Organic Chemistry Durham School Board March
... Petroleum is a mixture of hydrocarbons of varying molecular sizes and states; therefore, its composition varies widely from region to region around the world. Fractional distillation (Figure 5.9) is a process for separating petroleum into its hydrocarbon components using boiling points. Each hydroca ...
... Petroleum is a mixture of hydrocarbons of varying molecular sizes and states; therefore, its composition varies widely from region to region around the world. Fractional distillation (Figure 5.9) is a process for separating petroleum into its hydrocarbon components using boiling points. Each hydroca ...
Abbreviated Chapter 17 Powerpoint
... • This result seems curious because oxygen is a strongly electronegative group, yet it donates electron density to stabilize the transition state and the sigma complex. ...
... • This result seems curious because oxygen is a strongly electronegative group, yet it donates electron density to stabilize the transition state and the sigma complex. ...
Identification of Functional Groups
... Note that the above equations are unbalanced skeleton equations showing only the major organic and inorganic products of the reactions. The most important feature of the reactions with KMnO4, is the disappearance of the purple color characteristic of the MnO4- ions in solution and the appearance of ...
... Note that the above equations are unbalanced skeleton equations showing only the major organic and inorganic products of the reactions. The most important feature of the reactions with KMnO4, is the disappearance of the purple color characteristic of the MnO4- ions in solution and the appearance of ...
Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
... dodec2. Number the chain in the direction that gives any substituent a lower number. (Numbers are not used in common names) a. If numbering in both directions gives the same number to a substituent, number in the direction that gives the lowest number to the alphabetically first substituent. 3. Subs ...
... dodec2. Number the chain in the direction that gives any substituent a lower number. (Numbers are not used in common names) a. If numbering in both directions gives the same number to a substituent, number in the direction that gives the lowest number to the alphabetically first substituent. 3. Subs ...
CH 3 Br + Nu
... 10. Which statement(s) is/are true of an E1 elimination? A) it is a two-step process and has the same first step as a SN1 mechanism B) it involves the formation of the carbocation from elimination of a good leaving group C) a common competing reaction is rearrangement of a less stable carbocation t ...
... 10. Which statement(s) is/are true of an E1 elimination? A) it is a two-step process and has the same first step as a SN1 mechanism B) it involves the formation of the carbocation from elimination of a good leaving group C) a common competing reaction is rearrangement of a less stable carbocation t ...
Solubility
... 2. One hydroxyl group is able to allow short chain lengths (up to 3C) to be watersoluble via H-bonding with water. But one hydroxyl is not sufficient for longer chains. As chain length increases, solubility in water decreases. HCH p.207 ...
... 2. One hydroxyl group is able to allow short chain lengths (up to 3C) to be watersoluble via H-bonding with water. But one hydroxyl is not sufficient for longer chains. As chain length increases, solubility in water decreases. HCH p.207 ...
13_lecture_ppt
... Common Names of Aldehydes • These names are taken from Latin roots as are the first 5 carboxylic acids • Greek letters are used to indicate the position of substituents with the carbon atom adjacent or bonded to the carbonyl carbon being the a carbon ...
... Common Names of Aldehydes • These names are taken from Latin roots as are the first 5 carboxylic acids • Greek letters are used to indicate the position of substituents with the carbon atom adjacent or bonded to the carbonyl carbon being the a carbon ...
Lab #1: Borneol Oxidation
... IV. Table of Reagents. Synthesis experiments require a table of all reagents, including the chemical name, formula, molecular weight, molecular structure, and physical properties (melting point, boiling point, density). You should record information for borneol, camphor, acetone, and acetic acid. Al ...
... IV. Table of Reagents. Synthesis experiments require a table of all reagents, including the chemical name, formula, molecular weight, molecular structure, and physical properties (melting point, boiling point, density). You should record information for borneol, camphor, acetone, and acetic acid. Al ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 1
... polar protic solvent? Dielectric constants (e) are given in parenthesis. A) acetic acid (e = 6) B) water (e = 78) C) methanol (e = 33) D) formic acid (e = 58) ...
... polar protic solvent? Dielectric constants (e) are given in parenthesis. A) acetic acid (e = 6) B) water (e = 78) C) methanol (e = 33) D) formic acid (e = 58) ...
Amino alcohols. XVII. Arylethanolamines
... Seedlings obtained from flats sown in the first week in February were transplanted into the field in’early June in the several years of plantings. Replicated plots were established at the ScottsblufE Field Station in a spacing and yield study under irrigation. HE RENEWED interest in the growing of p ...
... Seedlings obtained from flats sown in the first week in February were transplanted into the field in’early June in the several years of plantings. Replicated plots were established at the ScottsblufE Field Station in a spacing and yield study under irrigation. HE RENEWED interest in the growing of p ...
