Functional Groups - Manasquan Public Schools
... Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. ...
... Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. ...
Advanced Practical Organic Chemistry
... also contain other elements. In fact, many common groups of atoms can occur within organic molecules, these groups of atoms are called functional groups. One good example is the hydroxyl functional group. The hydroxyl group consists of a single oxygen atom bound to a single hydrogen atom (-OH). The ...
... also contain other elements. In fact, many common groups of atoms can occur within organic molecules, these groups of atoms are called functional groups. One good example is the hydroxyl functional group. The hydroxyl group consists of a single oxygen atom bound to a single hydrogen atom (-OH). The ...
Polymers: Introduction
... Nylon-6,6 Since the reactants are in different phases, they can only react at the phase boundary. Once a layer of polymer forms, no more reaction occurs. Removing the polymer allows more reaction to occur. ...
... Nylon-6,6 Since the reactants are in different phases, they can only react at the phase boundary. Once a layer of polymer forms, no more reaction occurs. Removing the polymer allows more reaction to occur. ...
Chapter 12 Carboxylic Acids
... Carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonds with water, and the lower molecular-weight carboxylic acids (up through four carbon atoms) are miscible with water. As the length of the hydrocarbon chain increases, water solubility decreases until acids with more than 10 carbon atoms are essentially insoluble i ...
... Carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonds with water, and the lower molecular-weight carboxylic acids (up through four carbon atoms) are miscible with water. As the length of the hydrocarbon chain increases, water solubility decreases until acids with more than 10 carbon atoms are essentially insoluble i ...
Chemistry of DOW Glycol Ether Products
... esterification with acetic acid or anhydride. DOWANOL DPMA is the acetate resulting from the reaction of DOWANOL DPM with acetic acid or anhydride. ...
... esterification with acetic acid or anhydride. DOWANOL DPMA is the acetate resulting from the reaction of DOWANOL DPM with acetic acid or anhydride. ...
4Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... Without greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, more heat energy would escape, and Earth’s average temperature would be about 60 °F colder than it is now. The temperature outside of my office today would be below 0 °F, and even the sunniest U.S. cities would most likely be covered with snow. However, if ...
... Without greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, more heat energy would escape, and Earth’s average temperature would be about 60 °F colder than it is now. The temperature outside of my office today would be below 0 °F, and even the sunniest U.S. cities would most likely be covered with snow. However, if ...
Synthesis, spectroscopy, and electrochemistry of copper(II
... = 1.16 − 1.33 V attributable to metal centered Cu(II/III) and ligand centered ...
... = 1.16 − 1.33 V attributable to metal centered Cu(II/III) and ligand centered ...
summary spectral and magnetic investigations of
... metals the electronic structure and stereochemistry of sulphur nitrogen ligand complexes are comparatively much less understood. The added interest in them with reference to main group elements and probably also with early transition metals us due to the potential bond formation with soft or hard do ...
... metals the electronic structure and stereochemistry of sulphur nitrogen ligand complexes are comparatively much less understood. The added interest in them with reference to main group elements and probably also with early transition metals us due to the potential bond formation with soft or hard do ...
Forward
... 18-crown-6 is present. The reason for this has to do with the electron distribution of 18crown-6 as shown in Figure 16.2a. The electrostatic potential surface consists of essentially two regions: an electron-rich interior associated with the oxygens and a hydrocarbonlike exterior associated with the ...
... 18-crown-6 is present. The reason for this has to do with the electron distribution of 18crown-6 as shown in Figure 16.2a. The electrostatic potential surface consists of essentially two regions: an electron-rich interior associated with the oxygens and a hydrocarbonlike exterior associated with the ...
Functional Group Isomerism
... DIFFERENCES BETWEEN CHAIN ISOMERS Isomers show similar chemical properties because the same functional group is present. ...
... DIFFERENCES BETWEEN CHAIN ISOMERS Isomers show similar chemical properties because the same functional group is present. ...
A QUALITATIVE ?C - MOLECULAR ORBITAL RATIONALE FOR H
... steric interference of the two dppe ligands with the d, metal orbital, or even to orbital overlap between P-orbitals and metal d,, in as much as some degree of n-backbonding from M to P is believed to occur in these species as deducted from the observed MoP distances in trans-[Mo(CNMe) 2 (dppe) 2 ] ...
... steric interference of the two dppe ligands with the d, metal orbital, or even to orbital overlap between P-orbitals and metal d,, in as much as some degree of n-backbonding from M to P is believed to occur in these species as deducted from the observed MoP distances in trans-[Mo(CNMe) 2 (dppe) 2 ] ...
AP Chemistry Notes and Worksheets 2014
... o It stated that when two elements form a series of compounds, the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with 1 gram of the first element can always be reduced to small whole ...
