Catalysis
... As the [S] increased, the number of active sites which are occupied increases and hence the reaction rate also increases At very high [S], all the active sites are occupied at any time so that further increase in substrate concentration cannot further increase the formation of enzymesubstrate comple ...
... As the [S] increased, the number of active sites which are occupied increases and hence the reaction rate also increases At very high [S], all the active sites are occupied at any time so that further increase in substrate concentration cannot further increase the formation of enzymesubstrate comple ...
Forward
... us, alcohols. Alcohols were introduced in Chapter 4 and have appeared regularly since then. With this chapter we extend our knowledge of alcohols, particularly with respect to their relationship to carbonyl-containing compounds. In the course of studying alcohols, we shall also look at some relative ...
... us, alcohols. Alcohols were introduced in Chapter 4 and have appeared regularly since then. With this chapter we extend our knowledge of alcohols, particularly with respect to their relationship to carbonyl-containing compounds. In the course of studying alcohols, we shall also look at some relative ...
Ch. 16 Study Guide
... reactants that exist at equilibrium. 7. Another way of interpreting the value of K is that it tells you how far the equilibrium goes to formation of products. 8. When an equilibrium reaction is reversed, its equilibrium constant is the inverse of the original (1/K). 9. When an equilibrium equation i ...
... reactants that exist at equilibrium. 7. Another way of interpreting the value of K is that it tells you how far the equilibrium goes to formation of products. 8. When an equilibrium reaction is reversed, its equilibrium constant is the inverse of the original (1/K). 9. When an equilibrium equation i ...
4 Reactions Alcohol Thiols GOB Structures
... Draw the condensed structural formula for the major alkene produced by the dehydration of the following alcohol: ...
... Draw the condensed structural formula for the major alkene produced by the dehydration of the following alcohol: ...
Full Unit Summary Booklet
... have the general formula CnH2n burn to produce carbon dioxide and water boiling points,melting points and viscosity increases with increasing number of carbon atoms. are much more reactive than alkanes Alkenes can be identified by the –ene ending to their names. The names, molecular formulae ...
... have the general formula CnH2n burn to produce carbon dioxide and water boiling points,melting points and viscosity increases with increasing number of carbon atoms. are much more reactive than alkanes Alkenes can be identified by the –ene ending to their names. The names, molecular formulae ...
Question paper - Unit F322 - Chains, energy and resources
... (b) The ‘curly arrows’ model is used in reaction mechanisms to show the movement of electron pairs during chemical reactions. Choose a reaction mechanism that you have studied involving the curly arrow model. Name and describe your chosen reaction mechanism. In your answer, include: ...
... (b) The ‘curly arrows’ model is used in reaction mechanisms to show the movement of electron pairs during chemical reactions. Choose a reaction mechanism that you have studied involving the curly arrow model. Name and describe your chosen reaction mechanism. In your answer, include: ...
What is alcohol?
... Beer: It’s prepared by brewing and fermenting grains, then flavouring the mixture with hops, a flower that gives beer its bitterness. The alcohol content of beer usually ranges from 4% to 6% alcohol by volume. Wine: It’s made using fermented fruits (usually grapes). Wine is completely fermented and ...
... Beer: It’s prepared by brewing and fermenting grains, then flavouring the mixture with hops, a flower that gives beer its bitterness. The alcohol content of beer usually ranges from 4% to 6% alcohol by volume. Wine: It’s made using fermented fruits (usually grapes). Wine is completely fermented and ...
Unit 15 Organics Day 2 Cyclic Hydrocarbons: If you remove 2
... 1. Name the parent compound using the longest continuous carbon chain containing the hydroxyl group. parent name = take off the "e" add "ol" (you can use diol, triol etc if more than one) 2. Number the parent chain to give the lowest possible number to the carbon with the hydroxyl group. Place this ...
... 1. Name the parent compound using the longest continuous carbon chain containing the hydroxyl group. parent name = take off the "e" add "ol" (you can use diol, triol etc if more than one) 2. Number the parent chain to give the lowest possible number to the carbon with the hydroxyl group. Place this ...
KEY
... 3 is acting as a base. This means that it is a proton acceptor. To form the conjugate acid, it accepts a H making HNO3 . 031 10.0 points According to the Bronsted-Lowry concept of acids and bases, which of the following statements about a base is NOT true? 1. A base reacts with an acid to form a sal ...
... 3 is acting as a base. This means that it is a proton acceptor. To form the conjugate acid, it accepts a H making HNO3 . 031 10.0 points According to the Bronsted-Lowry concept of acids and bases, which of the following statements about a base is NOT true? 1. A base reacts with an acid to form a sal ...
Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization of Norbornene Catalyzed
... mmol) of norbornene were dissolved in CICH2CH2CI (DCE, 50 mL) and the mixture stirred at reflux temperature for one hour. The brownish gel formed was poured into vigorously stirred methanol to give a white precipitate and a brown solution. The solid was dried under reduced pressure to afford 6.5 g o ...
... mmol) of norbornene were dissolved in CICH2CH2CI (DCE, 50 mL) and the mixture stirred at reflux temperature for one hour. The brownish gel formed was poured into vigorously stirred methanol to give a white precipitate and a brown solution. The solid was dried under reduced pressure to afford 6.5 g o ...
testing for organic functional groups lab
... magenta-colored chemical potassium permanganate (KMnO4) to product manganese dioxide (MnO2), which is a brown solid. In other words, you can determine if a chemical has a double bond by adding KMnO4 and looking for the development of the brown solid MnO2. Example: 1-butene OH ...
