Inorganic and organic chemistry 1
... A hydrocarbon contains the elements carbon and hydrogen only. Hence there is 84.7 g of carbon present and 100 − 84.7 = 15.3 g of hydrogen. To find the empirical formula it is best to first calculate the number of moles of carbon and of hydrogen present. Moles C = 84.7/12.0 = 7.1 moles H = 15.3/1.0 = ...
... A hydrocarbon contains the elements carbon and hydrogen only. Hence there is 84.7 g of carbon present and 100 − 84.7 = 15.3 g of hydrogen. To find the empirical formula it is best to first calculate the number of moles of carbon and of hydrogen present. Moles C = 84.7/12.0 = 7.1 moles H = 15.3/1.0 = ...
N - Dr. May Notes
... Alkenes Alkenes have one or more double bond between two or more of the carbons. The carbons are sharing two pairs of electrons. Alkenes are unsaturated meaning that they can hold more hydrogens or that all the carbons do not have as much hydrogen around it as it could have. If hydrogen gas (plus a ...
... Alkenes Alkenes have one or more double bond between two or more of the carbons. The carbons are sharing two pairs of electrons. Alkenes are unsaturated meaning that they can hold more hydrogens or that all the carbons do not have as much hydrogen around it as it could have. If hydrogen gas (plus a ...
Learning Guide for Chapter 24
... attached will be higher in energy and therefore more reactive - the more electronegative elements pull electron density away from the already partially positive carbon. Another way to look at carboxylic acid derivative stability is to consider the stability of the substituents as independent ions - ...
... attached will be higher in energy and therefore more reactive - the more electronegative elements pull electron density away from the already partially positive carbon. Another way to look at carboxylic acid derivative stability is to consider the stability of the substituents as independent ions - ...
Rhenium(VII) Catalysis of Prins Cyclization Reactions
... Reaction was carried out with 1 mol % of O3ReOSiPh3. b Reaction was carried out with 30 mol % of VO(OPrn)3 instead of O3ReOSiPh3 and with 2 ...
... Reaction was carried out with 1 mol % of O3ReOSiPh3. b Reaction was carried out with 30 mol % of VO(OPrn)3 instead of O3ReOSiPh3 and with 2 ...
ch18 by dr. dina
... Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO2H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl compounds or carboxylic acid derivatives ...
... Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO2H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl compounds or carboxylic acid derivatives ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
... 5. Molecules with More Than Two Chirality Centers 6. Racemic Mixtures and Their Resolution 7. Physical Properties of Stereoisomers 8. A Brief Review of Isomerism ...
... 5. Molecules with More Than Two Chirality Centers 6. Racemic Mixtures and Their Resolution 7. Physical Properties of Stereoisomers 8. A Brief Review of Isomerism ...
CHAPTER 21 PHENOLS AND ARYL HALIDES
... (1) Having higher boiling points: phenols are able to form strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds . For example: phenol (bp,182℃) has a boiling point more than 70℃ higher than toluene(bp,110.6℃),even though the two molecular have almost the same molecular weight. (2) Modest solubility in water: the ab ...
... (1) Having higher boiling points: phenols are able to form strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds . For example: phenol (bp,182℃) has a boiling point more than 70℃ higher than toluene(bp,110.6℃),even though the two molecular have almost the same molecular weight. (2) Modest solubility in water: the ab ...
Organic Chemistry
... Chemistry of compounds that contain carbon (except: CO, CO 2, HCN, CO3-) Carbon is covalently bonded to another carbon, hydrogen and possibly to oxygen, a halogen or nitrogen Carbon joins other in chains or rings and can have branches coming off of these chains or rings One molecular formula can rep ...
... Chemistry of compounds that contain carbon (except: CO, CO 2, HCN, CO3-) Carbon is covalently bonded to another carbon, hydrogen and possibly to oxygen, a halogen or nitrogen Carbon joins other in chains or rings and can have branches coming off of these chains or rings One molecular formula can rep ...
