CN>Chapter 22CT>Carbonyl Alpha
... Base-promoted reaction occurs through an enolate anion intermediate. Monohalogenated products are themselves rapidly turned into enolate ...
... Base-promoted reaction occurs through an enolate anion intermediate. Monohalogenated products are themselves rapidly turned into enolate ...
Exam 2 - Wake Forest University
... Do not open or begin this exam until instructed. This exam consists of 5 pages plus the cover page. Before starting the exam, check to make sure that you have all of the pages. The exam has a total of 100 points and includes 13 questions. Only legible answers written on the exam will be considered f ...
... Do not open or begin this exam until instructed. This exam consists of 5 pages plus the cover page. Before starting the exam, check to make sure that you have all of the pages. The exam has a total of 100 points and includes 13 questions. Only legible answers written on the exam will be considered f ...
Fall.2008.Week9.Lesson.1 - reich
... (g) means the substance is a gas (l) means the substance is a liquid (s) means the substance is a solid (aq) means the substance is aqueous Aqueous means dissolved in water, which does not necessarily mean the compound was a liquid. Ethanol and sugar both become aqueous, but only one of them was a s ...
... (g) means the substance is a gas (l) means the substance is a liquid (s) means the substance is a solid (aq) means the substance is aqueous Aqueous means dissolved in water, which does not necessarily mean the compound was a liquid. Ethanol and sugar both become aqueous, but only one of them was a s ...
alcohols, alkyl halides, and nucleophilic substitutions
... test). Test 1-butanol, 2-butanol, t-butyl alcohol, t-amyl alcohol, benzyl alcohol, and phenol. If no reaction is observed after one hour, warm the test tube in bath of boiling water for a few minutes and allow to cool to room temperature. Report the results in tabular form. PART C: REACTIVITY OF HAL ...
... test). Test 1-butanol, 2-butanol, t-butyl alcohol, t-amyl alcohol, benzyl alcohol, and phenol. If no reaction is observed after one hour, warm the test tube in bath of boiling water for a few minutes and allow to cool to room temperature. Report the results in tabular form. PART C: REACTIVITY OF HAL ...
No Slide Title
... • Think of it as: If you wanted to bake a batch of peanut butter cookies and the recipe calls for 1 cup of peanut butter and all you have is ½ a cup, even though you have all the other ingredients, you can at most make ½ a batch of cookies. ...
... • Think of it as: If you wanted to bake a batch of peanut butter cookies and the recipe calls for 1 cup of peanut butter and all you have is ½ a cup, even though you have all the other ingredients, you can at most make ½ a batch of cookies. ...
Chapter 11
... One way to avoid this overoxidation is to use a Cr(VI) reagent in nonacidic conditions ...
... One way to avoid this overoxidation is to use a Cr(VI) reagent in nonacidic conditions ...
Lab 7
... because the carbonyl carbon is not oxidizable by common oxidizing agents. The carbonyl carbon is part of a ketone and does not have a hydrogen bonded to it. Nitric acid is a special oxidizing agent that can oxidize “non-oxidizable” carbon atoms of cyclic ketones. The reaction produces a diacid with ...
... because the carbonyl carbon is not oxidizable by common oxidizing agents. The carbonyl carbon is part of a ketone and does not have a hydrogen bonded to it. Nitric acid is a special oxidizing agent that can oxidize “non-oxidizable” carbon atoms of cyclic ketones. The reaction produces a diacid with ...
Carbon and Organic Compounds
... Each C can form a maximum of four single bonds, OR two single and one double bond, OR one single and triple bond. The arrangement of C atoms determines the skeleton, so a straight chain and a bent chain represent the same skeleton. Groups joined by single bonds can rotate, so a branch pointing down ...
... Each C can form a maximum of four single bonds, OR two single and one double bond, OR one single and triple bond. The arrangement of C atoms determines the skeleton, so a straight chain and a bent chain represent the same skeleton. Groups joined by single bonds can rotate, so a branch pointing down ...
Chapter 22 Organic chemistry
... Hardest known material High density (3.514 g/ cm3) High mp (3550 deg. C) ...
... Hardest known material High density (3.514 g/ cm3) High mp (3550 deg. C) ...
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015
... Formal product of the addition is the enol, which is often not isolated ...
... Formal product of the addition is the enol, which is often not isolated ...
Chapter 14 – Aldehydes and Ketones
... type of name is derived from the name used for a common carboxylic acid. The name of the carboxylic acid typically comes from a Latin origin. For example, formaldehyde (CH2O) is derived from formic acid (HCO2H). You may know of formic acid as the major component of an ant bite. The bite stings becau ...
... type of name is derived from the name used for a common carboxylic acid. The name of the carboxylic acid typically comes from a Latin origin. For example, formaldehyde (CH2O) is derived from formic acid (HCO2H). You may know of formic acid as the major component of an ant bite. The bite stings becau ...
Objective: The objective of the lab is to study the types of reactions
... This type of reaction is important in obtaining elements that are too reactive to be created naturally. This type of reaction is how we obtain sodium and potassium for example. Both of these two elements are very reactive with water, so early rainfalls when the earth was young would have caused thes ...
... This type of reaction is important in obtaining elements that are too reactive to be created naturally. This type of reaction is how we obtain sodium and potassium for example. Both of these two elements are very reactive with water, so early rainfalls when the earth was young would have caused thes ...
