Document
... acetate copolymer made from a mixture of equimolar Quantities of the two monomers. He found no polymer containing equal amounts of each monomer but, instead, found vinyl chloride: vinyl acetate ratios of 9:3, 7:3, 5:3 and 5:7 among the fractions. In 1936 Dostal made the first attach on the mechanism ...
... acetate copolymer made from a mixture of equimolar Quantities of the two monomers. He found no polymer containing equal amounts of each monomer but, instead, found vinyl chloride: vinyl acetate ratios of 9:3, 7:3, 5:3 and 5:7 among the fractions. In 1936 Dostal made the first attach on the mechanism ...
Terrahedron Letters. Vo1.32, No.43, pi 6089
... and formation of the acetonide 7 (72%) followed known chemistry in the methyl mannopyranoside tosylation of the equatorial hydroxyl4 was easily accomplished ...
... and formation of the acetonide 7 (72%) followed known chemistry in the methyl mannopyranoside tosylation of the equatorial hydroxyl4 was easily accomplished ...
WHAT IS MORPHINE -- ACTIVITY #1 What is morphine? What is it
... are surprisingly unreactive and are very useful as solvents for many many (but not all) classes of reaction ...
... are surprisingly unreactive and are very useful as solvents for many many (but not all) classes of reaction ...
Chem263_Nov 25_notes_2010
... Nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions usually take place in two steps: addition of the nucleophile and elimination of a leaving group. Although both steps can affect the overall rate of the reaction, it is generally the first step that is rate-limiting. Therefore any factor that makes the carbony ...
... Nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions usually take place in two steps: addition of the nucleophile and elimination of a leaving group. Although both steps can affect the overall rate of the reaction, it is generally the first step that is rate-limiting. Therefore any factor that makes the carbony ...
102 Lecture Ch14b
... • Oxidation can also be defined as a loss of bonds to hydrogen • This is because H is less electronegative than all other nonmetals (besides P which is the same), so adds electron density to any element with which it forms a covalent bond • Thiols can be oxidized to disulfides using I2 (or Br2) • In ...
... • Oxidation can also be defined as a loss of bonds to hydrogen • This is because H is less electronegative than all other nonmetals (besides P which is the same), so adds electron density to any element with which it forms a covalent bond • Thiols can be oxidized to disulfides using I2 (or Br2) • In ...
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION
... • Alcohols can readily be oxidised to the carbonyl moiety • This is an incredibly important reaction - you should realise that the carbonyl group is one of the cornerstones of C–C bond formation (organometallics, neutral nucleophiles, aldol, Julia, Peterson & Wittig reactions) R1 = H OH ...
... • Alcohols can readily be oxidised to the carbonyl moiety • This is an incredibly important reaction - you should realise that the carbonyl group is one of the cornerstones of C–C bond formation (organometallics, neutral nucleophiles, aldol, Julia, Peterson & Wittig reactions) R1 = H OH ...
revised hydrocarbons alkenes cycloalkenes
... These are heterogeneous catalyst as they are insoluble in reaction solution These noble metal catalysts can be filtered and reused. ...
... These are heterogeneous catalyst as they are insoluble in reaction solution These noble metal catalysts can be filtered and reused. ...
ppt
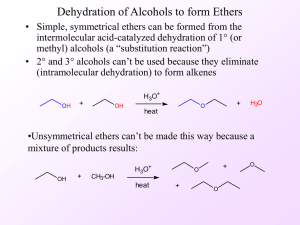
... The ether oxygen is sp3-hybridized and tetrahedral. In general, the C-O bonds of ethers have low reactivity. 16.3: Physical Properties of Ethers the O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Cr ...
... The ether oxygen is sp3-hybridized and tetrahedral. In general, the C-O bonds of ethers have low reactivity. 16.3: Physical Properties of Ethers the O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Cr ...
Retrosynthesis - Organic Chemistry
... • NOTE: the first bromination is of an alkane, EITHER Br2/light or NBS/light can be used, if we were brominating in an allylic position only NBS/light could have been used • then E2 elimination, which is the standard way to make an alkene avoiding cation intermediates Example Problem 2: Synthesize t ...
... • NOTE: the first bromination is of an alkane, EITHER Br2/light or NBS/light can be used, if we were brominating in an allylic position only NBS/light could have been used • then E2 elimination, which is the standard way to make an alkene avoiding cation intermediates Example Problem 2: Synthesize t ...
Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols
... • When C=C is conjugated with C=O, 1,2-addition or 1,4-addition may occur. • A 1,4-addition of an enolate ion is called the Michael reaction. ...
... • When C=C is conjugated with C=O, 1,2-addition or 1,4-addition may occur. • A 1,4-addition of an enolate ion is called the Michael reaction. ...
Document
... Carbocation Rearrangements in Hydrogen Halide Addition to Alkenes - In reactions involving carbocation intermediates, the carbocation may sometimes rearrange if a more stable carbocation can be formed by the rearrangement. These involve hydride and methyl shifts. H C ...
... Carbocation Rearrangements in Hydrogen Halide Addition to Alkenes - In reactions involving carbocation intermediates, the carbocation may sometimes rearrange if a more stable carbocation can be formed by the rearrangement. These involve hydride and methyl shifts. H C ...
Chemistry 209 - Experiment #4
... Corrosive!). In a few seconds, the mixture will turn dark, followed by a rather sudden rise in temperature to 5060C. Stir the mixture (still in the ice bath!) until its temperature has fallen to below 50C. NOTE: Do not use the thermometer as a stirring rod. Pour the mixture into a 250-mL (or large ...
