Syn Addition
... You can use a reduced activity catalyst (Lindlar), Pd and Pb, which stops at the alkene. You obtain a cis alkene. ...
... You can use a reduced activity catalyst (Lindlar), Pd and Pb, which stops at the alkene. You obtain a cis alkene. ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALCOHOLS: MANUFACTURE
... than one possible alcohol that could be formed. But in practice, most of the product will be only one of those possibilities. What would be the major product if you reacted the following alkenes with steam? (i) propene: CH3CH=CH2 (ii) but-1-ene: CH3CH2CH=CH2 2. Ethanol can also be made by fermentati ...
... than one possible alcohol that could be formed. But in practice, most of the product will be only one of those possibilities. What would be the major product if you reacted the following alkenes with steam? (i) propene: CH3CH=CH2 (ii) but-1-ene: CH3CH2CH=CH2 2. Ethanol can also be made by fermentati ...
Experiment 7
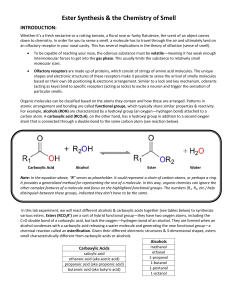
... atomic arrangement and bonding are called functional groups, which typically share similar properties & reactivity. For example, alcohols (ROH) are characterized by a hydroxyl group (an oxygen—hydrogen bond) attached to a carbon atom. A carboxylic acid (RCO2H), on the other hand, has a hydroxyl grou ...
... atomic arrangement and bonding are called functional groups, which typically share similar properties & reactivity. For example, alcohols (ROH) are characterized by a hydroxyl group (an oxygen—hydrogen bond) attached to a carbon atom. A carboxylic acid (RCO2H), on the other hand, has a hydroxyl grou ...
Chapter 1--Title
... Rearrangements of carbocations occur if a more stable carbocation can be obtained Example ...
... Rearrangements of carbocations occur if a more stable carbocation can be obtained Example ...
Chemistry - ais exams
... C. form alkaline aqueous solutions B. be solids at room temperature D. conduct electricity when molten 23. In which solid can layers of atoms slide over each other? A. diamond B. graphite C. haematite D. silica 24 .Which ion causes the acidity in dilute hydrochloric acid? A. Cl– B. H+ C. H2 D. OH– 2 ...
... C. form alkaline aqueous solutions B. be solids at room temperature D. conduct electricity when molten 23. In which solid can layers of atoms slide over each other? A. diamond B. graphite C. haematite D. silica 24 .Which ion causes the acidity in dilute hydrochloric acid? A. Cl– B. H+ C. H2 D. OH– 2 ...
assignment 4-2
... Ethylene glycol acts as antifreeze and is used in automobiles and computers. It is also used for preserving body organs and in the manufacture of capacitors. Its structure is shown below. The IUPAC name of this compound is a. ...
... Ethylene glycol acts as antifreeze and is used in automobiles and computers. It is also used for preserving body organs and in the manufacture of capacitors. Its structure is shown below. The IUPAC name of this compound is a. ...
A Direct Access to 3-(2-Oxoalkyl)indoles via
... milder nature of the reaction condition, the present methodology has advantages over the alkali mediated two step synthesis of 3a at elevated temperature (i.e., at 135-140 °C) as reported earlier.8g Compound 3a could be utilized for the synthesis of compounds of potential biological interest.16 For ...
... milder nature of the reaction condition, the present methodology has advantages over the alkali mediated two step synthesis of 3a at elevated temperature (i.e., at 135-140 °C) as reported earlier.8g Compound 3a could be utilized for the synthesis of compounds of potential biological interest.16 For ...
haloalkanes - Knockhardy
... This form of nucleophilic substitution is known as SN2; it is a bimolecular process. An alternative method involves the initial breaking of the C-X bond to form a carbocation, or carbonium ion, (a unimolecular process - SN1 mechanism), which is then attacked by the nucleophile. SN1 is favoured for t ...
... This form of nucleophilic substitution is known as SN2; it is a bimolecular process. An alternative method involves the initial breaking of the C-X bond to form a carbocation, or carbonium ion, (a unimolecular process - SN1 mechanism), which is then attacked by the nucleophile. SN1 is favoured for t ...
a) air c) milk f) beer
... compounds for a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole numbers. ...
... compounds for a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole numbers. ...
AlCl3 in modern chemistry of polyfluoroarenes
... AlCl3 application in the chemistry of polyfluoroarenes beginning since 1995y. As substrates or reagents there are given fluorinated compounds containing two and more fluorine atoms in one aromatic ring and the transformations are systematized according to the type of the reactions taking place. 1. F ...
... AlCl3 application in the chemistry of polyfluoroarenes beginning since 1995y. As substrates or reagents there are given fluorinated compounds containing two and more fluorine atoms in one aromatic ring and the transformations are systematized according to the type of the reactions taking place. 1. F ...
C h e m g u id e –... ACID ANHYDRIDES: INTRODUCTION
... 2. Ethanoyl chloride reacts with molecules containing a hydrogen atom attached to the electronegative atoms oxygen and nitrogen – for example water, alcohols and ammonia. We can summarise these as H-X. In each case the chlorine (in red in the diagram) is replaced and combines with the hydrogen to fo ...
... 2. Ethanoyl chloride reacts with molecules containing a hydrogen atom attached to the electronegative atoms oxygen and nitrogen – for example water, alcohols and ammonia. We can summarise these as H-X. In each case the chlorine (in red in the diagram) is replaced and combines with the hydrogen to fo ...