... o It stated that when two elements form a series of compounds, the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with 1 gram of the first element can always be reduced to small whole ...
coordination chemistry
... What is the coordination entity formed when excess of aqueous KCN is added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate? Why is it that no precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained when H2S(g) is passed through this solution? ...
... What is the coordination entity formed when excess of aqueous KCN is added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate? Why is it that no precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained when H2S(g) is passed through this solution? ...
Example 4
... Break the O-H bond of one alcohol. Break one of the C=O Break the H-H bond. bonds. Form a bond between the carbonyl carbon and the O of Break one of the C=O the alcohol. Form a bond between the H and the O of the bonds. Form a bond carbonyl to form a HEMIACETAL. between the alpha-carbon and one H. F ...
... Break the O-H bond of one alcohol. Break one of the C=O Break the H-H bond. bonds. Form a bond between the carbonyl carbon and the O of Break one of the C=O the alcohol. Form a bond between the H and the O of the bonds. Form a bond carbonyl to form a HEMIACETAL. between the alpha-carbon and one H. F ...
step by step Stoichiometry
... Or 80.3 divided by 55.847, multiplied by 3, divided by 2, multiplied by 28.01015 ...
... Or 80.3 divided by 55.847, multiplied by 3, divided by 2, multiplied by 28.01015 ...
Aromatic compounds
... • In step 1, resonance energy is lost as pi bond is disrupted as electrophile attaches to a C in ring • In step 2, resonance energy is regained with loss of proton (H+) • Step 1 is slow since it requires so much energy (Ea), thus is ratedetermining step • Step 2 is fast with low Ea ...
... • In step 1, resonance energy is lost as pi bond is disrupted as electrophile attaches to a C in ring • In step 2, resonance energy is regained with loss of proton (H+) • Step 1 is slow since it requires so much energy (Ea), thus is ratedetermining step • Step 2 is fast with low Ea ...
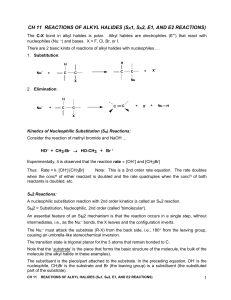
Alkyl Halides02
... This is also a qualitative test for identifying alcohols, i.e, the Lucas test. HCl with ZnCl 2 catalyst are used. 3 alcohols react quickly, 2 slowly, and 1 don’t react. Note that 1 and 2 alcohols will react with special reagents to produce alkyl halides (i.e., thionyl chloride, SOCl2, or PBr3) ...
... This is also a qualitative test for identifying alcohols, i.e, the Lucas test. HCl with ZnCl 2 catalyst are used. 3 alcohols react quickly, 2 slowly, and 1 don’t react. Note that 1 and 2 alcohols will react with special reagents to produce alkyl halides (i.e., thionyl chloride, SOCl2, or PBr3) ...
sure short question for class xii chemistry 2015-16
... Molality is not related to the volume of solution or solvent but it is related to the mass of solvent which does not change with temperature, hence the molality is independent of temperature. Q5. What is the relative lowering of the vapour pressure? Ans: Po A - P is known as relative lowering of the ...
... Molality is not related to the volume of solution or solvent but it is related to the mass of solvent which does not change with temperature, hence the molality is independent of temperature. Q5. What is the relative lowering of the vapour pressure? Ans: Po A - P is known as relative lowering of the ...
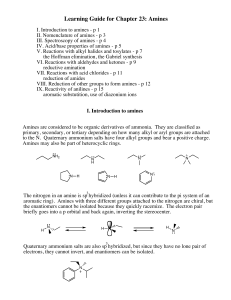
Learning Guide for Chapter 23: Amines
... Once an amine has been protonated, it is an ionic compound. Amine salts are solids, and are usually soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents. Most biologically active amines are used as their amine salts, which dissolve to make injectable or drinkable water solutions, and are also less pro ...
... Once an amine has been protonated, it is an ionic compound. Amine salts are solids, and are usually soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents. Most biologically active amines are used as their amine salts, which dissolve to make injectable or drinkable water solutions, and are also less pro ...
50 chemistry questions for class xii
... For example- heart has more β adrenergic receptors than α adrenergic receptors .This means that a drug designed to interact with β adrenergic receptors will act on heart rather than a tissue which are rich in α adrenergic receptors . Q49 Define the following terms with one example(Any two) (a) Antip ...
... For example- heart has more β adrenergic receptors than α adrenergic receptors .This means that a drug designed to interact with β adrenergic receptors will act on heart rather than a tissue which are rich in α adrenergic receptors . Q49 Define the following terms with one example(Any two) (a) Antip ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.