Ketones - WordPress.com
... orange precipitate with 2,4-DNPH. To differentiate, we may react the solution with Tollens’ reagent – a solution of silver nitrate in excess ...
... orange precipitate with 2,4-DNPH. To differentiate, we may react the solution with Tollens’ reagent – a solution of silver nitrate in excess ...
Unit 4 - INTEC Chemistry Blog
... Alcohols react with carboxylic acids to form esters. Write an equation for a typical esterification reaction. CH3COOH + C2H5OH CH3COOC2H5 + H2O Suggest how this type of reaction could be used to form polyesters Alcohol group at one end and acid group at the other React at each end Give another ...
... Alcohols react with carboxylic acids to form esters. Write an equation for a typical esterification reaction. CH3COOH + C2H5OH CH3COOC2H5 + H2O Suggest how this type of reaction could be used to form polyesters Alcohol group at one end and acid group at the other React at each end Give another ...
Microsoft Word
... bromohydrin 6 was isolated, regio- and stereospecifically, as the sole product. The structure of 6 was confirmed by transforming it to the acetonide 8. Thus deprotection of the silyl ether and subsequent reaction of the resulting diol 7 with 2,2dimethoxypropane in the presence of catalytic amounts o ...
... bromohydrin 6 was isolated, regio- and stereospecifically, as the sole product. The structure of 6 was confirmed by transforming it to the acetonide 8. Thus deprotection of the silyl ether and subsequent reaction of the resulting diol 7 with 2,2dimethoxypropane in the presence of catalytic amounts o ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
Microsoft Word
... L-Leucic acid t-butyl ester 29 was prepared from L-leucic acid 27 by treatment with acetyl chloride to convert the free -OH to -OAc. This crude acetate was converted to t-butyl ester with t-BuOH, DCC and DMAP to afford the compound 28 in 81% yield. The acetyl group was hydrolyzed with K2CO3 in metha ...
... L-Leucic acid t-butyl ester 29 was prepared from L-leucic acid 27 by treatment with acetyl chloride to convert the free -OH to -OAc. This crude acetate was converted to t-butyl ester with t-BuOH, DCC and DMAP to afford the compound 28 in 81% yield. The acetyl group was hydrolyzed with K2CO3 in metha ...
SMJK PEREMPUAN CHINA PULAU PINANG CHEMISTRY FORM 5
... (ii) Name reaction Y. [1m] ……………………………………………………… (e) Draw the structural formula for 2,3-dibromobutane. [1m] (f) Reaction B is a hydrogenation process. Identify substance P and the type of catalyst used. [2m] P: ………………………………………………………………………………. ...
... (ii) Name reaction Y. [1m] ……………………………………………………… (e) Draw the structural formula for 2,3-dibromobutane. [1m] (f) Reaction B is a hydrogenation process. Identify substance P and the type of catalyst used. [2m] P: ………………………………………………………………………………. ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
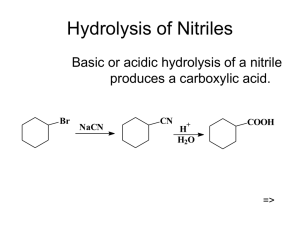
Hydrolysis of Nitriles
... Amine (base) removes a proton from the carboxylic acid to form a salt. Heating the salt above 100C drives off steam and forms the amide. O ...
... Amine (base) removes a proton from the carboxylic acid to form a salt. Heating the salt above 100C drives off steam and forms the amide. O ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 9) Carbon disulfide (CS2), sugar (C6H12O6) and pure water are examples of a) strong electrolytes b) Weak electrolytes c) non-electrolytes d)base 10) Which one of these produces the largest number of particles per mole of dissolved solute in water? a) NaCl b) C2H6 c) (NH4)2SO4 d) K3PO4 e) MgCl2 11) W ...
... 9) Carbon disulfide (CS2), sugar (C6H12O6) and pure water are examples of a) strong electrolytes b) Weak electrolytes c) non-electrolytes d)base 10) Which one of these produces the largest number of particles per mole of dissolved solute in water? a) NaCl b) C2H6 c) (NH4)2SO4 d) K3PO4 e) MgCl2 11) W ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry!
... 1. The oxidation number of any uncombined element is O. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equal the charge on the ion. 3. The more electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation number of fluorine in ...
... 1. The oxidation number of any uncombined element is O. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equal the charge on the ion. 3. The more electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation number of fluorine in ...
Nomenclature - Clydebank High School
... We must add back the water which is removed in the condensation reaction. This is not very successful with water alone so we add a dilute acid to catalyse it e.g. HCl or H2SO4. (Or an alkali.) They provide H+ ions to catalyse the reaction. It is a reversible reaction ( PPA – 2) ...
... We must add back the water which is removed in the condensation reaction. This is not very successful with water alone so we add a dilute acid to catalyse it e.g. HCl or H2SO4. (Or an alkali.) They provide H+ ions to catalyse the reaction. It is a reversible reaction ( PPA – 2) ...
2006 Practice Final Exam - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... Galactose is an aldohexose Galactose has 5 chiral carbons It can form a ring structure It is a carbohydrate ...
... Galactose is an aldohexose Galactose has 5 chiral carbons It can form a ring structure It is a carbohydrate ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.