
Mechanism of the oxymercuration of substituted cyclohexenes
... tion of equatorial alcohols on reduction. The total amount of equatorial alcohol approached 79 % after 10 days at 25" (see Table I). During this period of time a precipitate slowly formed. Due to the presence of the insoluble material it was not possible to determine the stereochemical relationship ...
... tion of equatorial alcohols on reduction. The total amount of equatorial alcohol approached 79 % after 10 days at 25" (see Table I). During this period of time a precipitate slowly formed. Due to the presence of the insoluble material it was not possible to determine the stereochemical relationship ...
3 金属材料合成3-2 B
... Mechanism of surfactant-directed metal nanorodgrowth:The single crystalline seed particles have facets that are differentiallyblocked by surfactant (or an initial halide layer that then electrostaticallyattracts the cationic surfactant). Subsequent addition of metal ...
... Mechanism of surfactant-directed metal nanorodgrowth:The single crystalline seed particles have facets that are differentiallyblocked by surfactant (or an initial halide layer that then electrostaticallyattracts the cationic surfactant). Subsequent addition of metal ...
carbonyl compound group
... (vi) Oxime: Oximes are a class of organic compounds having the general formula RR′CNOH, where R is an organic side chain and R′ is either hydrogen or an organic side chain. If R′ is H, then it is known as aldoxime and if R′ is an organic side chain, it is known as ketoxime. ...
... (vi) Oxime: Oximes are a class of organic compounds having the general formula RR′CNOH, where R is an organic side chain and R′ is either hydrogen or an organic side chain. If R′ is H, then it is known as aldoxime and if R′ is an organic side chain, it is known as ketoxime. ...
Belarus, National Final, 2008 (PDF 405K).
... roasting of a sulfide ore such as pyrite in oxygen-enriched air. The resulting sulfur dioxide is oxidized in the presence of a catalyst and the oxidation products are dissolved in dilute sulfuric acid. The residual gas is usually released into the atmosphere. The maximum allowable concentration of S ...
... roasting of a sulfide ore such as pyrite in oxygen-enriched air. The resulting sulfur dioxide is oxidized in the presence of a catalyst and the oxidation products are dissolved in dilute sulfuric acid. The residual gas is usually released into the atmosphere. The maximum allowable concentration of S ...
Exam #2
... solution, and soluble in dilute HCl. Which of the following compounds could the solid be? (A) CaCO3 (B) BaSO4 (C) Pb(NO3)2 (D) AgCl (E) Zn(OH)2 70. H2O(s) ---> H2O(l) When ice melts at its normal melting point, 273.16 K and 1 atmosphere, which of the following is true for the process shown above? (A ...
... solution, and soluble in dilute HCl. Which of the following compounds could the solid be? (A) CaCO3 (B) BaSO4 (C) Pb(NO3)2 (D) AgCl (E) Zn(OH)2 70. H2O(s) ---> H2O(l) When ice melts at its normal melting point, 273.16 K and 1 atmosphere, which of the following is true for the process shown above? (A ...
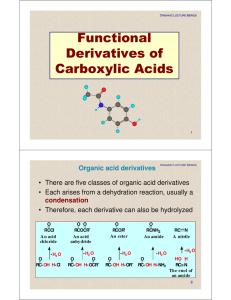
Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
... Imides are more acidic than amides because: 1. the electron-withdrawing inductive of the two adjacent C=O groups weakens the N-H bond, and 2. the imide anion is stabilized by resonance delocalization of the negative charge O ...
... Imides are more acidic than amides because: 1. the electron-withdrawing inductive of the two adjacent C=O groups weakens the N-H bond, and 2. the imide anion is stabilized by resonance delocalization of the negative charge O ...
Saturday Study Session 1 1st Class Reactions
... Answer the following questions that relate to chemical reactions. (a) Iron(III) oxide can be reduced with carbon monoxide according to the following equation. Fe2O3(s) + 3 CO(g) → 2 Fe(s) + 3 CO2(g) A 16.2 L sample of CO(g) at 1.50 atm and 200.°C is combined with 15.39 g of Fe2O3(s). (i) How many mo ...
... Answer the following questions that relate to chemical reactions. (a) Iron(III) oxide can be reduced with carbon monoxide according to the following equation. Fe2O3(s) + 3 CO(g) → 2 Fe(s) + 3 CO2(g) A 16.2 L sample of CO(g) at 1.50 atm and 200.°C is combined with 15.39 g of Fe2O3(s). (i) How many mo ...
