Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
... Nitriles are reduced to corresponding imine with stannous chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid, which on hydrolysis give corresponding aldehyde. ...
... Nitriles are reduced to corresponding imine with stannous chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid, which on hydrolysis give corresponding aldehyde. ...
Document
... ex: H2O (g) + CO (g) H2 (g) + CO2 (g) the “reverse arrow” indicates that the reaction can occur in either direction until equilibrium occurs ...
... ex: H2O (g) + CO (g) H2 (g) + CO2 (g) the “reverse arrow” indicates that the reaction can occur in either direction until equilibrium occurs ...
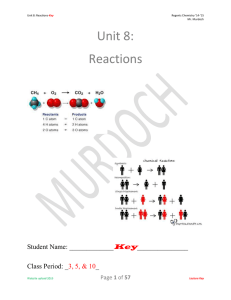
Unit 8: Reactions
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
step by step Stoichiometry
... Or 80.3 divided by 55.847, multiplied by 3, divided by 2, multiplied by 28.01015 ...
... Or 80.3 divided by 55.847, multiplied by 3, divided by 2, multiplied by 28.01015 ...
Chapter 2- Acids and Bases
... would form if NH3 was added directly to the starting carboxylic acid? O ...
... would form if NH3 was added directly to the starting carboxylic acid? O ...
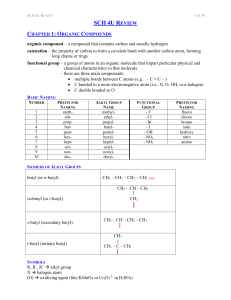
sch4ureview
... polar (due to hydroxyl group) hydrogen bonding and dispersion forces high (due to capacity for hydrogen bonding) very soluble in polar solvents and nonpolar solvents (due to OH- group) ...
... polar (due to hydroxyl group) hydrogen bonding and dispersion forces high (due to capacity for hydrogen bonding) very soluble in polar solvents and nonpolar solvents (due to OH- group) ...
12 U Chem Review
... polar (due to hydroxyl group) hydrogen bonding and dispersion forces high (due to capacity for hydrogen bonding) very soluble in polar solvents and nonpolar solvents (due to OH- group) ...
... polar (due to hydroxyl group) hydrogen bonding and dispersion forces high (due to capacity for hydrogen bonding) very soluble in polar solvents and nonpolar solvents (due to OH- group) ...
Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic Acid
... Electronic Effect: Relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions is due the positive charge on carbonyl carbon. Greater positive charge means greater reactivity. Electron releasing power of two alkyl groups in ketones is more than one in aldehyde. Therefore positi ...
... Electronic Effect: Relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions is due the positive charge on carbonyl carbon. Greater positive charge means greater reactivity. Electron releasing power of two alkyl groups in ketones is more than one in aldehyde. Therefore positi ...
Camp 1
... – Problem: draw a condensed structural formula for the single carboxylic acid of molecular formula C3H6O2 • Solution: the only way the carbon atoms can be written is three in a chain; the -COOH group must be on an end carbon of the chain O CH3 CH2 COH or CH3 CH2 COOH ...
... – Problem: draw a condensed structural formula for the single carboxylic acid of molecular formula C3H6O2 • Solution: the only way the carbon atoms can be written is three in a chain; the -COOH group must be on an end carbon of the chain O CH3 CH2 COH or CH3 CH2 COOH ...
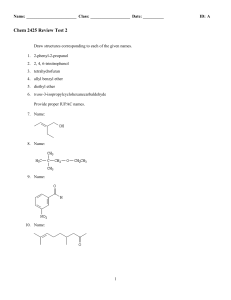
Chem 2425-Test 2 Review
... Consider the data below to answer the following question(s). Cyanohydrins are important intermediates in the synthesis of α-hydroxycarboxylic acids from ketones and aldehydes. The nitrile functional group can be hydrolyzed by aqueous acid to yield a carboxylic acid. Nitriles can also be hydrolyzed t ...
... Consider the data below to answer the following question(s). Cyanohydrins are important intermediates in the synthesis of α-hydroxycarboxylic acids from ketones and aldehydes. The nitrile functional group can be hydrolyzed by aqueous acid to yield a carboxylic acid. Nitriles can also be hydrolyzed t ...
HPLC - College of the Canyons
... atoms are joined together in each molecule. In a separation similar to liquid chromatography, a splash of spaghetti sauce on clothing may partly wash out with water. The rest of the stain can be removed with a different solvent, such as soapy water or dry-cleaning fluid, which attracts the oily part ...
... atoms are joined together in each molecule. In a separation similar to liquid chromatography, a splash of spaghetti sauce on clothing may partly wash out with water. The rest of the stain can be removed with a different solvent, such as soapy water or dry-cleaning fluid, which attracts the oily part ...
Chemical Equations
... Balancing Oxidation-Reduction ("Redox") Reactions These kinds of reactions often require a more methodical approach to balancing. In aqueous solution, these can also be balanced in acidic solution or basic solution. They are part of the general topic of oxidation and reduction, oxidation numbers, ha ...
... Balancing Oxidation-Reduction ("Redox") Reactions These kinds of reactions often require a more methodical approach to balancing. In aqueous solution, these can also be balanced in acidic solution or basic solution. They are part of the general topic of oxidation and reduction, oxidation numbers, ha ...
organic compounds in three dimensions
... Two or more compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms are called isomers. Isomers differ in one or more physical or chemical properties such as boiling point, color, solubility, reactivity, and density. Several different types of isomerism are possible for organic ...
... Two or more compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms are called isomers. Isomers differ in one or more physical or chemical properties such as boiling point, color, solubility, reactivity, and density. Several different types of isomerism are possible for organic ...
Chemistry Project on Carboxyl Acids
... are immiscible with water. A sweet fruity smell gives out. 2. After reduction, there is no observable change for the reactions. 3. When ammonium carboxylates are heated in the process 2 of amide formation, dehydration takes place and white solid amides are formed. ...
... are immiscible with water. A sweet fruity smell gives out. 2. After reduction, there is no observable change for the reactions. 3. When ammonium carboxylates are heated in the process 2 of amide formation, dehydration takes place and white solid amides are formed. ...
2015 chemistry
... (iii) This conversion can also be catalysed by an enzyme. Explain why the percentage of oil converted in an enzyme-catalysed reaction is very low at high temperatures. _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________ ...
... (iii) This conversion can also be catalysed by an enzyme. Explain why the percentage of oil converted in an enzyme-catalysed reaction is very low at high temperatures. _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________ ...
Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Carbonyl
... The parent of an aldehyde or ketone is the longest, continuous carbon chain that contains the carbonyl carbon of the functional group. The parent name reflects the total number of carbon atoms in the chain (2 carbons = ethan, 3 carbons = propan, etc..). The parent chain is numbered from one end of t ...
... The parent of an aldehyde or ketone is the longest, continuous carbon chain that contains the carbonyl carbon of the functional group. The parent name reflects the total number of carbon atoms in the chain (2 carbons = ethan, 3 carbons = propan, etc..). The parent chain is numbered from one end of t ...
Ch 4 Carbon student
... Hermann _____________________________________ Wohler’s student made _____________________________________ acid from inorganic compounds Abiotic synthesis of organic compounds from early life’s elementsAP Biology ...
... Hermann _____________________________________ Wohler’s student made _____________________________________ acid from inorganic compounds Abiotic synthesis of organic compounds from early life’s elementsAP Biology ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.