Nucleophilic Substitution and b
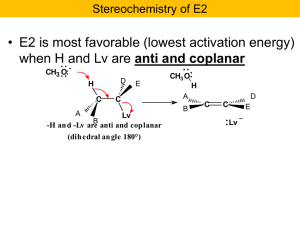
... Here is the crux of the matter: how can the non-reacting carbon change its configuration??? Further it does not always change but only if configuration of the reacting carbon changes!! We got a mixture of enantiomers, a racemic mixture. Something strange is happening!! Expect sulfur to attack the C- ...
... Here is the crux of the matter: how can the non-reacting carbon change its configuration??? Further it does not always change but only if configuration of the reacting carbon changes!! We got a mixture of enantiomers, a racemic mixture. Something strange is happening!! Expect sulfur to attack the C- ...
Stereoselective Reduction of Ketones with Sodium Borohydride
... Grignard Reagents – Developed by Victor Grignard in the turn of the 20th century – Discovered: Organic halides and magnesium form organomagnesium reagents Called organometallic compounds ...
... Grignard Reagents – Developed by Victor Grignard in the turn of the 20th century – Discovered: Organic halides and magnesium form organomagnesium reagents Called organometallic compounds ...
Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions
... Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions Addition of Organometallic Reagents to Carbonyl Derivatives • addition to aldehydes & ketones ...
... Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions Addition of Organometallic Reagents to Carbonyl Derivatives • addition to aldehydes & ketones ...
Camp 1 - TypePad
... • Phenols are weak acids and react with NaOH and other strong bases to form water-soluble salts. OH + NaOH ...
... • Phenols are weak acids and react with NaOH and other strong bases to form water-soluble salts. OH + NaOH ...
ppt
... reagent to a carboxylic acid with an addition carbon (the CO2H group). The CO2H group is derived from CO2. Mg(0) R-Br ...
... reagent to a carboxylic acid with an addition carbon (the CO2H group). The CO2H group is derived from CO2. Mg(0) R-Br ...
ppt
... Spectra of Aldehydes and Ketones: The 1H chemical shift range for the aldehyde proton is 9-10 ppm The aldehyde proton will couple to the protons on the -carbon with a typical coupling constant of J 2 Hz A carbonyl will slightly deshield the protons on the -carbon; ...
... Spectra of Aldehydes and Ketones: The 1H chemical shift range for the aldehyde proton is 9-10 ppm The aldehyde proton will couple to the protons on the -carbon with a typical coupling constant of J 2 Hz A carbonyl will slightly deshield the protons on the -carbon; ...
Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids
... equilibrium lies far to the right; K is ~ 1011 as long as the molecular weight of the acid is not too high, sodium and potassium carboxylate salts are soluble in water ...
... equilibrium lies far to the right; K is ~ 1011 as long as the molecular weight of the acid is not too high, sodium and potassium carboxylate salts are soluble in water ...
Nucleophilic Addition: The Grignard reagent
... Transfer the dry ethyl ether to an Erlenmeyer flask and evaporate the ether using a 50 °C water bath and a gentle stream of compressed air. Add 3 mL of petroleum ether to the oily solid that remains after the ethyl ether has evaporated. Warm the resulting suspension in a 50 °C water bath for a few m ...
... Transfer the dry ethyl ether to an Erlenmeyer flask and evaporate the ether using a 50 °C water bath and a gentle stream of compressed air. Add 3 mL of petroleum ether to the oily solid that remains after the ethyl ether has evaporated. Warm the resulting suspension in a 50 °C water bath for a few m ...
HIGHER CfE CHEMISTRY Nature`s Chemistry
... During oxidation, what happens to the ratio of O:H atoms in a hydrocarbon? ...
... During oxidation, what happens to the ratio of O:H atoms in a hydrocarbon? ...
Types of Functional Groups Amines
... If more than one OH group, then use prefix indicating how many OH there are Also indicate the location of the OH groups using numbers EX: 1,1-propandiol ...
... If more than one OH group, then use prefix indicating how many OH there are Also indicate the location of the OH groups using numbers EX: 1,1-propandiol ...
File
... Ethanol is used as a solvent for perfumes, varnishes, and some medicines, such as tincture of iodine. ...
... Ethanol is used as a solvent for perfumes, varnishes, and some medicines, such as tincture of iodine. ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.