(C3H7)3NH[CrO3X],(X=F, Cl), Reagents for Oxidation of
... 500 spectrometer at 500, 125, 470.66 MHz. All the chemical shifts are quoted in ppm using the high-frequency positive convention; 1H and 13C NMR spectra were referenced to external SiMe4 and 19F NMR spectra to external CFCl3. Chromium was estimated iodometrically. In the case of the reduced product ...
... 500 spectrometer at 500, 125, 470.66 MHz. All the chemical shifts are quoted in ppm using the high-frequency positive convention; 1H and 13C NMR spectra were referenced to external SiMe4 and 19F NMR spectra to external CFCl3. Chromium was estimated iodometrically. In the case of the reduced product ...
anhydride cured-epoxy matrices
... The secondary alcohol may be a product of esterification or on the backbone of the epoxy. If the equivalents of anhydride used to cure the epoxy is less than one, the tendency for etherification increases. In relation to the catalyst type, acid catalysts tend to promote more etherification than basi ...
... The secondary alcohol may be a product of esterification or on the backbone of the epoxy. If the equivalents of anhydride used to cure the epoxy is less than one, the tendency for etherification increases. In relation to the catalyst type, acid catalysts tend to promote more etherification than basi ...
Hydrothermal Reactions of Pyruvic Acid
... decomposes at T >150°C to a mixture of H2O+CO2 +H2, and thus provides a convenient method to explore effects of volatile chemistry on reaction products. We employed pyruvic acid (Aldrich 98%), oxalic acid dihydrate (Aldrich >99%), and distilled deionized water in these experiments. We loaded each go ...
... decomposes at T >150°C to a mixture of H2O+CO2 +H2, and thus provides a convenient method to explore effects of volatile chemistry on reaction products. We employed pyruvic acid (Aldrich 98%), oxalic acid dihydrate (Aldrich >99%), and distilled deionized water in these experiments. We loaded each go ...
Organic Structures
... from a Level 1 functional group to a Level 3 functional group. Reducing a ketone to a secondary alcohol is a change from a level 2 functional group to a level 1 functional group. In contrast, substituting one heteroatom for another will not change the functional group level. Substitution only change ...
... from a Level 1 functional group to a Level 3 functional group. Reducing a ketone to a secondary alcohol is a change from a level 2 functional group to a level 1 functional group. In contrast, substituting one heteroatom for another will not change the functional group level. Substitution only change ...
ppt - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Equilibrium – condition of a chemical reaction in which chemical change ceases and no further change occurs spontaneously Equilibrium – a dynamic equilibrium between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. At Equilibrium: ...
... Equilibrium – condition of a chemical reaction in which chemical change ceases and no further change occurs spontaneously Equilibrium – a dynamic equilibrium between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. At Equilibrium: ...
Amino Alcohol Oxidation with Gold Catalysts: The Effect of Amino
... present in the proteins, or it cannot be obtained by biotechnology, it can be prepared by classical methods such as Gabriel synthesis [2], the Sorensen method [3], and Strecker synthesis [4]. In particular, Glycine is normally obtained from chloroacetic acid by amination with an excess of ammonia [5 ...
... present in the proteins, or it cannot be obtained by biotechnology, it can be prepared by classical methods such as Gabriel synthesis [2], the Sorensen method [3], and Strecker synthesis [4]. In particular, Glycine is normally obtained from chloroacetic acid by amination with an excess of ammonia [5 ...
Chem 171 Review - Exam 1
... Hematite, Fe2O3, is an important ore of iron. Iron metal is obtained by reacting hematite with carbon monoxide (CO) in a blast furnace. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is: Fe2O3 (s) + 3 CO (g) 2 Fe (s) + 3 CO2 (g) Calculate the mass (in g) of iron that can be produced from the com ...
... Hematite, Fe2O3, is an important ore of iron. Iron metal is obtained by reacting hematite with carbon monoxide (CO) in a blast furnace. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is: Fe2O3 (s) + 3 CO (g) 2 Fe (s) + 3 CO2 (g) Calculate the mass (in g) of iron that can be produced from the com ...
jDonvert the following Fischer projections to dimensional formulas
... Q.6 Complete the following reactions by writing structures of missing compounds. Show stereochemistry whenever applicable, and write NR if the reaction would not ...