Basic Organic Nomenclature and Functional Groups Notes
... If there chains, the nitrogen is counted as being attached to the longest chain, and an italic N is used to show the shorter chains are attached to the nitrogen ...
... If there chains, the nitrogen is counted as being attached to the longest chain, and an italic N is used to show the shorter chains are attached to the nitrogen ...
Final - Courses
... But a newer body of research says we should look instead at the molecules before deprotonation for the real explanation of the difference in acidity between carboxylic acids and alcohols. What might this explanation be, and which one do you think is correct? ...
... But a newer body of research says we should look instead at the molecules before deprotonation for the real explanation of the difference in acidity between carboxylic acids and alcohols. What might this explanation be, and which one do you think is correct? ...
Chemical Properties of Organic Compounds
... The products of complete combustion of organic compounds are carbon dioxide and water. Incomplete combustion can result in intermediate oxidation states of carbon and form any of the functional groups. One way to observe complete and incomplete combustion is to adjust the collar near the base of a B ...
... The products of complete combustion of organic compounds are carbon dioxide and water. Incomplete combustion can result in intermediate oxidation states of carbon and form any of the functional groups. One way to observe complete and incomplete combustion is to adjust the collar near the base of a B ...
Analysing Alcohols
... 3. Put 10cm of the alcohol in a test tube and add 1cm3 of potassium dichromate then add 5cm of sulphuric acid. 4. Label the test tubes and place them in the water bath 5. Check for colour changes and if the colour of the unknown liquid goes green then it is a secondary or primary alcohol. However if ...
... 3. Put 10cm of the alcohol in a test tube and add 1cm3 of potassium dichromate then add 5cm of sulphuric acid. 4. Label the test tubes and place them in the water bath 5. Check for colour changes and if the colour of the unknown liquid goes green then it is a secondary or primary alcohol. However if ...
unsaturated hydrocarbon
... molecule (Ex: carboxylic acid group) 10. Hydrocarbon – an organic molecule containing only carbon and hydrogen 11. Isomer – molecules that have the same molecular formula and different structural formulas 12. Monomer – a single molecule or subunit 13. Organic chemistry – the study of molecules conta ...
... molecule (Ex: carboxylic acid group) 10. Hydrocarbon – an organic molecule containing only carbon and hydrogen 11. Isomer – molecules that have the same molecular formula and different structural formulas 12. Monomer – a single molecule or subunit 13. Organic chemistry – the study of molecules conta ...
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to
... t The cyano group can be hydrolyzed or reduced l Hydrolysis of a cyanohydrin produces an α -hydroxycarboxylic acid l Reduction of a cyanohydrin produces a β -aminoalcohol ...
... t The cyano group can be hydrolyzed or reduced l Hydrolysis of a cyanohydrin produces an α -hydroxycarboxylic acid l Reduction of a cyanohydrin produces a β -aminoalcohol ...
Full Article-PDF - UNC
... The synthesis of the vinyl pivalate is shown in Scheme 2. The enolate of methyl isobutyrate was alkylated with allyl bromide to form methyl 2,2-dimethyl-4-pentenoate which was then hydrolyzed to the acid under basic conditions. The dianion of isobutyric acid can also be alkylated with allyl bromide ...
... The synthesis of the vinyl pivalate is shown in Scheme 2. The enolate of methyl isobutyrate was alkylated with allyl bromide to form methyl 2,2-dimethyl-4-pentenoate which was then hydrolyzed to the acid under basic conditions. The dianion of isobutyric acid can also be alkylated with allyl bromide ...
Unit 3: Reactions of Alkenes. Thermodynamics and Kinetics
... This symbol indicates that the reaction takes place under standard conditions --all species at 1 M, 25 OC, and 1 atm. ...
... This symbol indicates that the reaction takes place under standard conditions --all species at 1 M, 25 OC, and 1 atm. ...
1) In the reaction H2O + CH3COOH H3O+ + CH3COO
... 7) (20 points) Let's say that a galvanic cell (spontaneous oxidation/reduction reaction like a battery) is constructed using the half reactions Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Cu(s) (E0 = +0.34V) and Zn2+ + 2e- Zn(s) (E0 = -0.76). What ratio of concentrations, Zn2+/Cu2+, in the electrolyte will be required if o ...
... 7) (20 points) Let's say that a galvanic cell (spontaneous oxidation/reduction reaction like a battery) is constructed using the half reactions Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Cu(s) (E0 = +0.34V) and Zn2+ + 2e- Zn(s) (E0 = -0.76). What ratio of concentrations, Zn2+/Cu2+, in the electrolyte will be required if o ...
Carbonyl Compounds
... addition elimination (condensation) reactions with NH2OH and ,2,4-DNPH . Oxidation (aldehyde can be easily oxidized to RCOOH, but ketone is resistant to oxidation & cannot be easily oxidized) ...
... addition elimination (condensation) reactions with NH2OH and ,2,4-DNPH . Oxidation (aldehyde can be easily oxidized to RCOOH, but ketone is resistant to oxidation & cannot be easily oxidized) ...
File
... • Simple alcohols are named from the alkane of the parent chain. The –e is dropped from the end of the alkane name and is replaced with –ol. For example, the simplest alcohol, with one carbon atom, has the IUPAC name “methanol”. • The number of carbon atoms in the alcohol is communicated by the stan ...
... • Simple alcohols are named from the alkane of the parent chain. The –e is dropped from the end of the alkane name and is replaced with –ol. For example, the simplest alcohol, with one carbon atom, has the IUPAC name “methanol”. • The number of carbon atoms in the alcohol is communicated by the stan ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.