... Corrosive!). In a few seconds, the mixture will turn dark, followed by a rather sudden rise in temperature to 5060C. Stir the mixture (still in the ice bath!) until its temperature has fallen to below 50C. NOTE: Do not use the thermometer as a stirring rod. Pour the mixture into a 250-mL (or large ...
HIGHER CfE CHEMISTRY Nature`s Chemistry
... a) Which type of natural substance has the structure shown? b) Draw the structural formulae for the molecules formed when the fragment is hydrolysed. c) To which class of substances do the hydrolysed products belong to? d) Why can the molecule shown be called a polypeptide? 24. Peptides are molecule ...
... a) Which type of natural substance has the structure shown? b) Draw the structural formulae for the molecules formed when the fragment is hydrolysed. c) To which class of substances do the hydrolysed products belong to? d) Why can the molecule shown be called a polypeptide? 24. Peptides are molecule ...
Alkaloids - Angelfire
... When the alkaloid is heated with hydroiodic acid at 150-300 C under pressure, Nmethyl groups are converted into methyl iodide CH3CONH-CH3 + HI CH 3CO NH2 + CH3 I CH3CON-CH3 +2 HI CH 3CONH2 +2CH3I I CH3 Lecture2 8.Hofmann's exhaustive methylation method Hofmann's exhaustive methylation method (18 ...
... When the alkaloid is heated with hydroiodic acid at 150-300 C under pressure, Nmethyl groups are converted into methyl iodide CH3CONH-CH3 + HI CH 3CO NH2 + CH3 I CH3CON-CH3 +2 HI CH 3CONH2 +2CH3I I CH3 Lecture2 8.Hofmann's exhaustive methylation method Hofmann's exhaustive methylation method (18 ...
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... Benzylic Radicals and Cations When toluene undergoes hydrogen abstraction from its methyl group it produces a benzyl radical ...
... Benzylic Radicals and Cations When toluene undergoes hydrogen abstraction from its methyl group it produces a benzyl radical ...
Chapter 24 Organic Chemistry
... August 28, 2009 [PROBLEM SET FROM R. CHANG TEST BANK] 36. Which choice gives the structures of the reaction products when the ester below is hydrolyzed in acid solution? ...
... August 28, 2009 [PROBLEM SET FROM R. CHANG TEST BANK] 36. Which choice gives the structures of the reaction products when the ester below is hydrolyzed in acid solution? ...
1 - University of Missouri
... Initial volume of bromobenzene Initial weight of bromobenzene (g) Initial weight of magnesium (g) Initial weight of benzophenone (g) Limiting Reactant Final amount of product Theoretical yield % yield melting point (°C) ...
... Initial volume of bromobenzene Initial weight of bromobenzene (g) Initial weight of magnesium (g) Initial weight of benzophenone (g) Limiting Reactant Final amount of product Theoretical yield % yield melting point (°C) ...
2 Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones GOB Structures
... • Aldehydes and ketones containing 3 to 10 carbon atoms are liquids. • The polar carbonyl group with a partially negative oxygen atom and a partially positive carbon atom has an influence on the boiling points and the solubility of aldehydes and ketones in water. ...
... • Aldehydes and ketones containing 3 to 10 carbon atoms are liquids. • The polar carbonyl group with a partially negative oxygen atom and a partially positive carbon atom has an influence on the boiling points and the solubility of aldehydes and ketones in water. ...
Document
... Several derivatives of carboxylic acids, i.e., acid chlorides, esters, and nitriles are more easily reduced than the parent carboxylic acid. These can be reduced to aldehydes with 1 equivalent of a milder reducing agent, which will not further reduce the aldehyde to a 1 alcohol. A suitable, ‘mild’ ...
... Several derivatives of carboxylic acids, i.e., acid chlorides, esters, and nitriles are more easily reduced than the parent carboxylic acid. These can be reduced to aldehydes with 1 equivalent of a milder reducing agent, which will not further reduce the aldehyde to a 1 alcohol. A suitable, ‘mild’ ...
WADE7Lecture10a
... The longest chain contains six carbon atoms, but it does not contain the carbon bonded to the hydroxyl group. The longest chain containing the carbon bonded to the —OH group is the one outlined by the green box, containing five carbon atoms. This chain is numbered from right to left in order to give ...
... The longest chain contains six carbon atoms, but it does not contain the carbon bonded to the hydroxyl group. The longest chain containing the carbon bonded to the —OH group is the one outlined by the green box, containing five carbon atoms. This chain is numbered from right to left in order to give ...
Grignard Reaction - OpenBU
... polarized, placing a partial negative charge on the carbon directly attached to the metal. The magnesium itself had a partial positive charge and the bromide has a partial negative charge. Mgo R ...
... polarized, placing a partial negative charge on the carbon directly attached to the metal. The magnesium itself had a partial positive charge and the bromide has a partial negative charge. Mgo R ...
Grignard Reaction - OpenBU
... polarized, placing a partial negative charge on the carbon directly attached to the metal. The magnesium itself had a partial positive charge and the bromide has a partial negative charge. Mgo R ...
... polarized, placing a partial negative charge on the carbon directly attached to the metal. The magnesium itself had a partial positive charge and the bromide has a partial negative charge. Mgo R ...
Grignard Reaction - Synthesis of Substituted Benzoic Acids
... polarized, placing a partial negative charge on the carbon directly attached to the metal. The magnesium itself had a partial positive charge and the bromide has a partial negative charge. Mgo R ...
... polarized, placing a partial negative charge on the carbon directly attached to the metal. The magnesium itself had a partial positive charge and the bromide has a partial negative charge. Mgo R ...
Document
... :B can be the excess of the amine Since it can provide the mixture of products, this process is less applied (see later) ...
... :B can be the excess of the amine Since it can provide the mixture of products, this process is less applied (see later) ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.