... Q.6 Complete the following reactions by writing structures of missing compounds. Show stereochemistry whenever applicable, and write NR if the reaction would not ...
2016 - Specimen Paper 4 - Cambridge International Examinations
... number of moles of CoCl2.6H2O formed = ………………………………………..…..… mass of one mole of CoCl2.6H2O = 238 g maximum yield of CoCl2.6H2O = …………………………………………………..…..… g to show that cobalt(II) carbonate is in excess: number of moles of HCl used = ……………………….……… (use your value from above) mass of one mole of Co ...
... number of moles of CoCl2.6H2O formed = ………………………………………..…..… mass of one mole of CoCl2.6H2O = 238 g maximum yield of CoCl2.6H2O = …………………………………………………..…..… g to show that cobalt(II) carbonate is in excess: number of moles of HCl used = ……………………….……… (use your value from above) mass of one mole of Co ...
Oxidation-Reduction and Electrochemistry
... Oxidation‐Reduction Reactions • This can be more easily observed by writing the net ionic equation for the reaction: Cu (s) + 2 Ag+ (aq) 2 Ag (s) + Cu2+ (aq) • The metallic Cu atoms are uncombined, so they are considered to have an oxidation number of zero. • The initial combined Ag+ ions are ...
... Oxidation‐Reduction Reactions • This can be more easily observed by writing the net ionic equation for the reaction: Cu (s) + 2 Ag+ (aq) 2 Ag (s) + Cu2+ (aq) • The metallic Cu atoms are uncombined, so they are considered to have an oxidation number of zero. • The initial combined Ag+ ions are ...
the beginnings of synthetic organic chemistry: zinc alkyls and the
... into the reactions of dialkylzincs begun by Butlerov, and the credit for developing and extending the scope of this synthetic method really belongs to Zaitsev and his students. In 1865 Frankland and Duppa reported the reaction between diethylzinc and diethyl oxalate to give the ethyl ester of a-ethy ...
... into the reactions of dialkylzincs begun by Butlerov, and the credit for developing and extending the scope of this synthetic method really belongs to Zaitsev and his students. In 1865 Frankland and Duppa reported the reaction between diethylzinc and diethyl oxalate to give the ethyl ester of a-ethy ...
Mock Exam One
... c.) Nucleophilic addition to carbonyl groups can be catalyzed by acid or base. d.) Addition of a nucleophile to a carbonyl group changes the hybridization of the carbonyl carbon from sp3 to sp2. ...
... c.) Nucleophilic addition to carbonyl groups can be catalyzed by acid or base. d.) Addition of a nucleophile to a carbonyl group changes the hybridization of the carbonyl carbon from sp3 to sp2. ...
Horseradish peroxidase catalyzed free radical cannot free move in
... phenomenon showed the free radical produced by the enzyme catalyze has not diffused into the solution, only happened on enzyme surface, so the product formed adhered to surface of the immobilized HRP (agar-agar bead). The above result may explain that peroxidase catalyzed the phenol polyreaction is ...
... phenomenon showed the free radical produced by the enzyme catalyze has not diffused into the solution, only happened on enzyme surface, so the product formed adhered to surface of the immobilized HRP (agar-agar bead). The above result may explain that peroxidase catalyzed the phenol polyreaction is ...
Document
... Stronger conditions (e.g. HNO3) allow oxidation of both the terminal carbons of aldose: ...
... Stronger conditions (e.g. HNO3) allow oxidation of both the terminal carbons of aldose: ...
Chapter 5
... 13. The octane rating of gasoline refers to its A. percentage C8H18 by volume. B. radiation dose. C. alcohol level. D. ability to resist engine knocking. E. percentage of unsaturated hydrocarbons ...
... 13. The octane rating of gasoline refers to its A. percentage C8H18 by volume. B. radiation dose. C. alcohol level. D. ability to resist engine knocking. E. percentage of unsaturated hydrocarbons ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.







![(C3H7)3NH[CrO3X],(X=F, Cl), Reagents for Oxidation of](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015838257_1-b7e4138a4ed1f989d8dc5b682bb74b7a-300x300.png)