Final Sc. Ed. 423. Chemistry II
... Convert aldehydes and ketones into alcohols, alkanes by reduction processes. ...
... Convert aldehydes and ketones into alcohols, alkanes by reduction processes. ...
Chemistry - WordPress.com
... a. RN2 ??? 68. Several organic compounds are given, which compound has water solubility characteristics: a. The structure showing a phosphate salt 69. Given the chemical structures of quinine & quinidine, these are: a. Optical isomers 70. In the shown structure: ...
... a. RN2 ??? 68. Several organic compounds are given, which compound has water solubility characteristics: a. The structure showing a phosphate salt 69. Given the chemical structures of quinine & quinidine, these are: a. Optical isomers 70. In the shown structure: ...
advanced chem
... 7. If 2 or more “like” groups are in the chain, use prefixes (di-,tri-, tetra-) before the radical name with the #’s of the carbons they are attached to ...
... 7. If 2 or more “like” groups are in the chain, use prefixes (di-,tri-, tetra-) before the radical name with the #’s of the carbons they are attached to ...
EXPERIMENT 6 (Organic Chemistry II) Pahlavan/Cherif
... Aldehydes and ketones share the carbonyl functional group which features carbon doubly bonded to oxygen. In the case of ketones there are two carbon atoms bonded to the carbonyl carbon and no hydrogens. In the case of aldehydes there is at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbonyl carbon, the other ...
... Aldehydes and ketones share the carbonyl functional group which features carbon doubly bonded to oxygen. In the case of ketones there are two carbon atoms bonded to the carbonyl carbon and no hydrogens. In the case of aldehydes there is at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbonyl carbon, the other ...
Petrochemicals: Builder Molecules
... Experiments have determined that all carbon – carbon bonds in benzene are identical, with the bonding electrons shared among all 6 atoms. Benzene’s symbol is composed of two parts: the inner ring represents the equal sharing of bonding electrons among the carbon atoms, and ...
... Experiments have determined that all carbon – carbon bonds in benzene are identical, with the bonding electrons shared among all 6 atoms. Benzene’s symbol is composed of two parts: the inner ring represents the equal sharing of bonding electrons among the carbon atoms, and ...
Recall
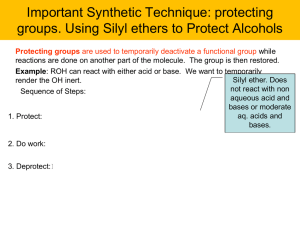
... groups. Using Silyl ethers to Protect Alcohols Protecting groups are used to temporarily deactivate a functional group while reactions are done on another part of the molecule. The group is then restored. Example: ROH can react with either acid or base. We want to temporarily Silyl ether. Does rende ...
... groups. Using Silyl ethers to Protect Alcohols Protecting groups are used to temporarily deactivate a functional group while reactions are done on another part of the molecule. The group is then restored. Example: ROH can react with either acid or base. We want to temporarily Silyl ether. Does rende ...
91391 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic
... Reactivity of organic compounds is limited to: substitution reactions using the following reagents: concentrated HCl, HBr, SOCl2, NaOH, KOH (in alcohol or aqueous solution), concentrated NH3, primary amines, primary alcohols/H+, H2O/H+, H2O/OH– (Substitution reactions include esterification, conde ...
... Reactivity of organic compounds is limited to: substitution reactions using the following reagents: concentrated HCl, HBr, SOCl2, NaOH, KOH (in alcohol or aqueous solution), concentrated NH3, primary amines, primary alcohols/H+, H2O/H+, H2O/OH– (Substitution reactions include esterification, conde ...
Year 1 Foundation course, section B2
... Year 1 Foundation course, section B2; Structure and reactivity of specific functional groups Alkanes - the most basic of all organic compounds, composed of only C and H, with no functional groups. General formulae CnH2n+2 (unless cyclic in which case it is CnH2n). Alkanes are generally quite unreac ...
... Year 1 Foundation course, section B2; Structure and reactivity of specific functional groups Alkanes - the most basic of all organic compounds, composed of only C and H, with no functional groups. General formulae CnH2n+2 (unless cyclic in which case it is CnH2n). Alkanes are generally quite unreac ...
$doc.title
... • Soaps are produced by the reac4on of natural fats and oils (triesters of glycerols) with a strong base • The polar carboxylate end of soap is hydrophilic and dissolves easily in waterThe nonpolar h ...
... • Soaps are produced by the reac4on of natural fats and oils (triesters of glycerols) with a strong base • The polar carboxylate end of soap is hydrophilic and dissolves easily in waterThe nonpolar h ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.