... magenta-colored chemical potassium permanganate (KMnO4) to product manganese dioxide (MnO2), which is a brown solid. In other words, you can determine if a chemical has a double bond by adding KMnO4 and looking for the development of the brown solid MnO2. Example: 1-butene OH ...
Petrochemicals: Builder Molecules
... • Ethene or ethylene is an alkene, a hydrocarbon with a double covalent bond between the carbon atoms. • Because of the high reactivity of its double bond, ethene is readily transformed into many useful products. • A simple example—the formation of ethanol (ethyl alcohol) from water and ethene—illus ...
... • Ethene or ethylene is an alkene, a hydrocarbon with a double covalent bond between the carbon atoms. • Because of the high reactivity of its double bond, ethene is readily transformed into many useful products. • A simple example—the formation of ethanol (ethyl alcohol) from water and ethene—illus ...
Lectures 32-33 - U of L Class Index
... properties of a pair of enantiomers are identical unless they are in a chiral environment (such as any biological system). Your hands are chiral and can be used as an analogy for enantiomers - left and right hands are mirror images that cannot be superimposed. If you have a right-hand glove, it will ...
... properties of a pair of enantiomers are identical unless they are in a chiral environment (such as any biological system). Your hands are chiral and can be used as an analogy for enantiomers - left and right hands are mirror images that cannot be superimposed. If you have a right-hand glove, it will ...
Organic Chemistry PowerPoint
... carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group (OH). Weak acids because they ionize only slightly in solution to give a carboxylate ion and a hydrogen ion. Using the IUPAC system, replace the “e” ending of the longest continuous carbon chain containing the carboxyl group with the ending “oic acid”. Man ...
... carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group (OH). Weak acids because they ionize only slightly in solution to give a carboxylate ion and a hydrogen ion. Using the IUPAC system, replace the “e” ending of the longest continuous carbon chain containing the carboxyl group with the ending “oic acid”. Man ...
Phenol File
... conc. nitric acid and conc. sulphuric acid (catalyst) conditions reflux at 55°C equation C6H6 + HNO3 ...
... conc. nitric acid and conc. sulphuric acid (catalyst) conditions reflux at 55°C equation C6H6 + HNO3 ...
04_lecture_presentation
... • Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties – Structural isomers have different covalent arrangements of their atoms – Cis-trans isomers have the same covalent bonds but differ in spatial arrangements – Enantiomers are isomers that are mirror image ...
... • Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties – Structural isomers have different covalent arrangements of their atoms – Cis-trans isomers have the same covalent bonds but differ in spatial arrangements – Enantiomers are isomers that are mirror image ...
CH4 Student Revision Guides pdf | GCE AS/A
... The first step is to look at the two groups at the end of the double bond and rank the two groups in terms of the atomic number of the atoms concerned. The atom with the higher atomic number takes precedence (higher priority). This is done for both ends of the double bond. If the higher priority gro ...
... The first step is to look at the two groups at the end of the double bond and rank the two groups in terms of the atomic number of the atoms concerned. The atom with the higher atomic number takes precedence (higher priority). This is done for both ends of the double bond. If the higher priority gro ...
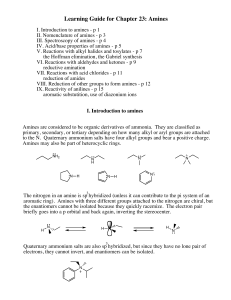
Learning Guide for Chapter 23: Amines
... Amides are formed when acid chlorides react with ammonia, primary or secondary amines. The amine attacks the carbonyl carbon, pushing the electrons onto the oxygen. The electrons then come down, pushing off the chloride. In order to deprotonate the amide, two equivalents of the amine must be used, o ...
... Amides are formed when acid chlorides react with ammonia, primary or secondary amines. The amine attacks the carbonyl carbon, pushing the electrons onto the oxygen. The electrons then come down, pushing off the chloride. In order to deprotonate the amide, two equivalents of the amine must be used, o ...
La chimica del carbonio
... Alcohols are compounds that have the hydroxyl functional group —OH attached to an aliphatic chain. As this functional group contains a strongly polarised bond, strong intermolecular forces exist between the alcohol molecules that are more intense than those between the apolar hydrocarbon molecules. ...
... Alcohols are compounds that have the hydroxyl functional group —OH attached to an aliphatic chain. As this functional group contains a strongly polarised bond, strong intermolecular forces exist between the alcohol molecules that are more intense than those between the apolar hydrocarbon molecules. ...
Solid-Phase Organic Synthesis: Creation of Carbon
... handle20, and N-Fmoc-p-nitrophenylalanine was added by standard DIPCDI/HOBtmediated coupling. Fmoc removal to release free amino functions was achieved by treatment with piperidine–DMF (1 : 4) at 25 °C for 2 + 10 min. This experimental design ensured that following solid-phase organic synthesis and ...
... handle20, and N-Fmoc-p-nitrophenylalanine was added by standard DIPCDI/HOBtmediated coupling. Fmoc removal to release free amino functions was achieved by treatment with piperidine–DMF (1 : 4) at 25 °C for 2 + 10 min. This experimental design ensured that following solid-phase organic synthesis and ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.