless compound into a colored one, which absorbs light at a particular wavelength. figure 7-9 ...
... produced by glucose oxidase to convert a colorless compound into a colored one, which absorbs light at a particular wavelength. figure 7-9 ...
Zn(BH4)2/Al2O3: A new synthetic method for the efficient
... agent is neutral and can be used in a range of aprotic solvents, such as ether, THF and DMF. In spite of this, zinc tetrahydroborate has been used less than regular reducing agents in laboratories for the reduction of organic compounds, probably because of its non-availability as a commercial reagen ...
... agent is neutral and can be used in a range of aprotic solvents, such as ether, THF and DMF. In spite of this, zinc tetrahydroborate has been used less than regular reducing agents in laboratories for the reduction of organic compounds, probably because of its non-availability as a commercial reagen ...
Zn mediated regioselective Barbier reaction of propargylic bromides
... alcohols but unsubstituted propargyl halides always gave the corresponding propargylic alcohols with high selectivity [9]. It was reported recently that allenic alcohols were obtained with high selectivity by indium-mediated coupling of propargylic halides with aldehydes in aqueous media [7]. The zi ...
... alcohols but unsubstituted propargyl halides always gave the corresponding propargylic alcohols with high selectivity [9]. It was reported recently that allenic alcohols were obtained with high selectivity by indium-mediated coupling of propargylic halides with aldehydes in aqueous media [7]. The zi ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.